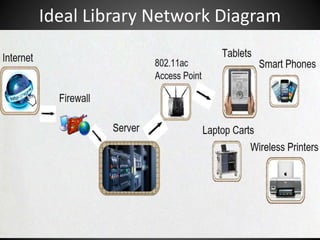
Wireless networking in schools provides mobility for students and supports e-learning. It allows students to access the curriculum and research resources from anywhere in the school using devices like laptops and tablets. Wireless networks eliminate the need to run cables and wires, making installation faster and more flexible. They also reduce costs compared to wired networks. While wireless improves access and mobility, schools must also implement security measures to protect their network and devices on it. Newer wireless standards like 802.11ac provide faster speeds and greater capabilities to meet the needs of students' use of technology in schools.