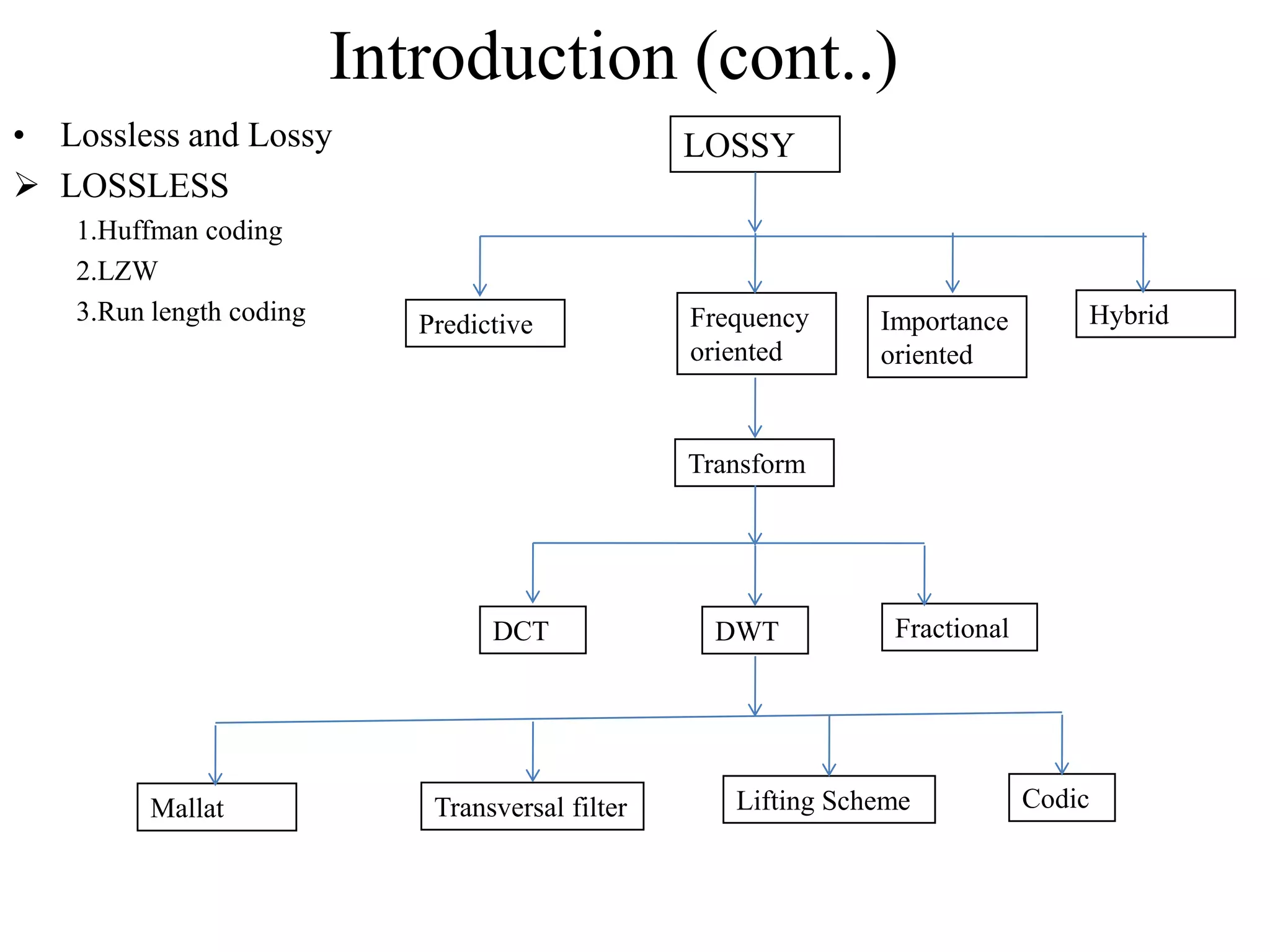
