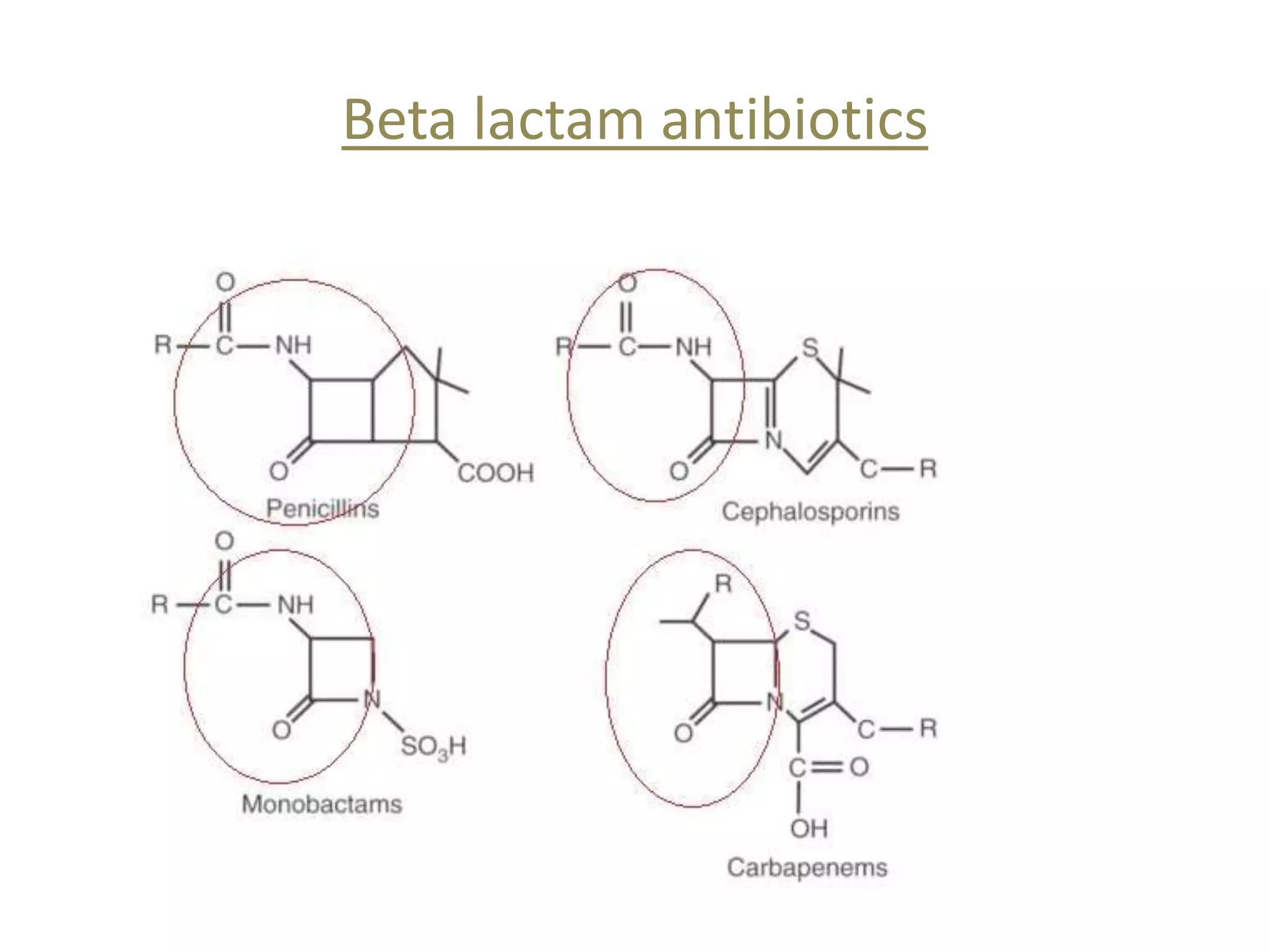
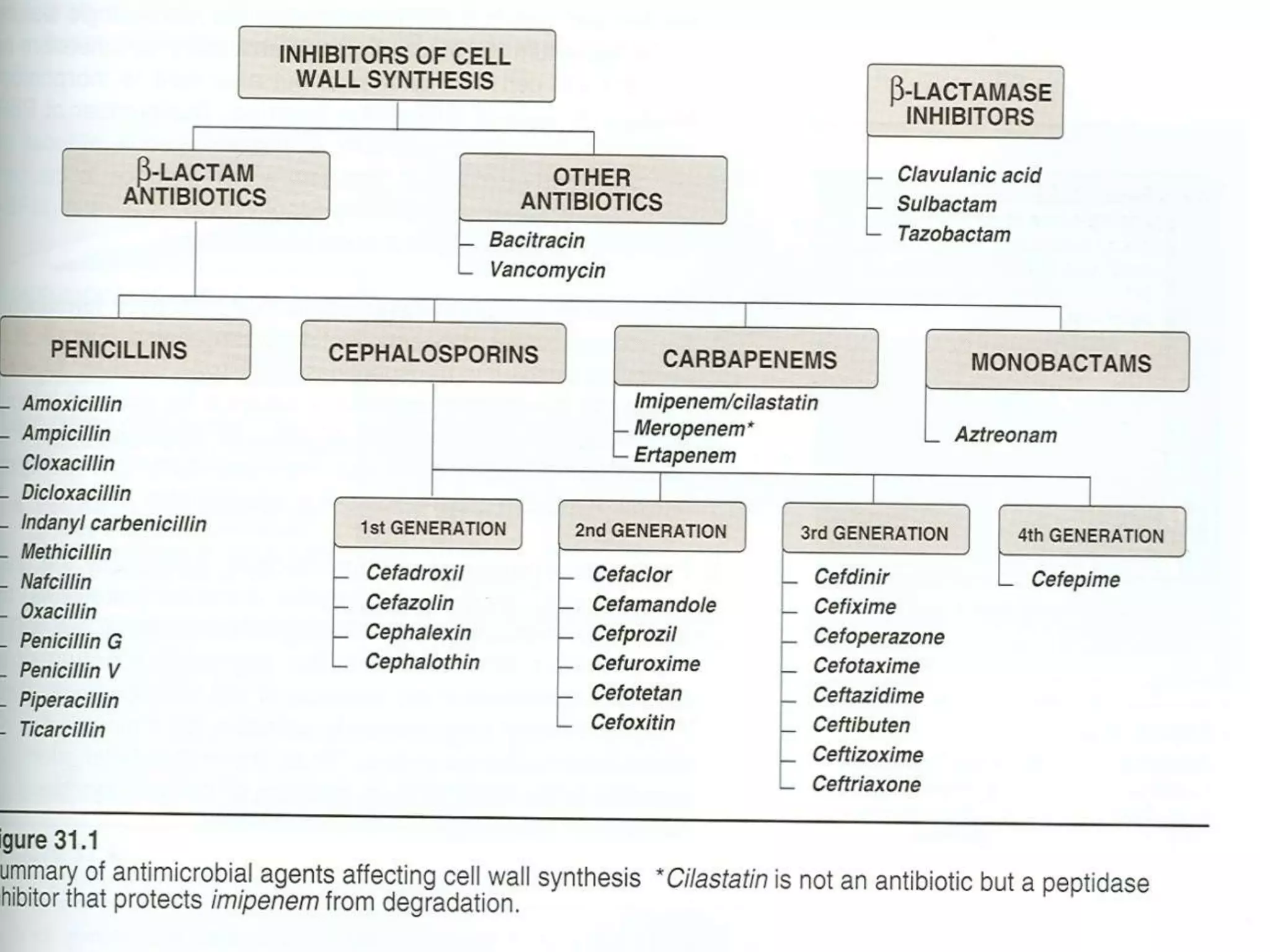
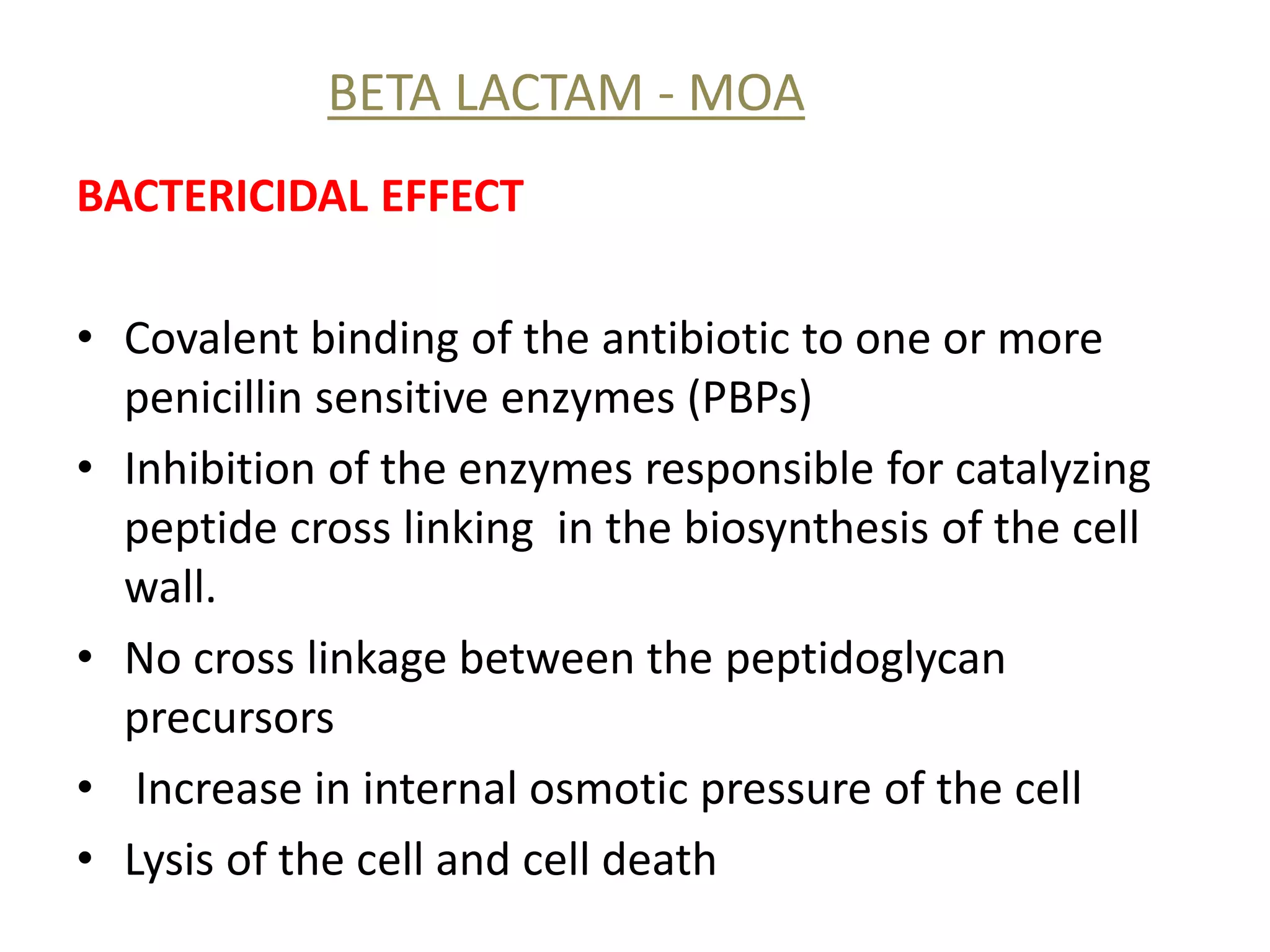
