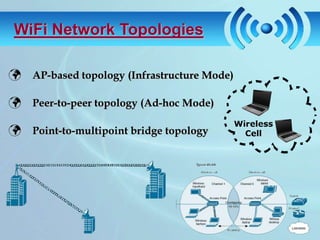
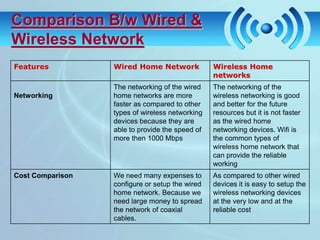
The document discusses wireless fidelity (WiFi) and IEEE 802.11 standards. It describes the setup required for WiFi including access points and wireless cards. It then covers how WiFi works using radio waves, the network topologies of AP-based and peer-to-peer, and common WiFi security threats like eavesdropping and denial of service attacks. It also lists advantages, disadvantages, and applications of WiFi networks.