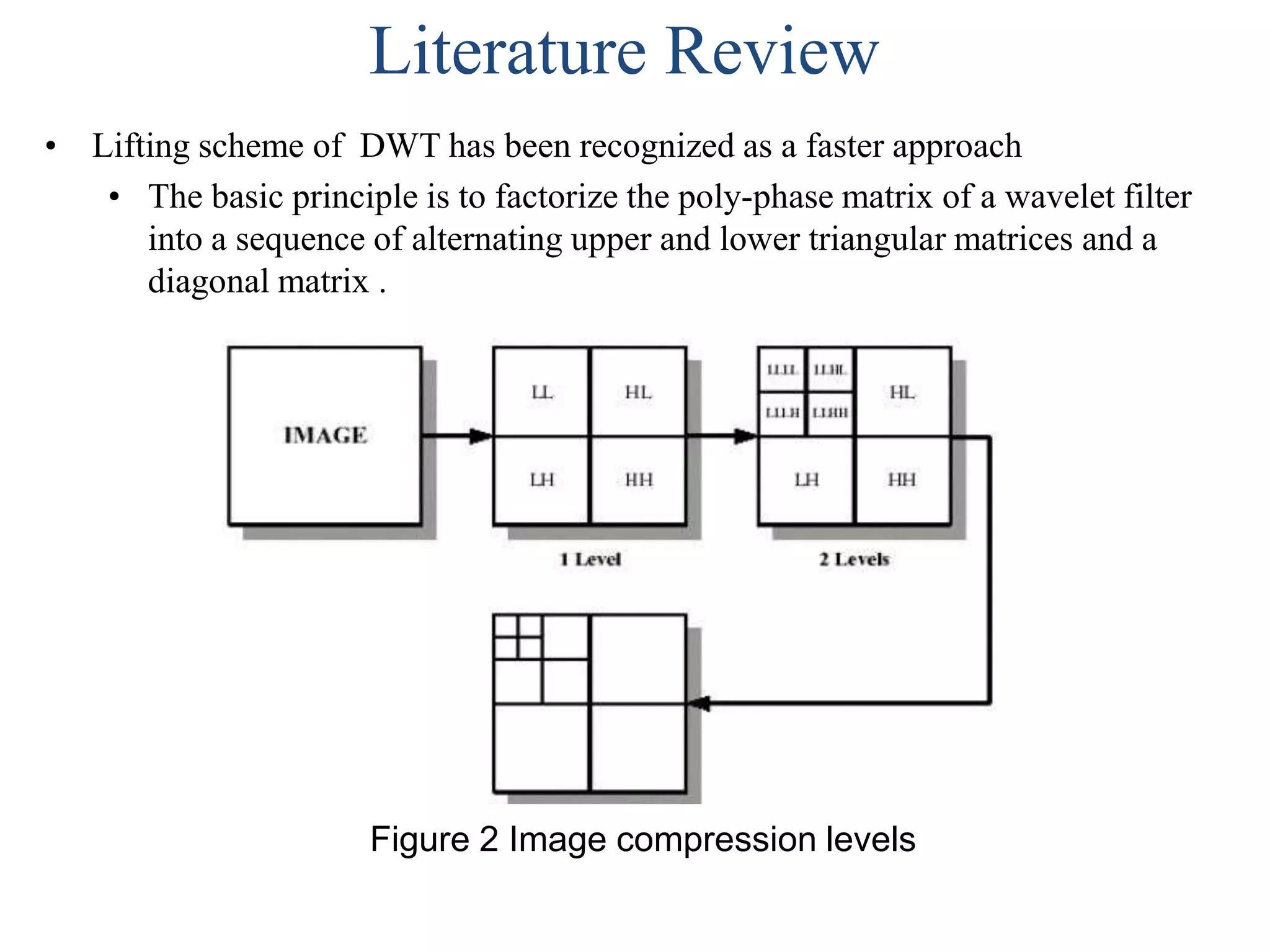