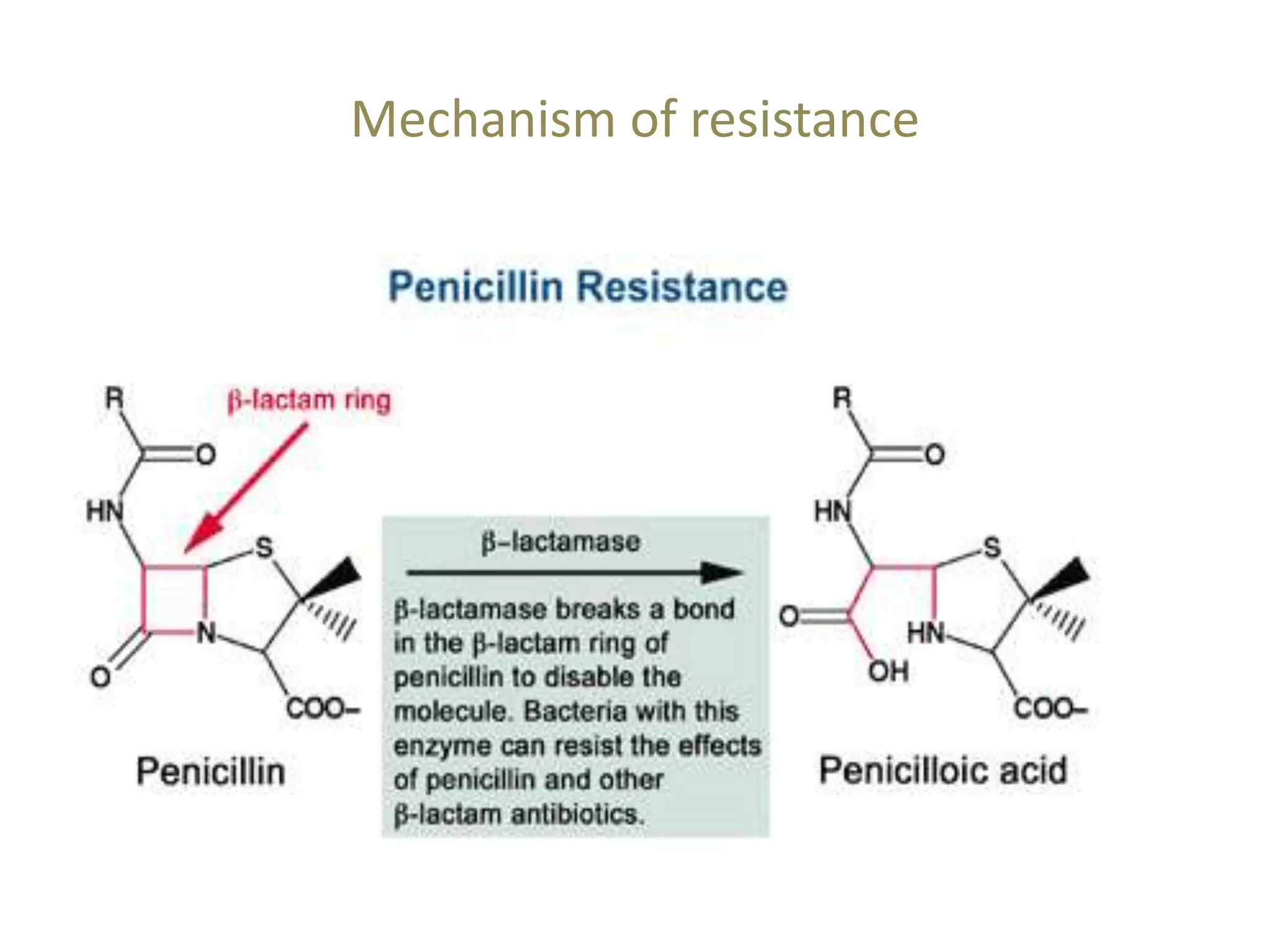
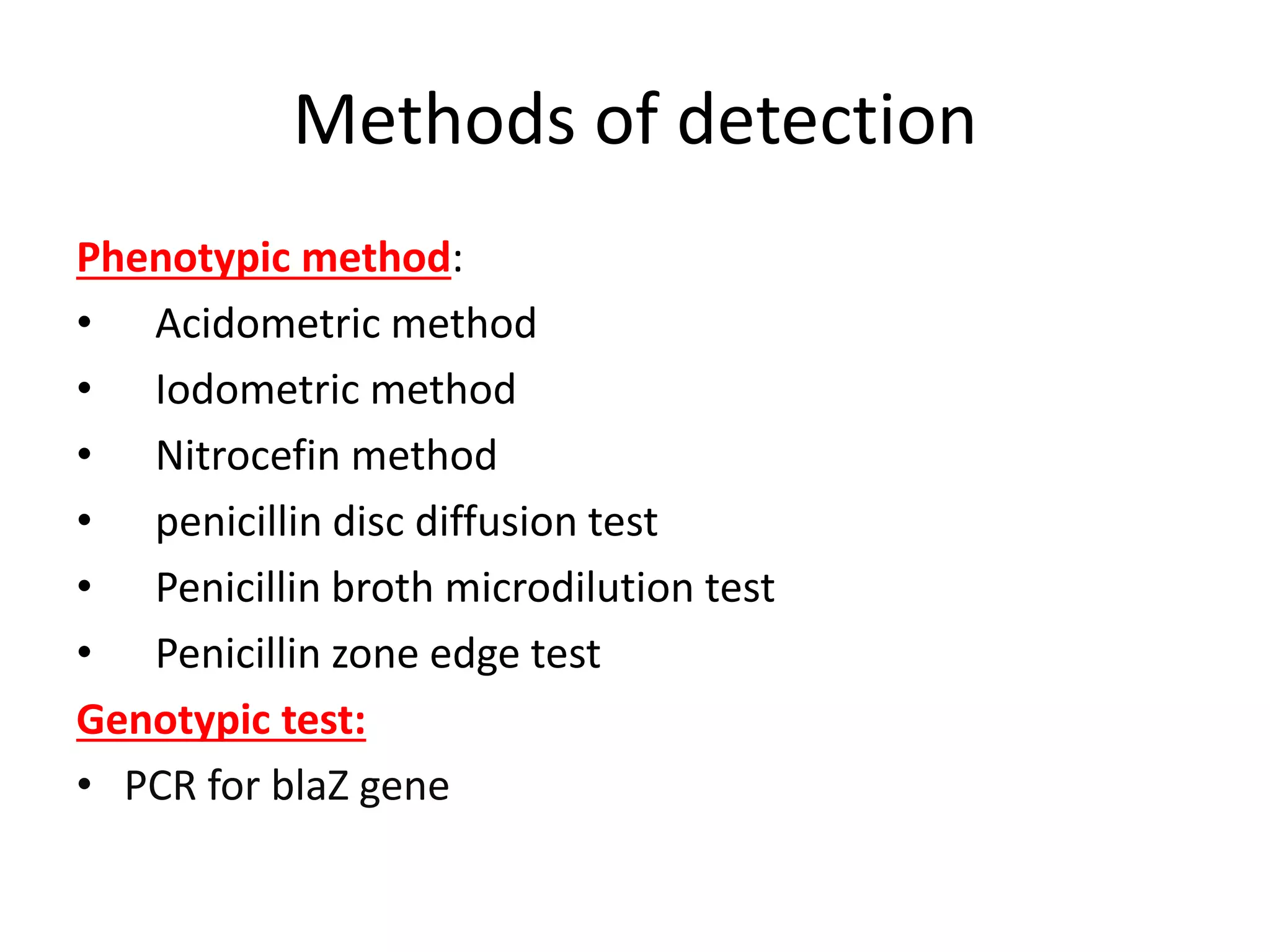
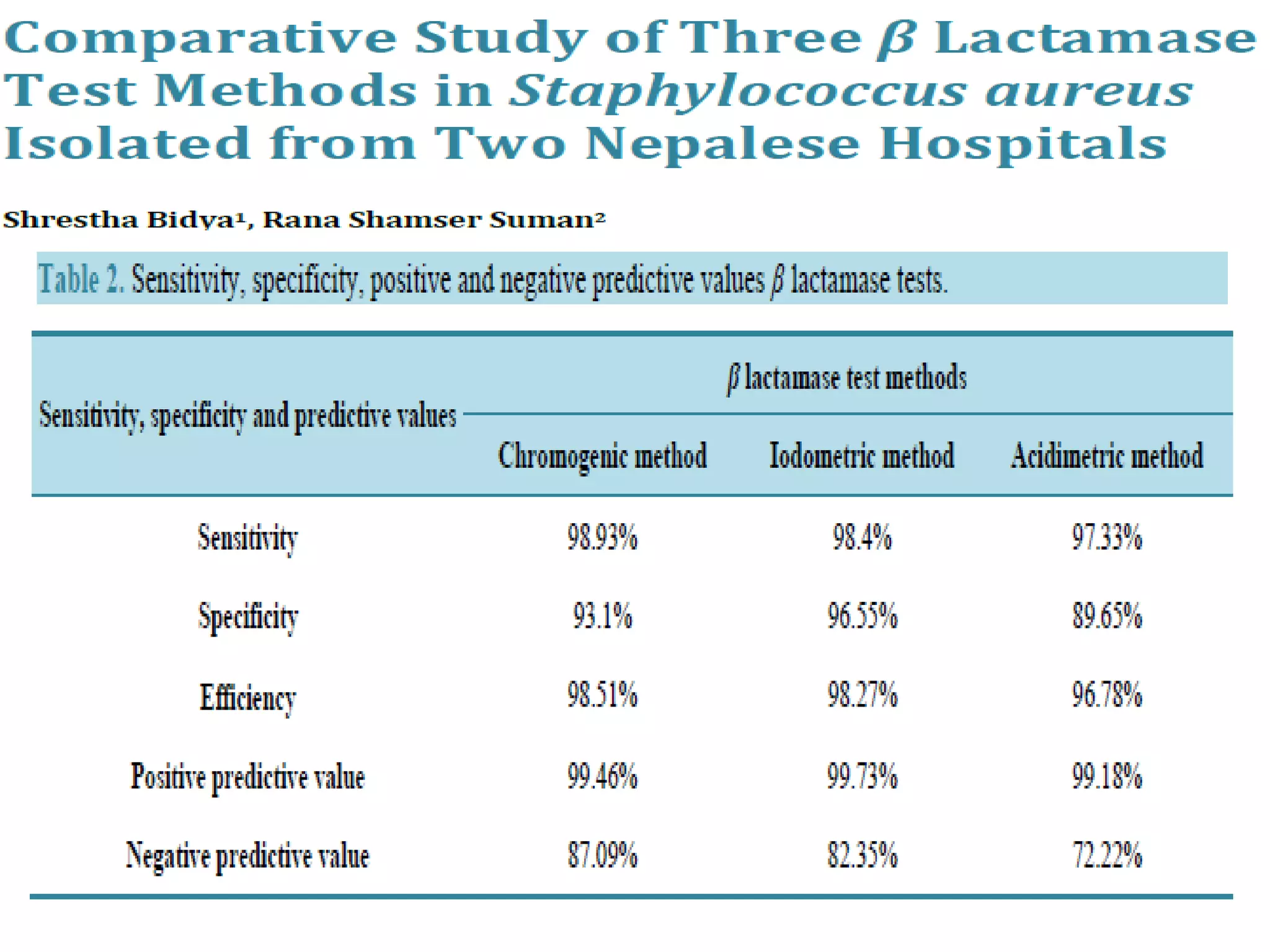
