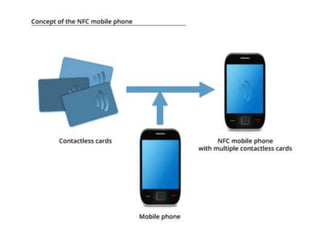
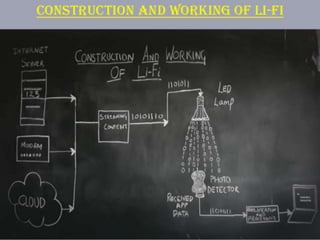
Wireless communication allows transfer of information between two or more points without wires. Common forms of wireless communication include Bluetooth, NFC, WiFi, and LiFi. Bluetooth uses short-range radio links to connect devices like headphones, keyboards and printers. It transmits data via low-power radio waves at a frequency of 2.45 gigahertz and can connect up to eight devices simultaneously. NFC operates at a very short range through electromagnetic induction, allowing data exchange when devices are touched or in close proximity. It is commonly used for contactless payments and data sharing. WiFi enables internet access from any location within range of a base station using radio waves, providing cable-like speeds wirelessly. LiFi is a wireless optical