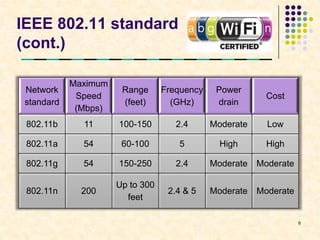
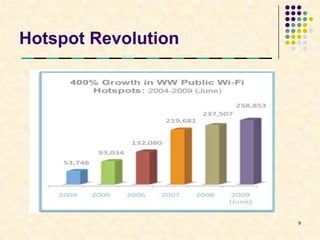
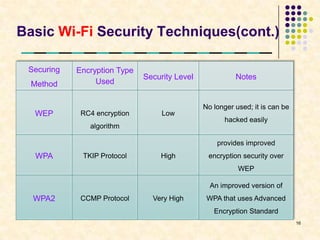
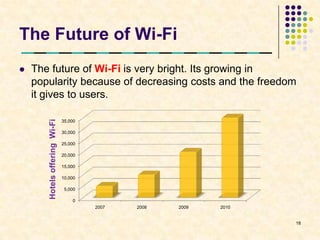
This document summarizes Wi-Fi technology. It defines Wi-Fi as a wireless networking standard that allows devices to connect to the Internet without wires. It describes the various IEEE 802.11 wireless standards and their characteristics. It also discusses hotspots, the elements of a Wi-Fi network like access points and adapters, how a Wi-Fi network works, advantages and limitations of Wi-Fi, security techniques, and the future growth of Wi-Fi access.