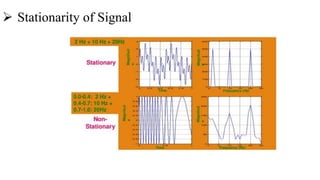
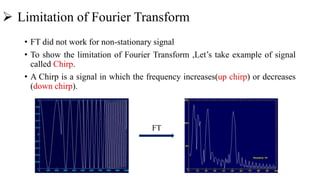
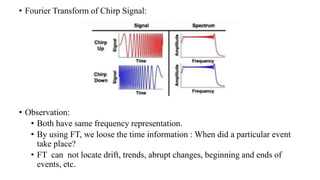
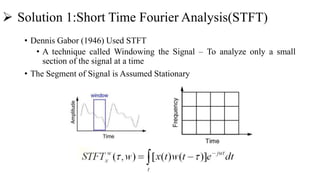
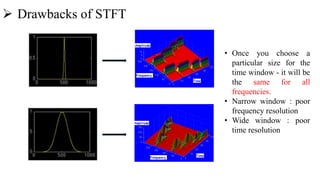
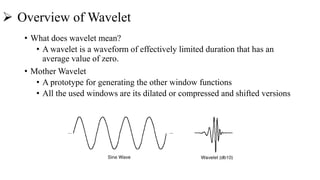
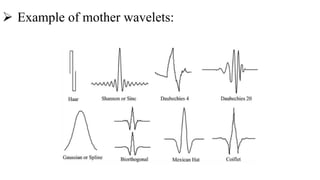
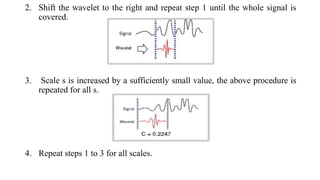
This document introduces the wavelet transform, which can analyze non-stationary signals like the Fourier transform cannot. It discusses the limitations of the Fourier transform and short-time Fourier analysis for non-stationary signals. The continuous wavelet transform analyzes signals at different scales and translations using wavelets derived from a mother wavelet. The discrete wavelet transform uses filters at different scales to decompose signals into high and low frequency components. Wavelet transforms have applications in signal compression, denoising, and time-frequency analysis due to their ability to analyze signals locally in both time and frequency.




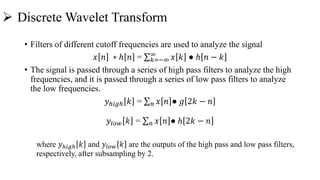
![• x[n] is the original signal to be decomposed
• h[n] and g[n] are low pass and high pass filters.
• The bandwidth of the signal at every level is
marked on the figure as "f".
• At every level, the filtering and subsampling
will result in half the number of samples (and
hence half the time resolution) and half the
frequency band spanned (and hence double the
frequency resolution).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wavelettransform-181205061952/85/Wavelet-transform-17-320.jpg)


