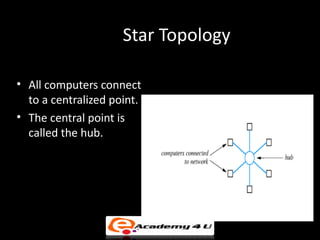
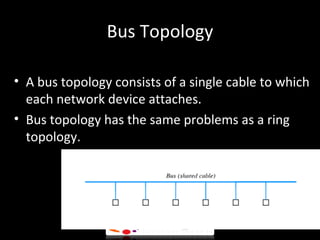
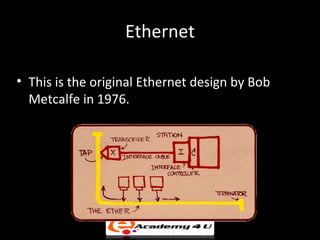
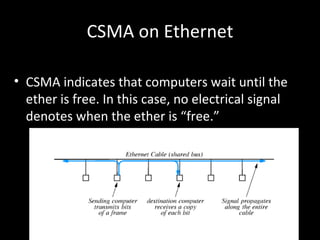
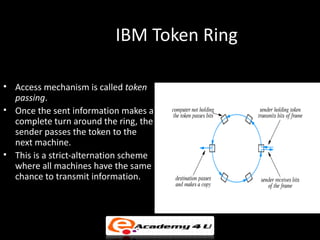
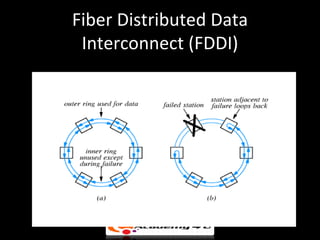
There are three main types of local area network (LAN) topologies: star, ring, and bus. The star topology uses a central hub that all computers connect to. The ring topology connects each computer to the two adjacent computers, forming a ring. The bus topology uses a single cable that all network devices attach to. Ethernet and LocalTalk are examples of bus networks that use Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) to determine when devices can transmit data. Token ring networks use a token passing mechanism where devices must possess a token to transmit and then pass it to the next device.