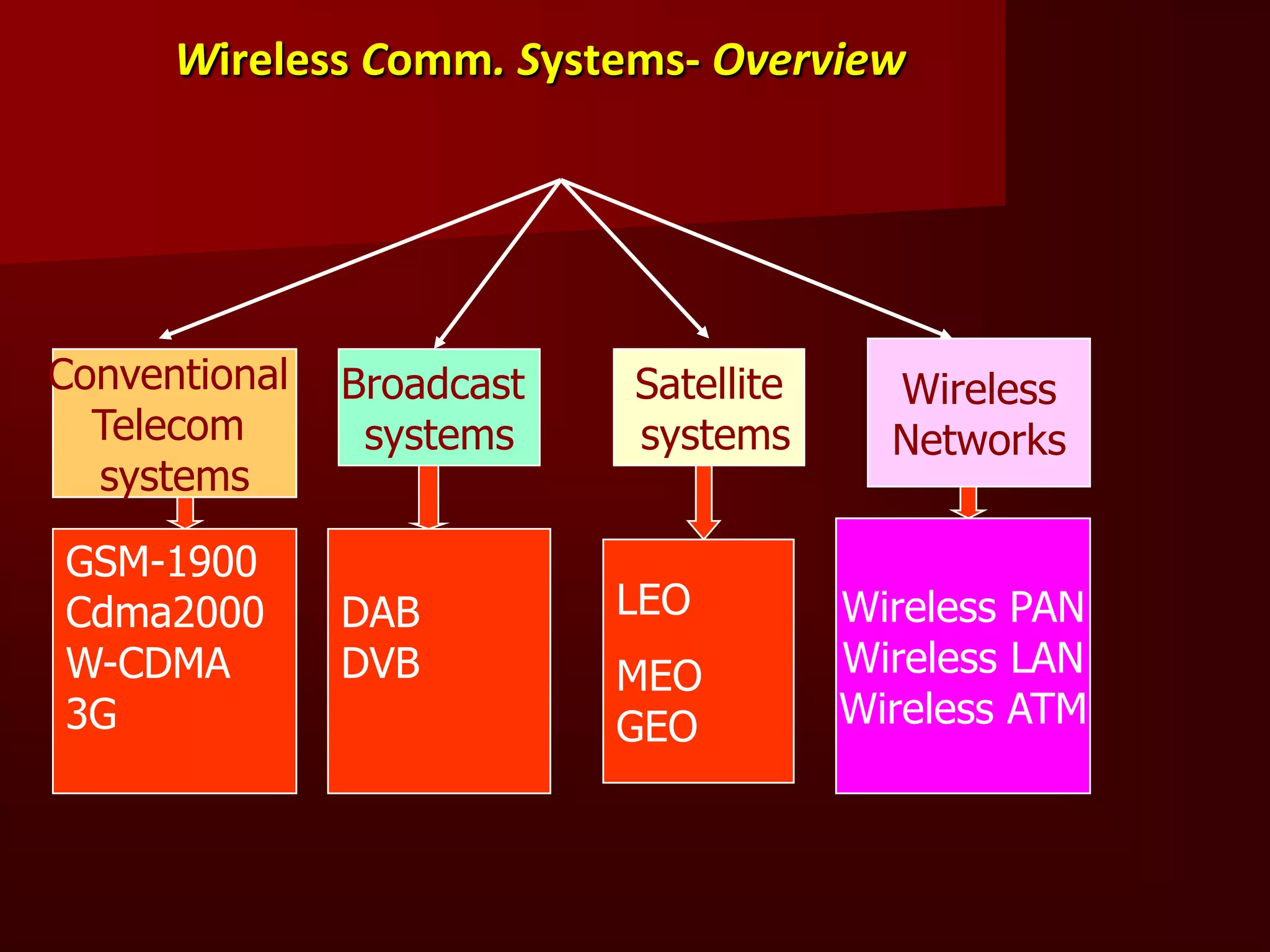
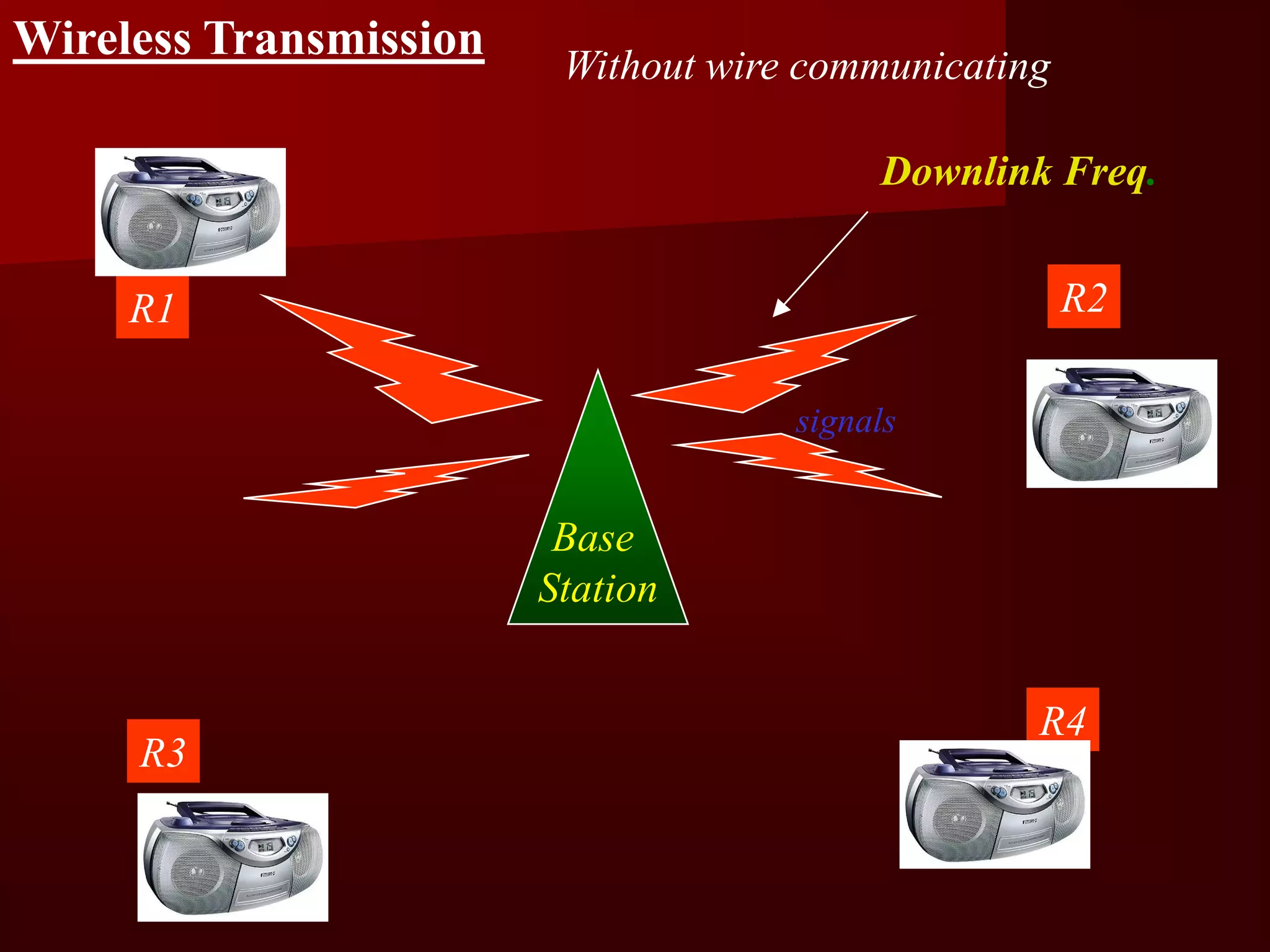
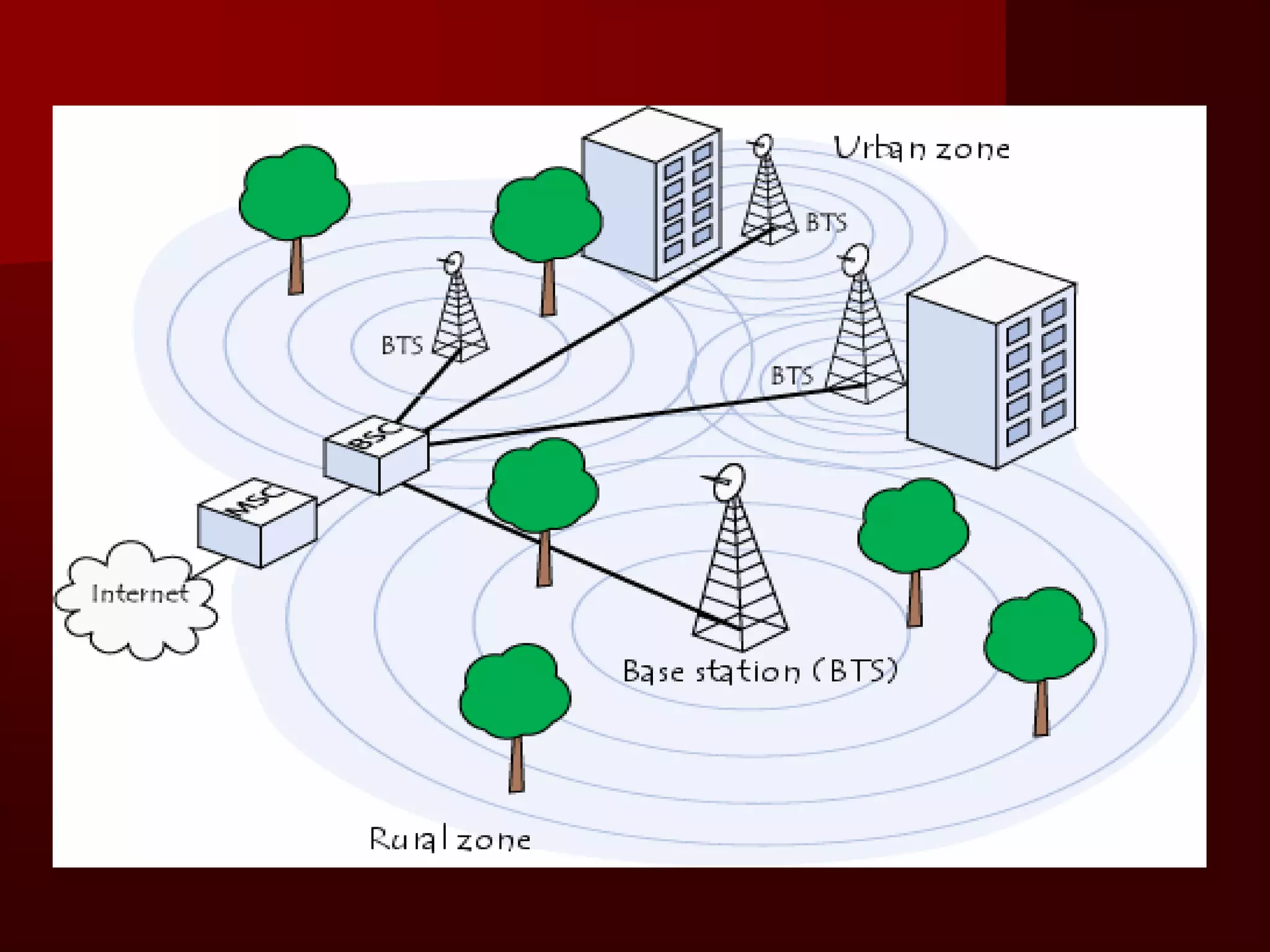
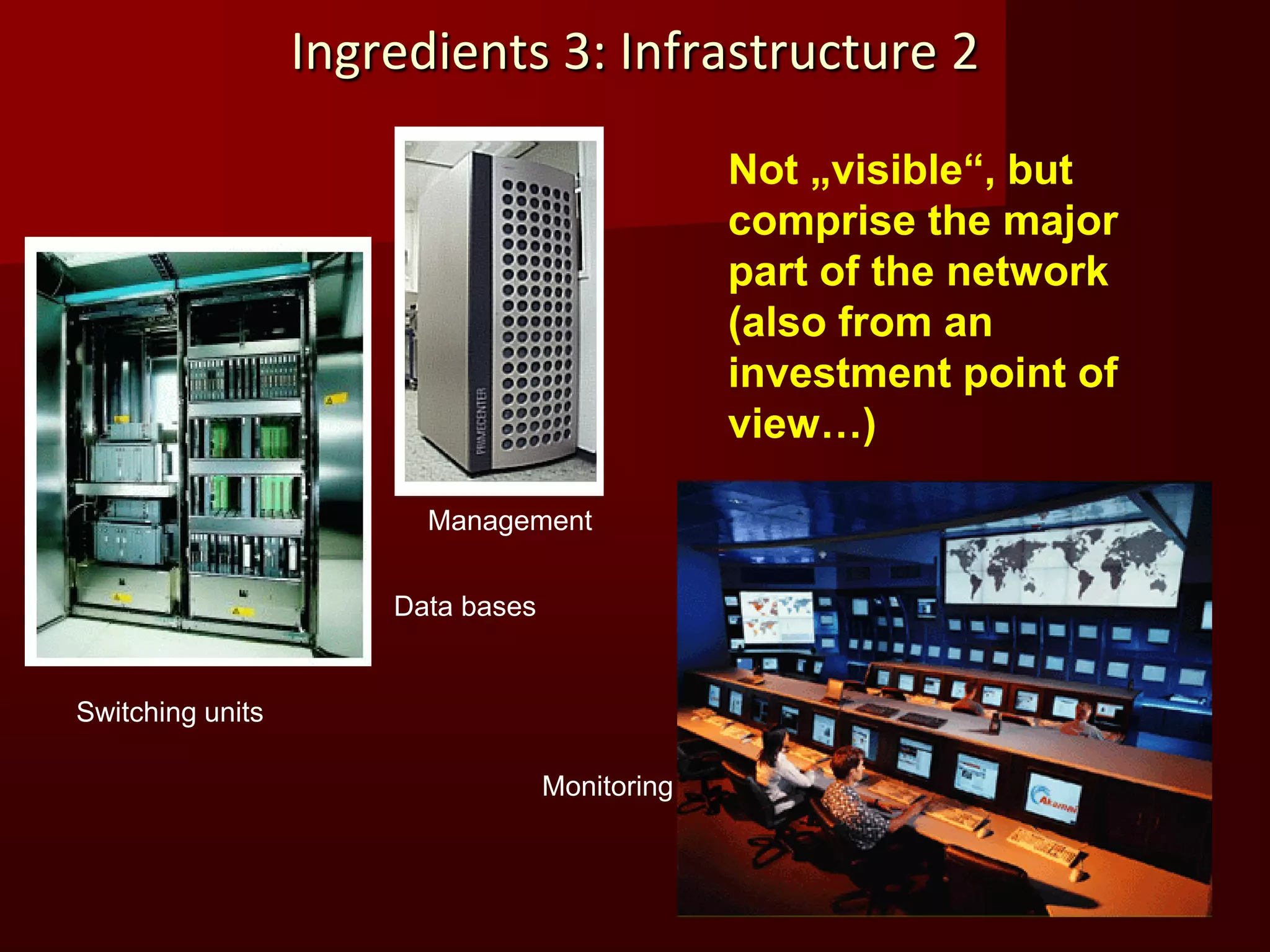