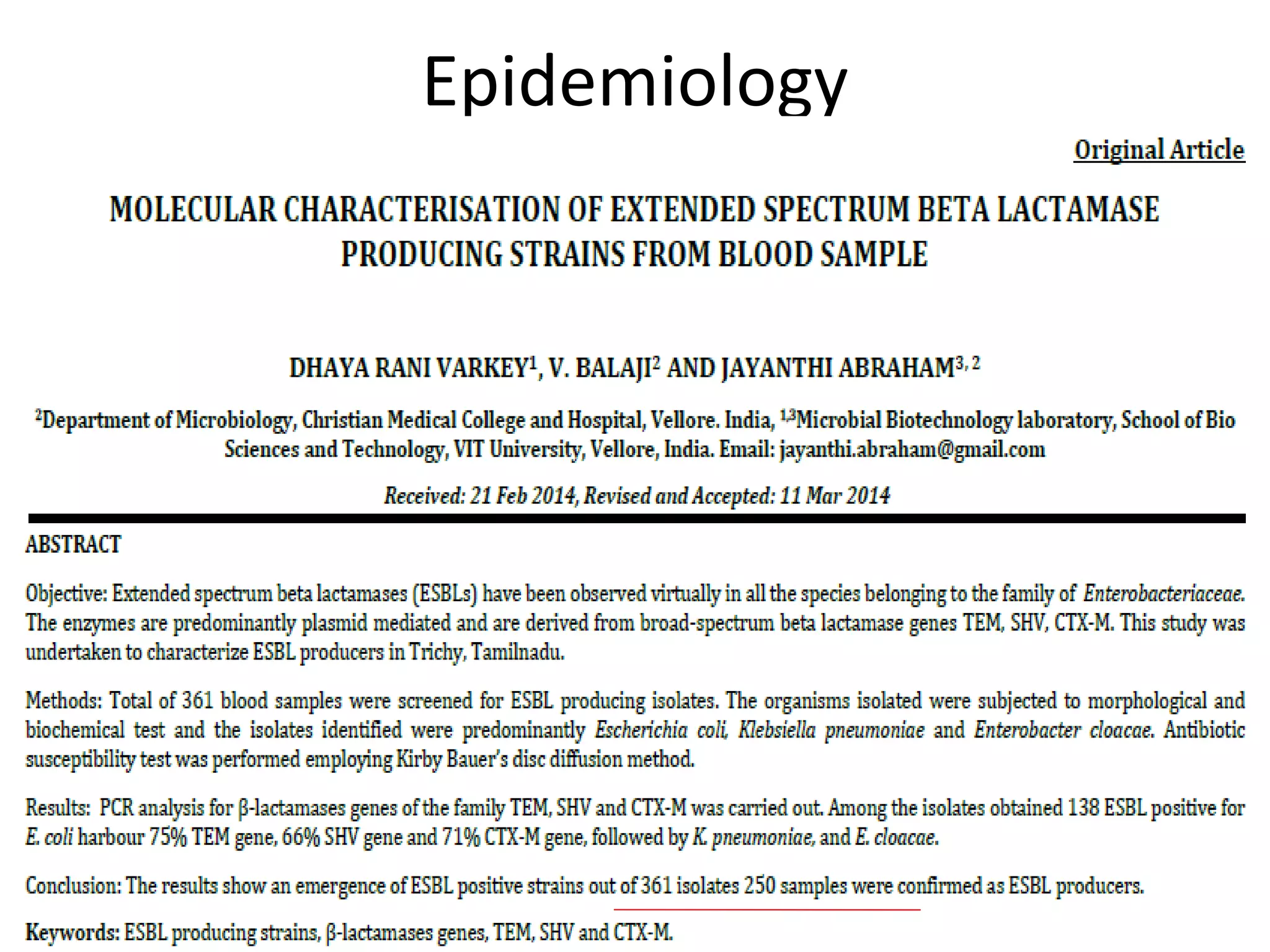
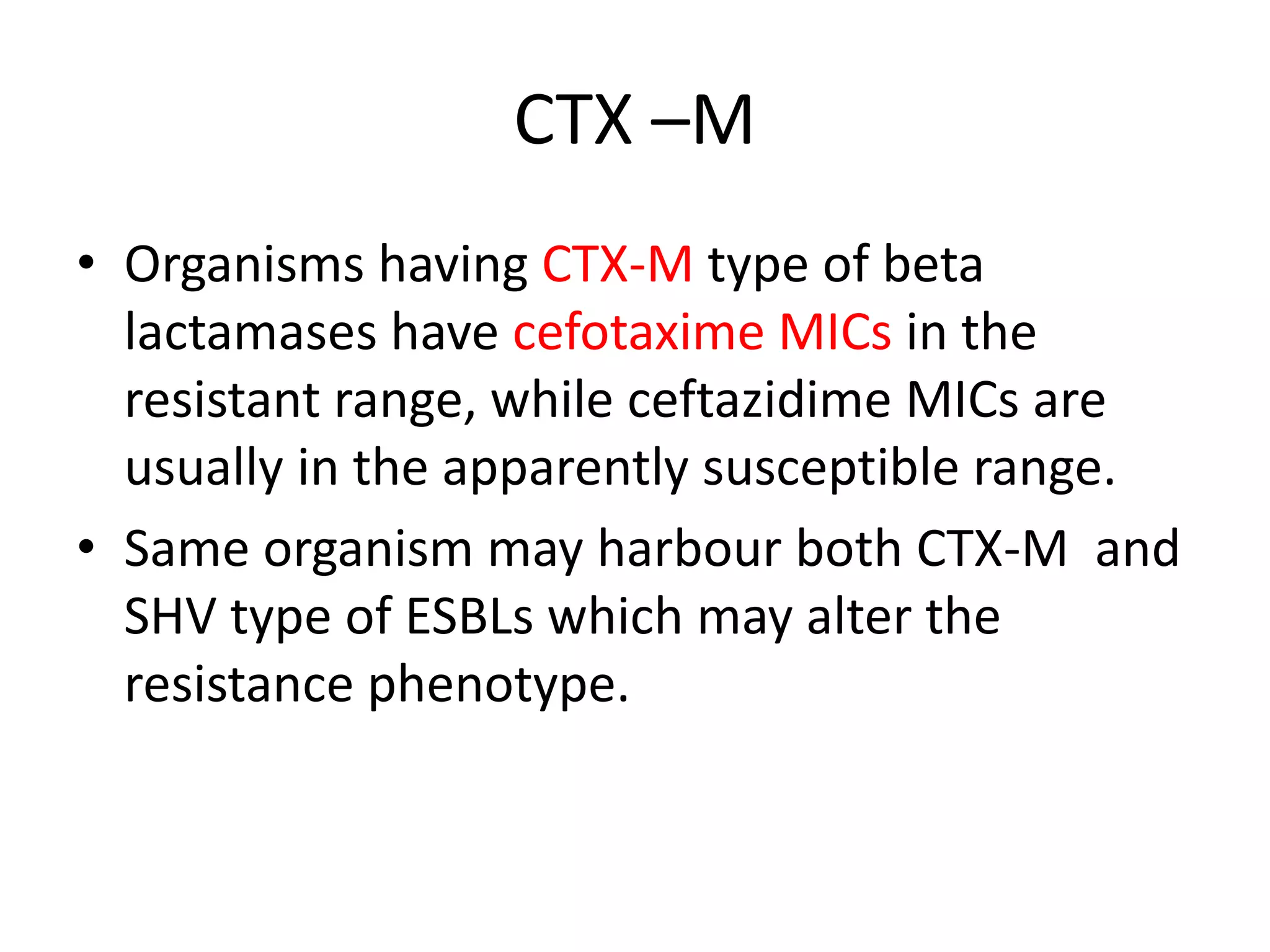
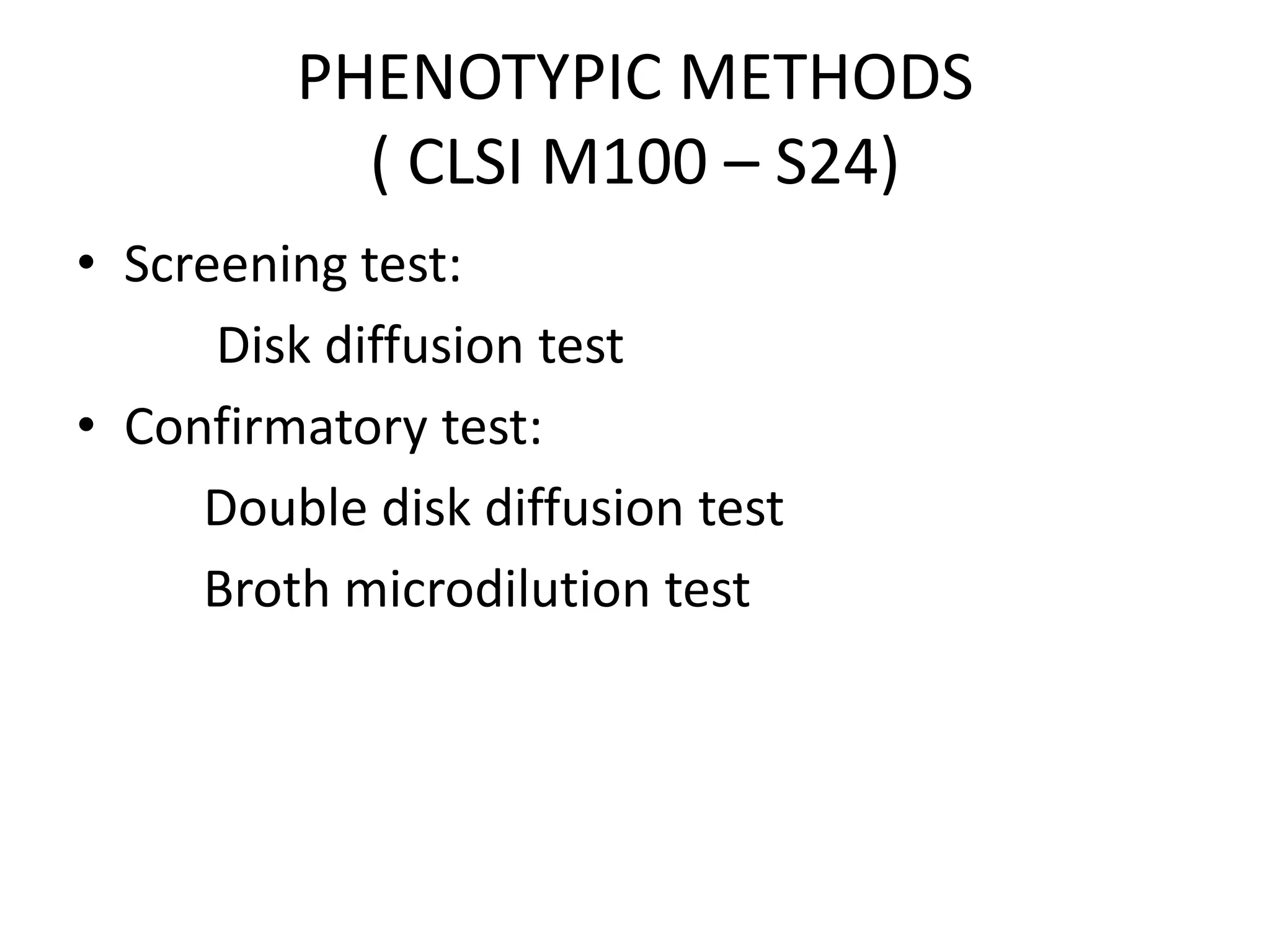
