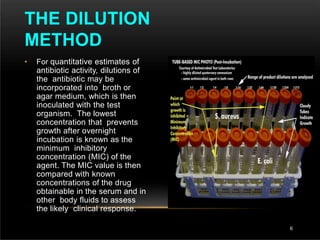
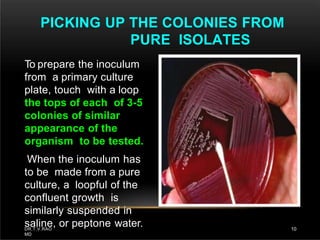
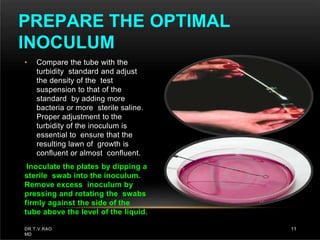
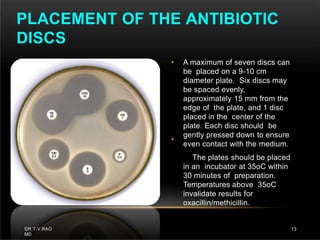
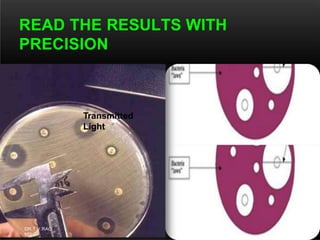
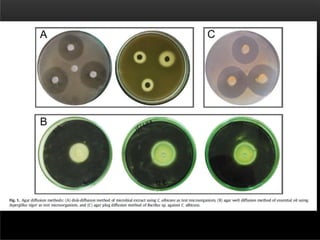
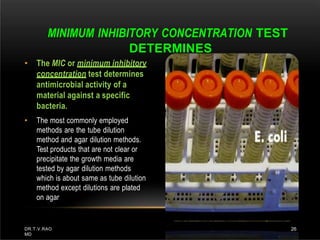
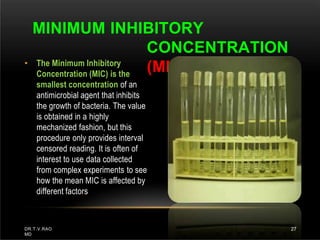
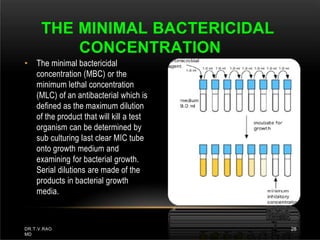
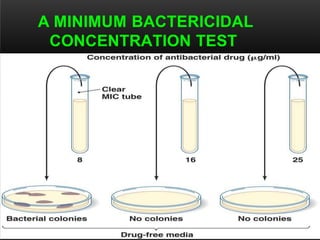
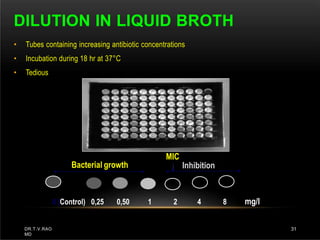
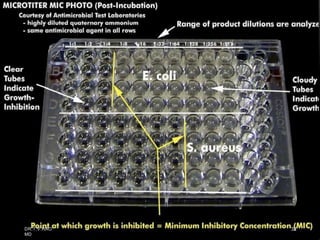
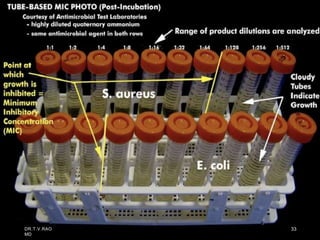
The document discusses antibiotic susceptibility testing and the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method. Antibiotic susceptibility testing determines how effective antibiotic therapy is against bacterial infections. The Kirby-Bauer method involves placing disks impregnated with antibiotics onto an agar plate inoculated with the bacterial isolate. The zone of inhibition is measured after incubation and used to determine if the bacteria is susceptible, intermediate, or resistant to the antibiotic. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is also determined to assess the clinical response to antibiotic treatment.