The document provides an overview of wireless networks, including:
1. Wireless networks interconnect systems capable of providing mobile service within a geographic region without physical cables.
2. Components include base stations, mobile switching centers, and public telephone networks. Wireless networks offer mobility, lower installation costs, and flexibility over wired networks but have lower speeds and security.
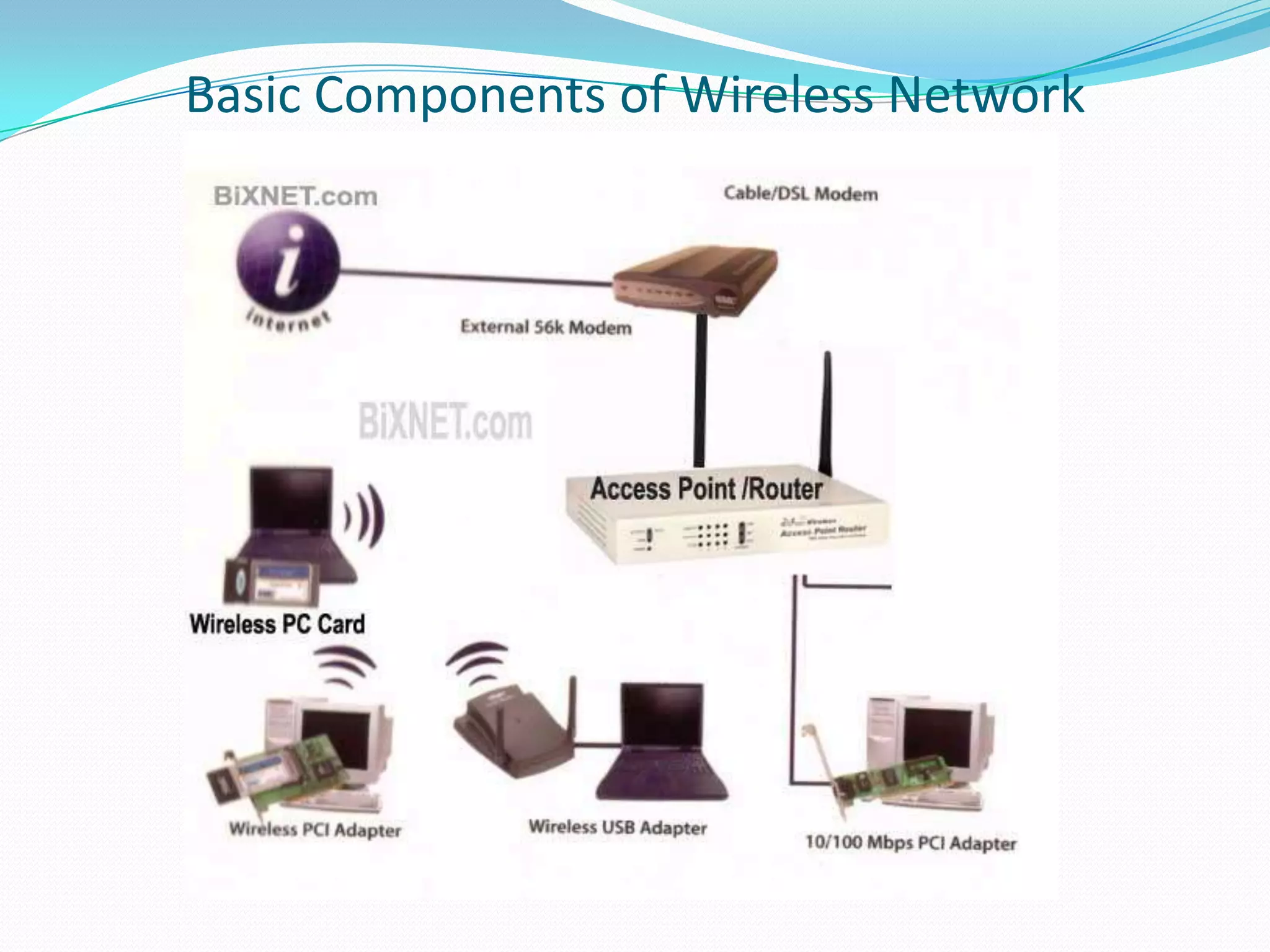
3. Basic components are wireless network interface cards, access points, and hardware like antennas. Wireless modes include ad-hoc peer-to-peer and infrastructure with access points. Security methods are SSIDs, MAC filtering, and encryption.