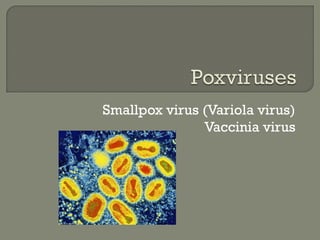
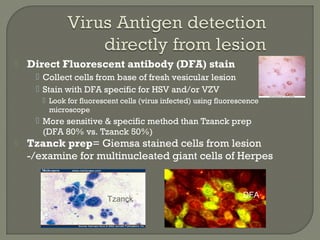
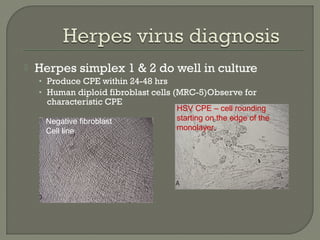
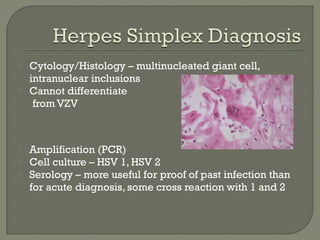
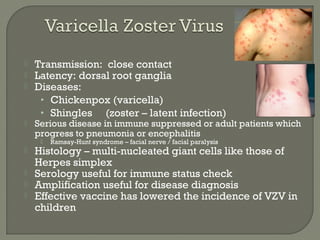
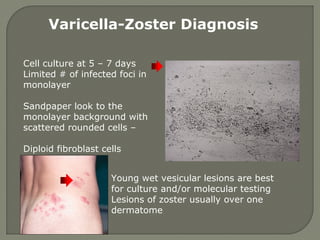
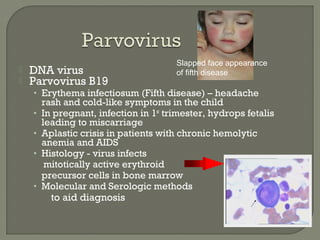
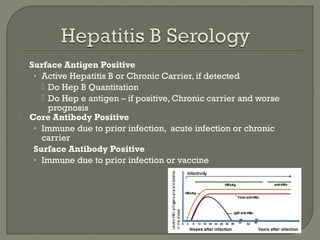
1. Direct fluorescent antibody staining of cells from a herpes simplex lesion can detect fluorescent infected cells under a fluorescence microscope, providing a more sensitive and specific method of diagnosis than a Tzanck prep.
2. Enzyme immunoassays are often used to detect non-culturable viruses like rotavirus, influenza, and respiratory syncytial virus from nasal/NP swabs at the point-of-care.
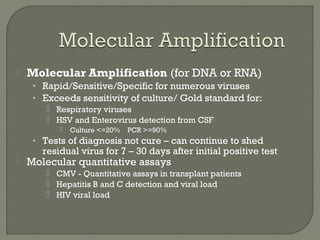
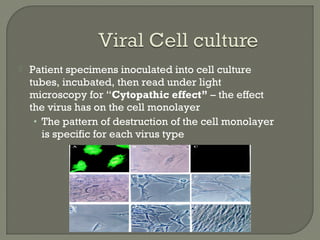
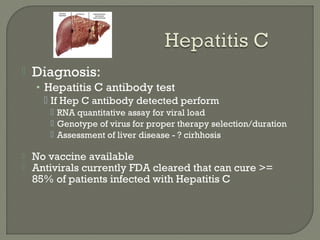
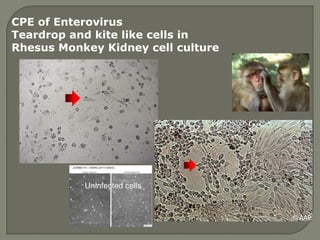
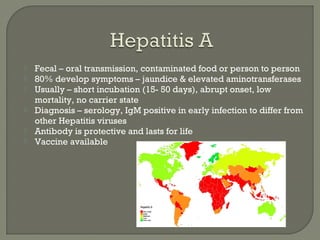
3. Molecular amplification tests exceed the sensitivity of viral culture and are the gold standard for diagnosing many respiratory viruses, herpes simplex from CSF, and enterovirus detection.













![ HH6
• Roseola [sixth disease]
• 6m-2yr high fever & rash
HH8
• Kaposi’s sarcoma
• Castleman disease
• Primary effusion
lymphoma
Onion skin pattern of
Castleman disease](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virologyupdate2017-170307154702/85/Virology-Update-2017-25-320.jpg)





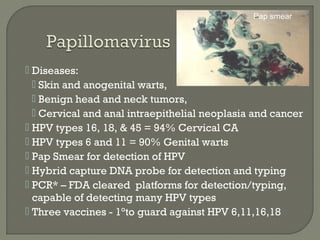
![• JC virus [John Cunningham]
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy -
PML -Encephalitis of immune suppressed
Destroys oligodendrocytes in brain
• BK virus
Causes latent virus infection in kidney
Progression due to immune suppression
Hemorrhagic cystitis
• Histology/PCR to aid diagnosis
Giant Glial Cells of JCV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virologyupdate2017-170307154702/85/Virology-Update-2017-34-320.jpg)











![ Disease: fever, malaise …. Death from respiratory
complications or secondary bacterial infection
Diagnosis
• Cell culture obsolete [RMK]
• Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) lateral flow membrane can be
used in point of care testing
• Amplification (PCR) gold standard for detection
Treatment: Amantadine and Tamiflu (Oseltamivir)
• Seasonal variation in susceptibility but Tamiflu usually
sensitive
Influenza B
• Milder form of Influenza like illness
• Usually <=10% of cases /year
Vaccinate – Trivalent vaccine -2 A viruses/1 B virus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virologyupdate2017-170307154702/85/Virology-Update-2017-52-320.jpg)

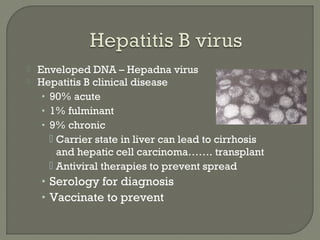
![• Fever, Rash, Dry Cough, Runny Nose,
Sore throat, inflamed eyes (photosensitive)
Can invade lung
• Respiratory spread - very contagious
• Koplik’s spots – bluish discoloration inner
lining of the cheek is pathognomonic
• Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis [SSPE]
Rare chronic degenerative neurological disease
Persistent infection with a mutated measles virus, due to
mutated virus there is total lack of an immune response
• Diagnosis: Clinical symptoms and Serology
• Vaccinate – MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella) vaccine
• Treatment: Nothing specific, Immune globulin, vitamin A
Measlessyncytium
H and E stain/ lung](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/virologyupdate2017-170307154702/85/Virology-Update-2017-54-320.jpg)