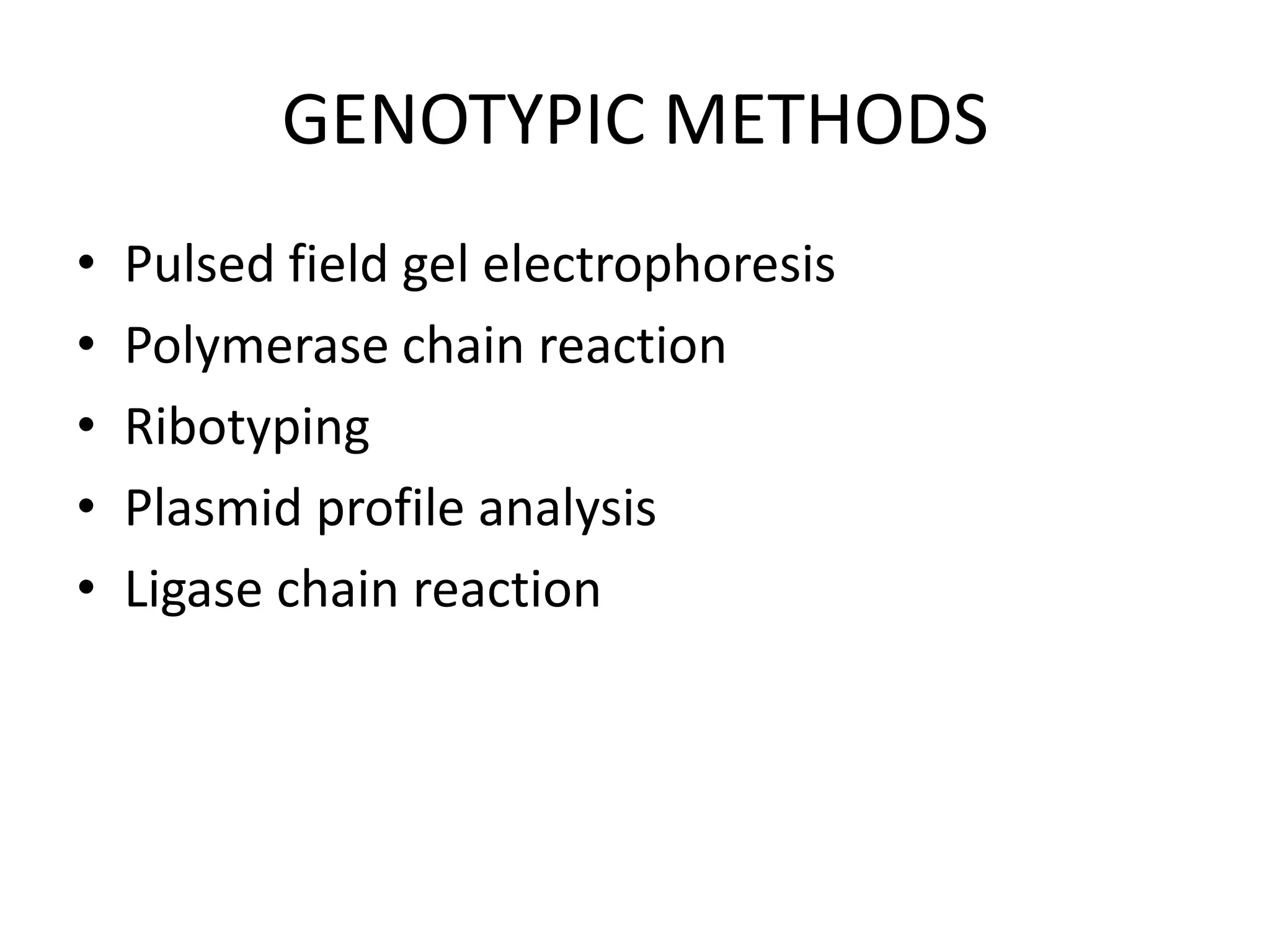
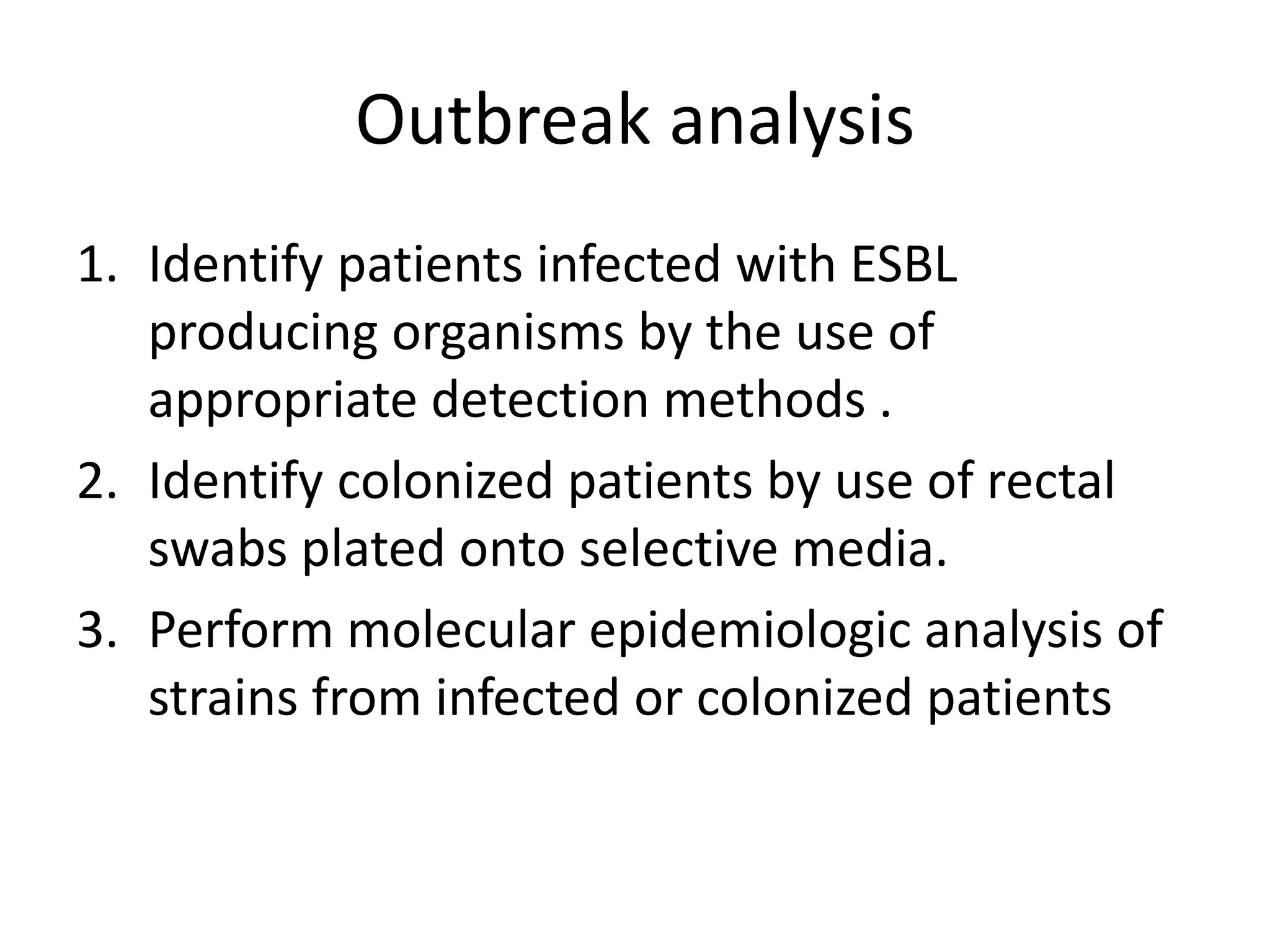
This document discusses beta lactamases and extended spectrum beta lactamases (ESBLs). It defines beta lactamases as enzymes produced by bacteria that confer resistance to beta lactam antibiotics by hydrolyzing the beta lactam ring. ESBLs are a type of beta lactamase that hydrolyze penicillins, cephalosporins, and aztreonam but are inhibited by beta lactamase inhibitors. The document outlines methods for detecting beta lactamases, such as the penicillin zone edge test, and ESBLs, including disk diffusion and broth microdilution tests. It also discusses