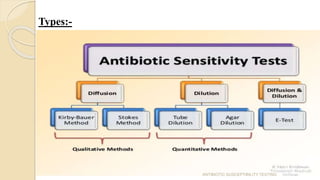
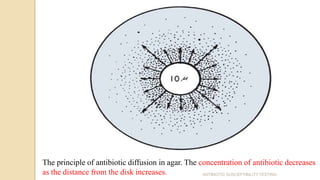
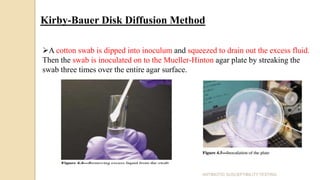
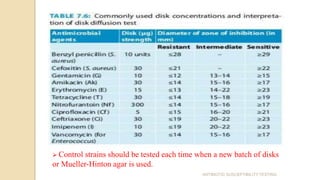
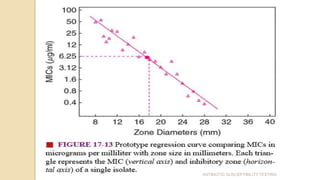
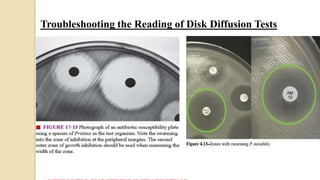
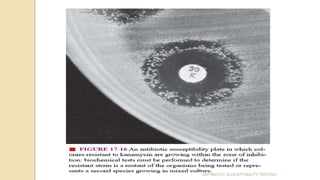
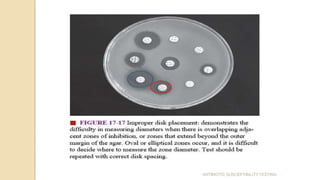
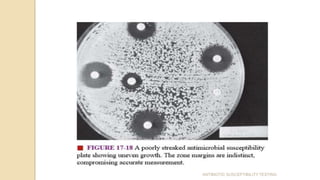
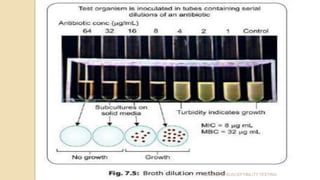
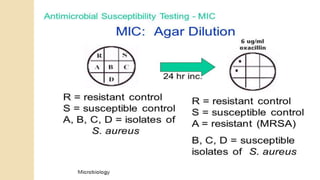
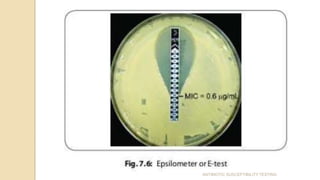
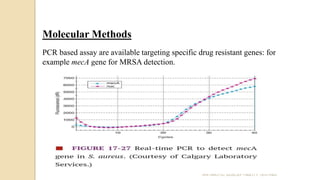
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing determines how effective antibiotic therapy is against bacterial infections. There are several methods for testing, including disk diffusion, dilution tests, and automated systems. Disk diffusion involves placing disks impregnated with antibiotics onto inoculated agar plates and measuring inhibition zones. Mueller-Hinton agar is commonly used as the growth medium. Dilution tests determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antibiotics using serial dilutions in broth or agar. Automated systems streamline the testing process. Proper technique and controls are important for accurate and reproducible results.