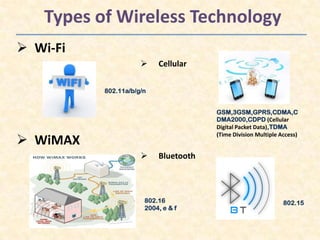
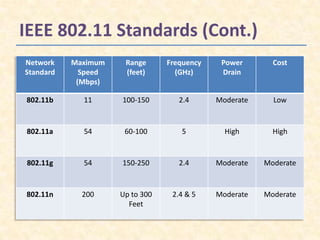
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that allows devices to connect to the Internet without being physically connected with wires. It uses radio waves to transmit data between devices like computers, smartphones and access points. Common standards include 802.11b, 802.11g and 802.11n. Wi-Fi networks have advantages like mobility and easy installation but also limitations such as limited range, security risks from interference and potential hacks. Basic security techniques are used to encrypt Wi-Fi connections and protect data transmission.