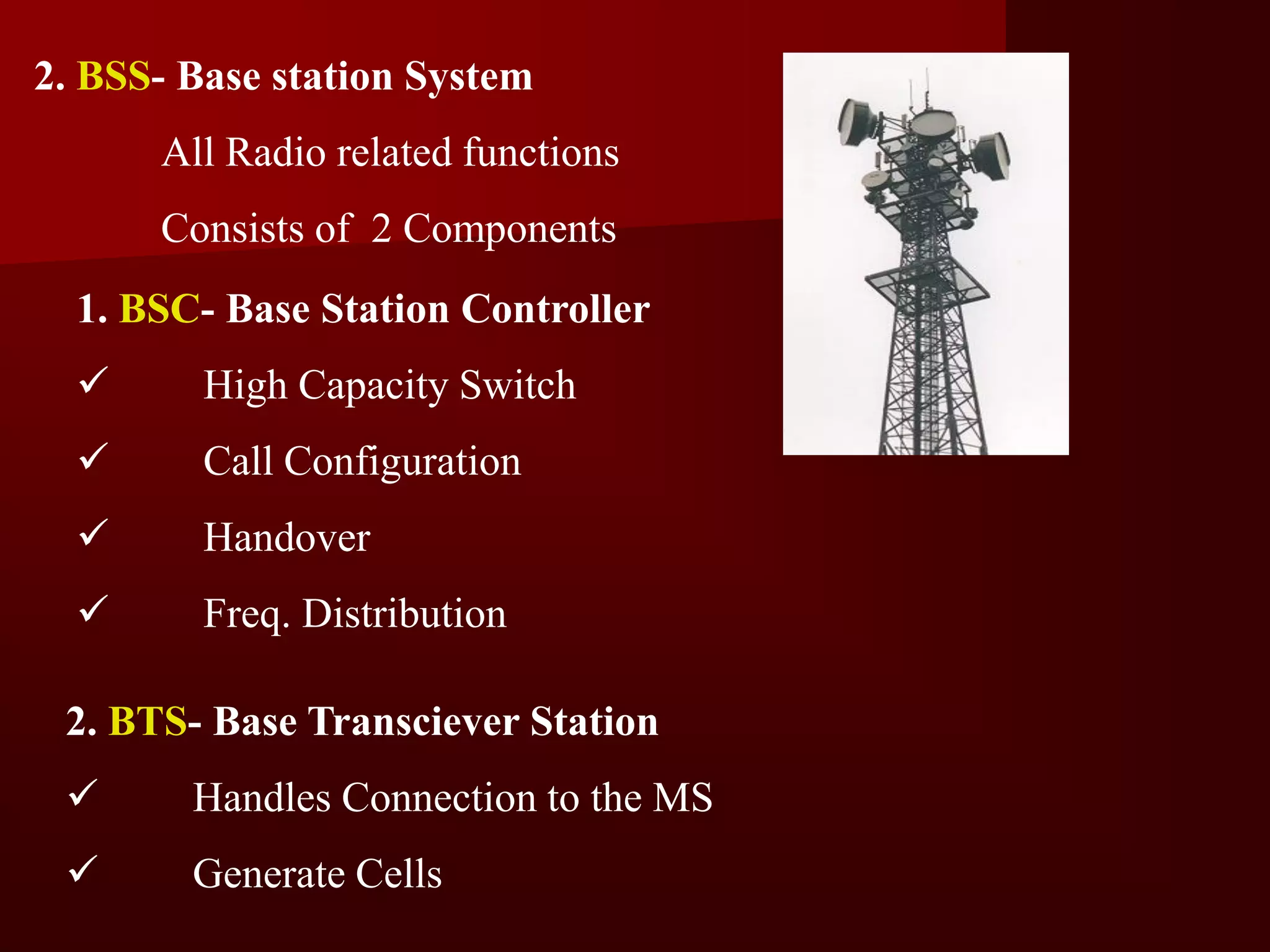
The document summarizes the history of mobile communication from 1G to 4G technologies. It discusses the evolution from early analog 1G systems developed in the 1970s-80s to 2G digital GSM networks in the 1980s-90s capable of voice and limited data. 3G systems launched in the late 1990s provided improved voice quality and higher speed data up to 2Mbps. Emerging 4G technologies are expected to offer data rates from 20-100Mbps. The document also provides an overview of the fundamental principles of cellular networks and discusses GSM as the most widely used 2G digital standard globally.