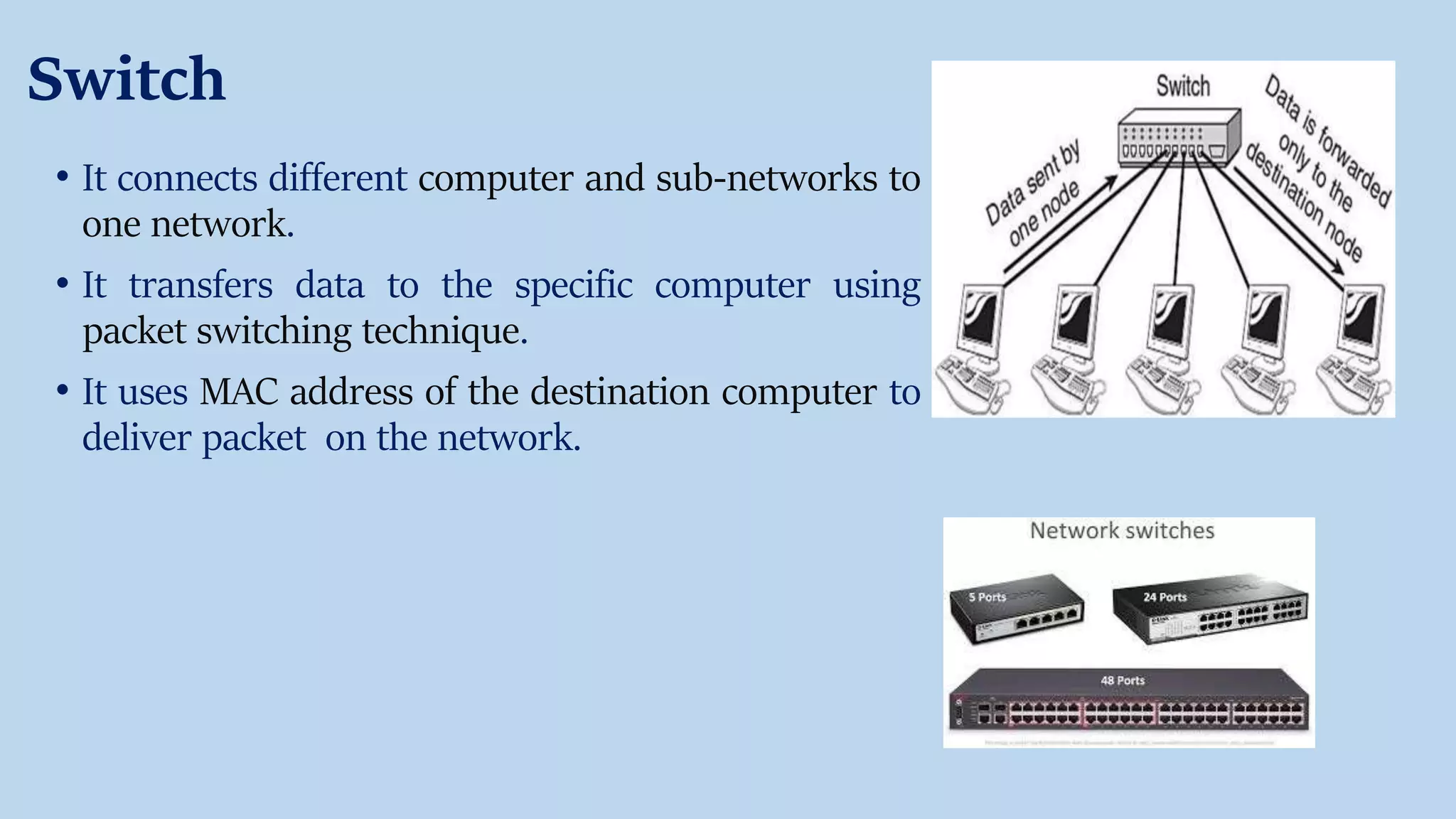
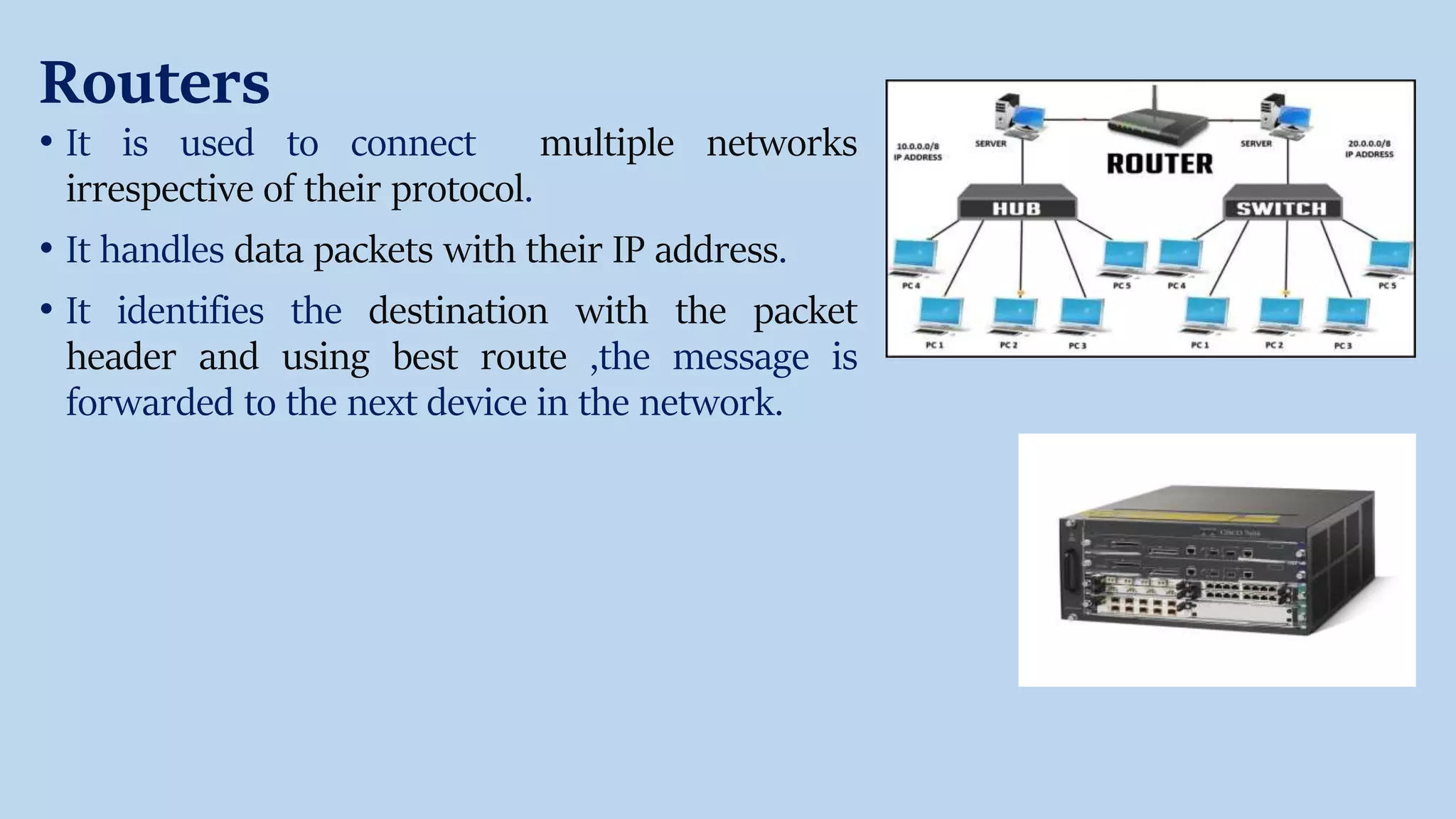
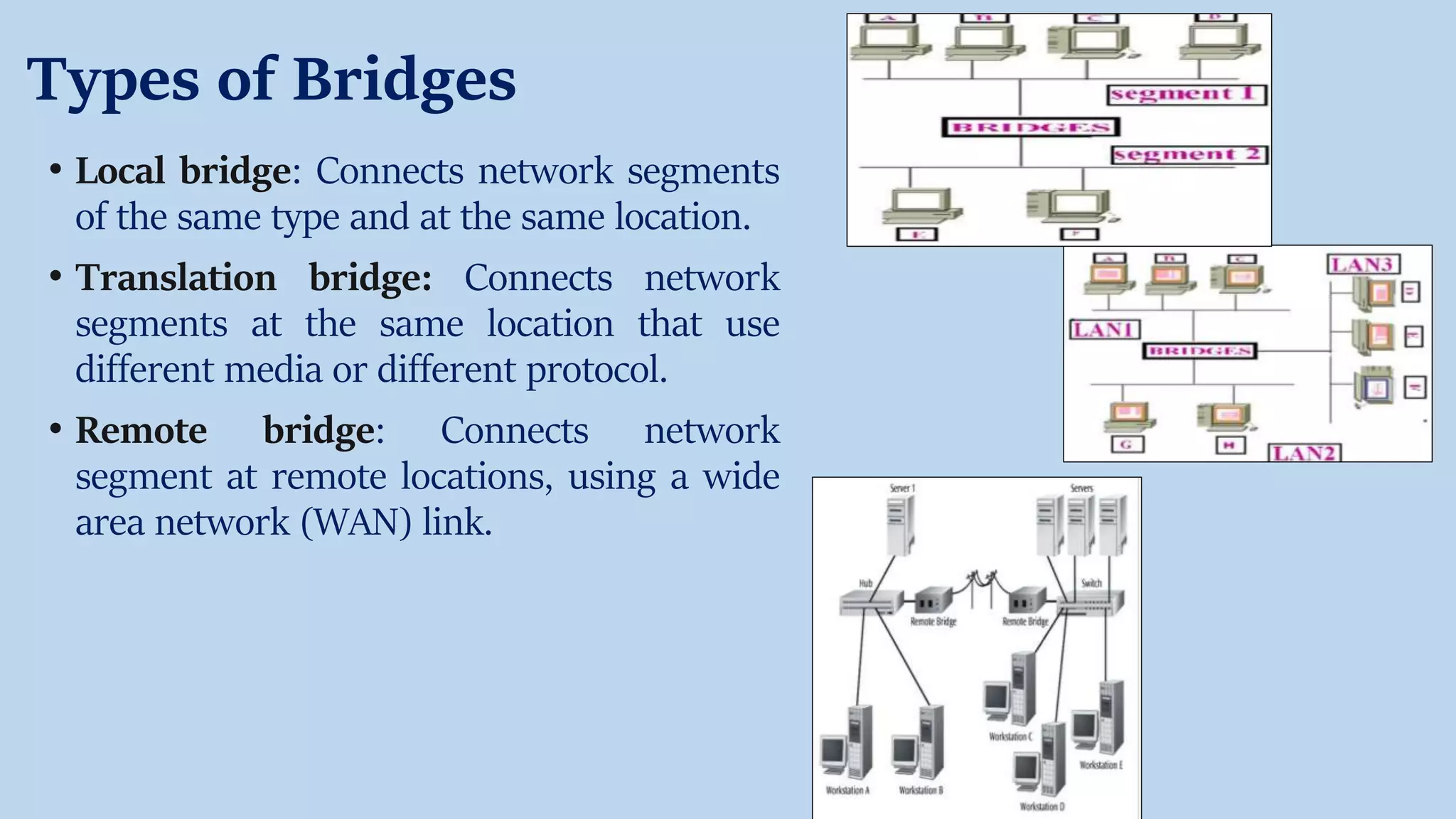
The document provides an overview of various network devices including hubs, switches, routers, modems, repeaters, bridges, and gateways, explaining their functions and types. It introduces key concepts such as MAC and IP addresses and communication protocols like TCP/IP. Each device is described in terms of its role in facilitating network connectivity and data transmission, with distinctions between types of each device.