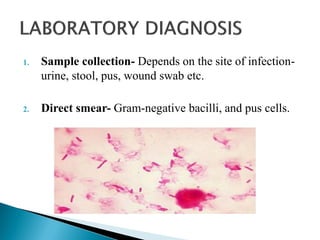
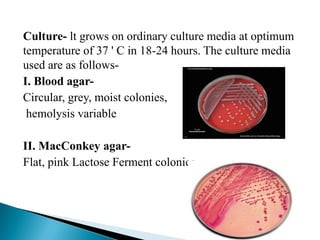
This document discusses the properties and identification of members of the Enterobacteriaceae family. It notes that they are gram-negative, facultative anaerobic bacilli that are commonly found in the human intestine and can cause various infections. The document focuses on Escherichia coli as the most common and important human pathogen in the family. It describes the virulence factors, diseases caused, and methods to identify E. coli through culture, biochemical tests, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing.