The document discusses various properties of signals including:
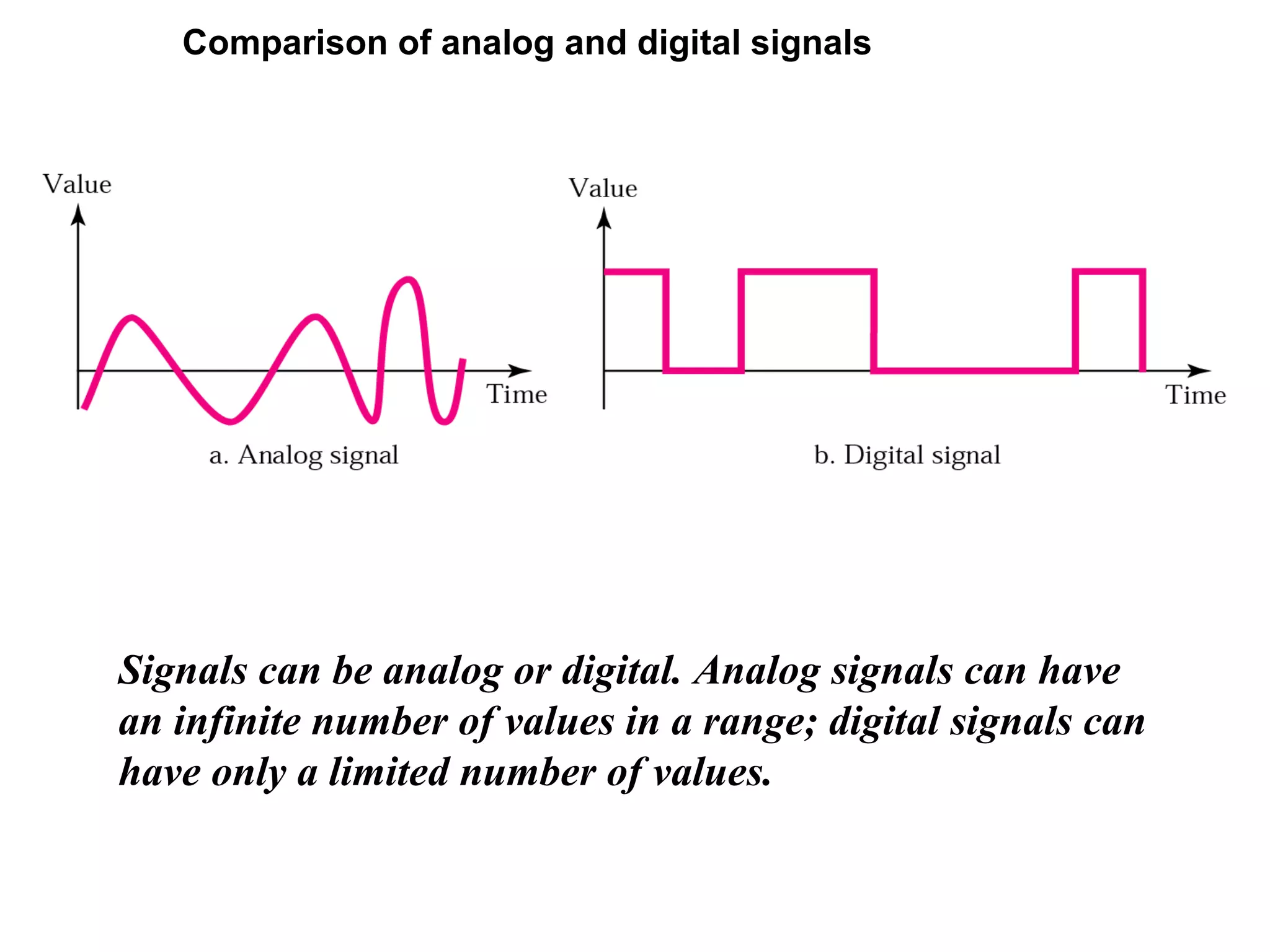
- Analog signals can have an infinite number of values while digital signals are limited to a set of values.
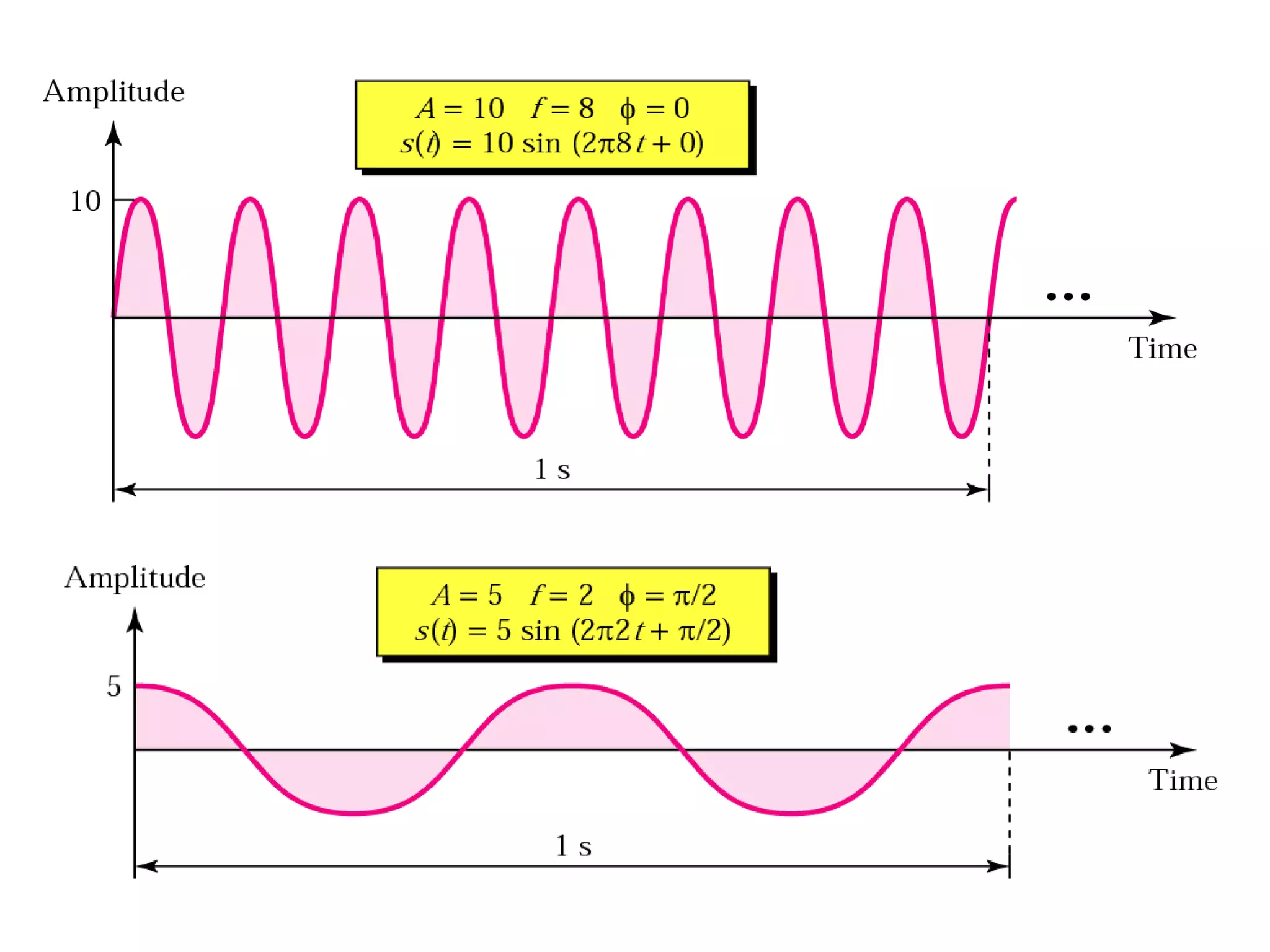
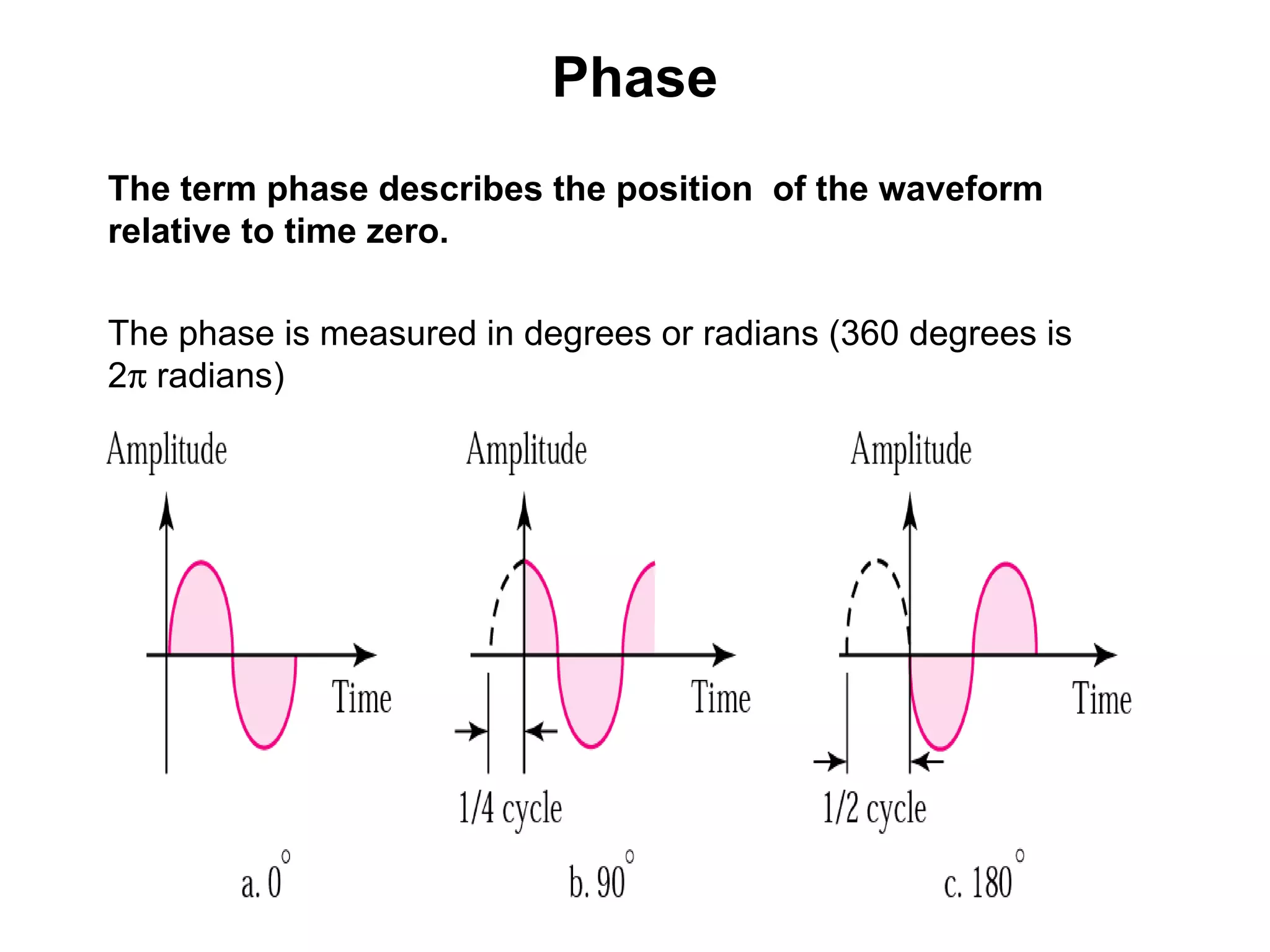
- Phase describes the position of a waveform relative to a reference point in time.
- Total energy and average power of continuous and discrete signals can be calculated through integrals and sums.
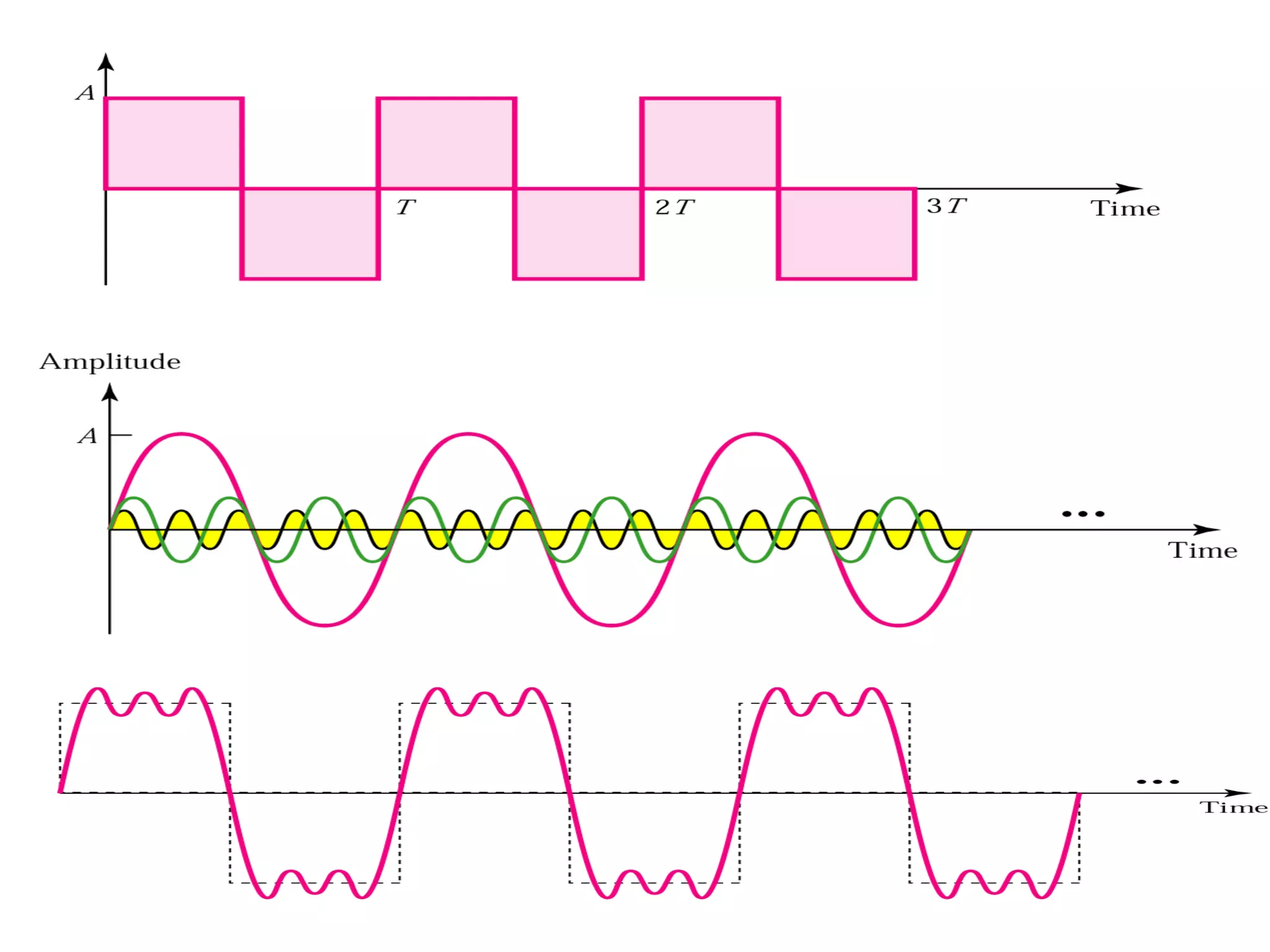
- Periodic, even, odd, exponential, and sinusoidal signals are described.
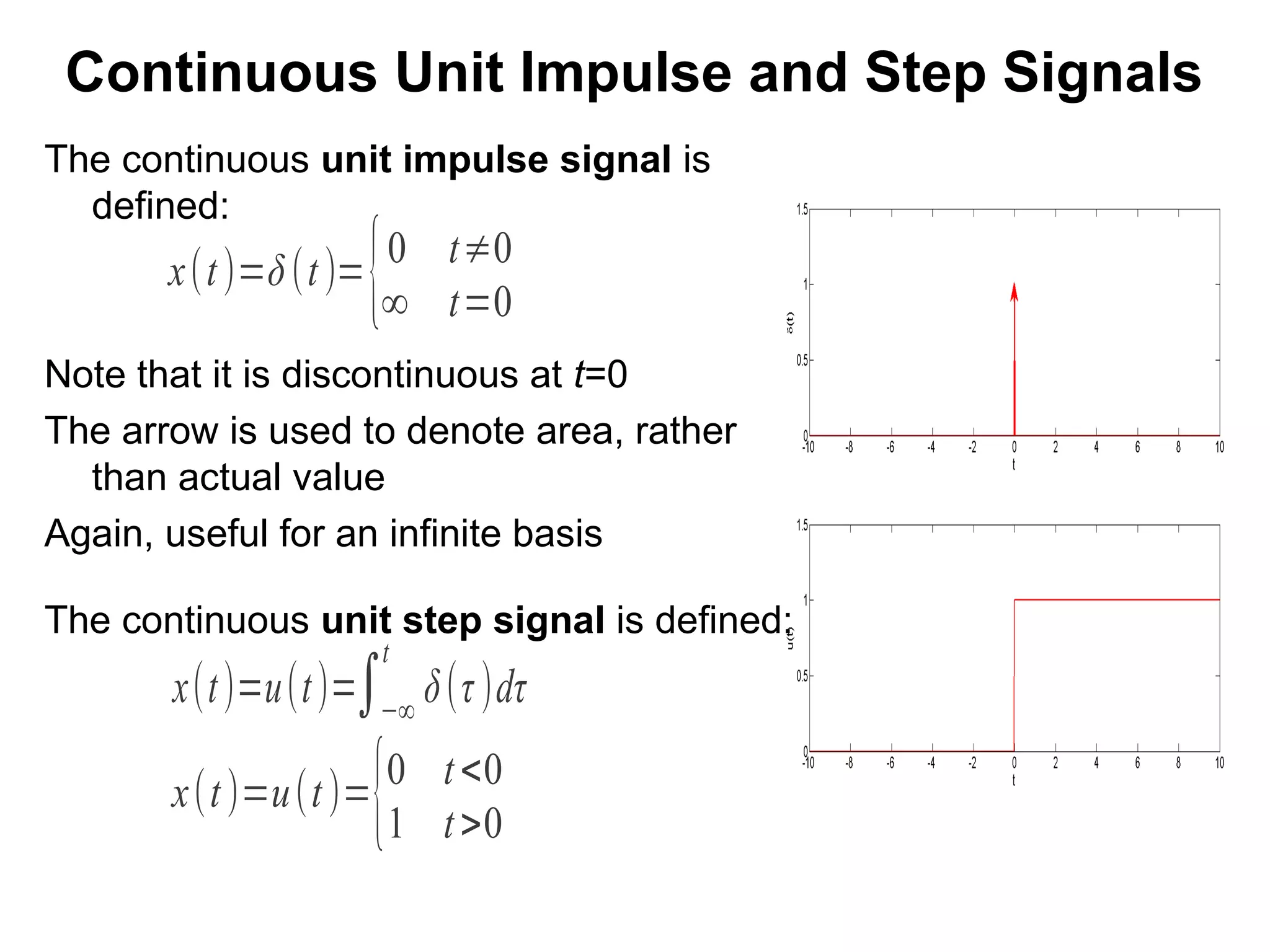
- Unit impulse and step signals are defined for both discrete and continuous time domains.
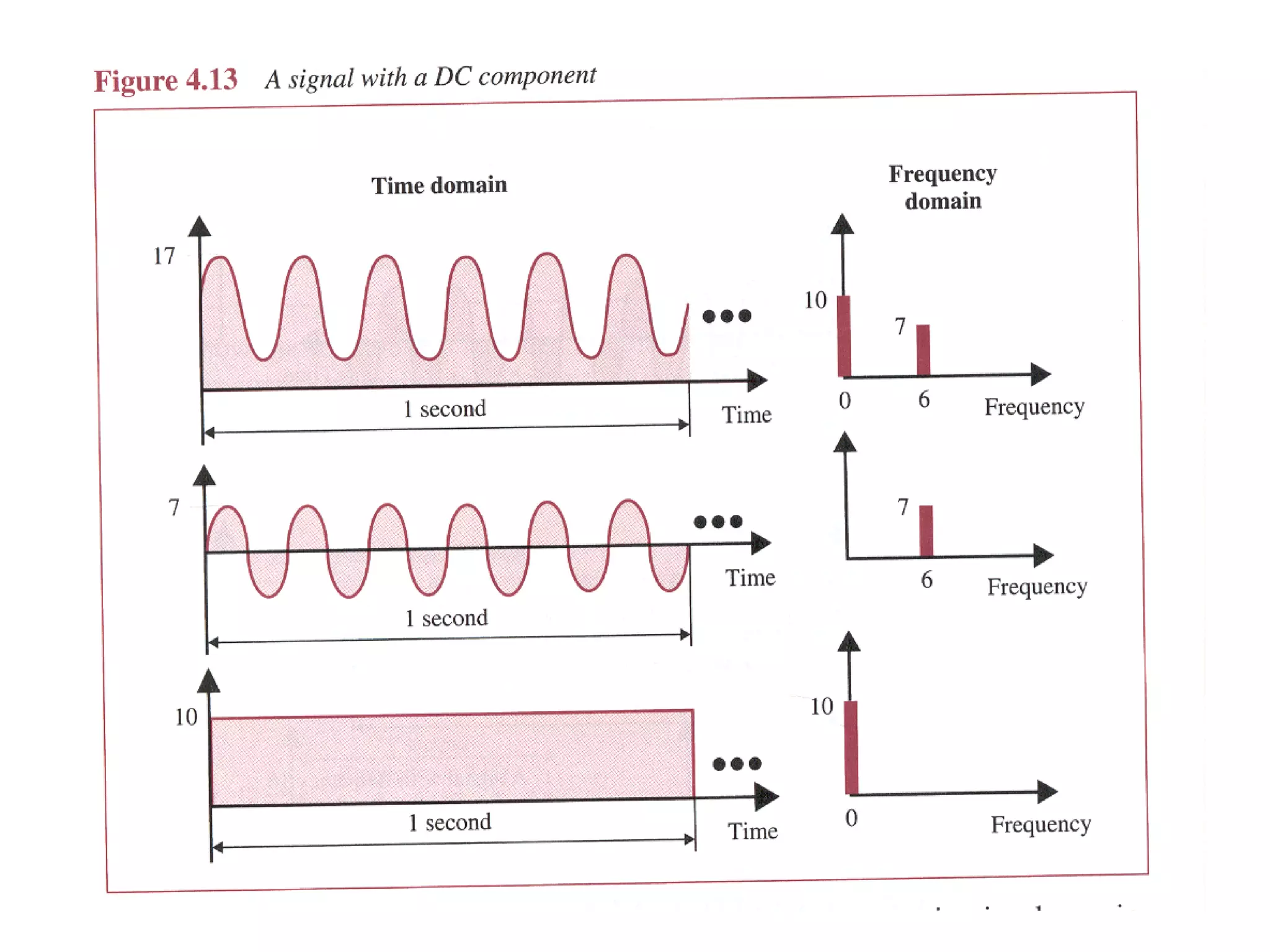
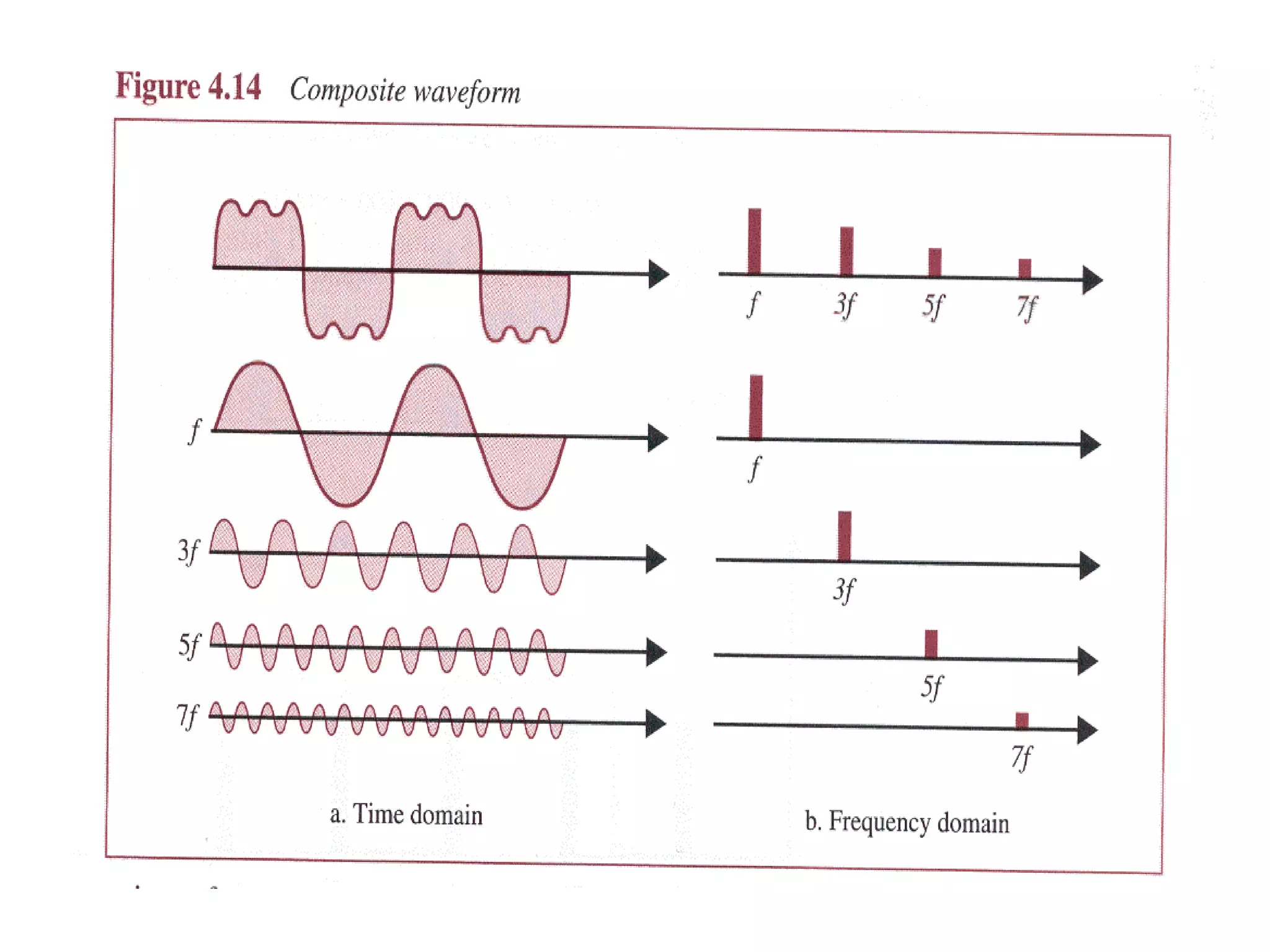
- A signal's frequency spectrum shows the collection of component frequencies and bandwidth is the range of these frequencies.

![Signal Energy and Power
Total energy of a continuous signal x(t) over [t1, t2] is:
where |.| denote the magnitude of the (complex) number.
Similarly for a discrete time signal x[n] over [n1, n2]:
By dividing the quantities by (t2-t1) and (n2-n1+1), respectively,
gives the average power, P
Note that these are similar to the electrical analogies
(voltage), but they are different, both value and dimension.
E=∫t1
t2
∣x(t)∣2
dt
E=∑n=n1
n2
∣x[n]∣2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150721121925-lva1-app6891/75/3-Properties-of-signals-4-2048.jpg)
![Energy and Power over Infinite Time
For many signals, we’re interested in examining the power and energy
over an infinite time interval (-∞, ∞). These quantities are therefore
defined by:
If the sums or integrals do not converge, the energy of such a signal is
infinite.
Two important (sub)classes of signals
1. Finite total energy (and therefore zero average power)
2. Finite average power (and therefore infinite total energy)
E∞=limT→∞∫−T
T
∣x(t)∣
2
dt=∫−∞
∞
∣x(t)∣
2
dt
E∞=limN →∞ ∑n=−N
N
∣x[n ]∣
2
=∑n=−∞
∞
∣x[n]∣
2
P∞=limT →∞
1
2T
∫−T
T
∣x(t)∣
2
dt
P∞=limN →∞
1
2N+1
∑n=−N
N
∣x[n]∣
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150721121925-lva1-app6891/75/3-Properties-of-signals-5-2048.jpg)






![Discrete Unit Impulse and Step Signals
The discrete unit impulse signal is defined:
Useful as a basis for analyzing other signals
The discrete unit step signal is defined:
Note that the unit impulse is the first
difference (derivative) of the step signal
Similarly, the unit step is the running sum
(integral) of the unit impulse.
x[n]=δ[n]={0 n≠0
1 n=0
x[n]=u[ n]={0 n<0
1 n≥0
δ[n]=u[n]−u[n−1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150721121925-lva1-app6891/75/3-Properties-of-signals-12-2048.jpg)