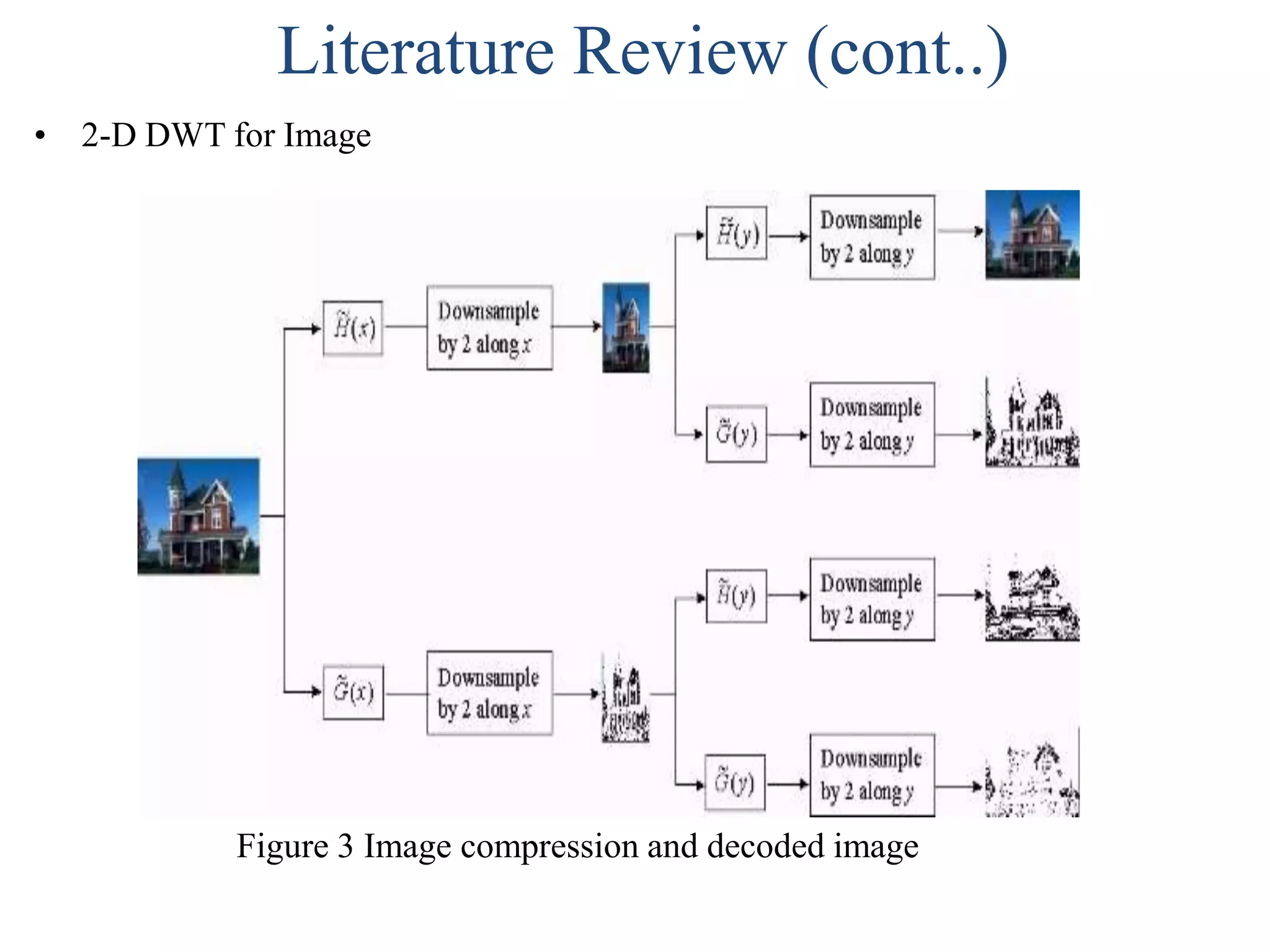
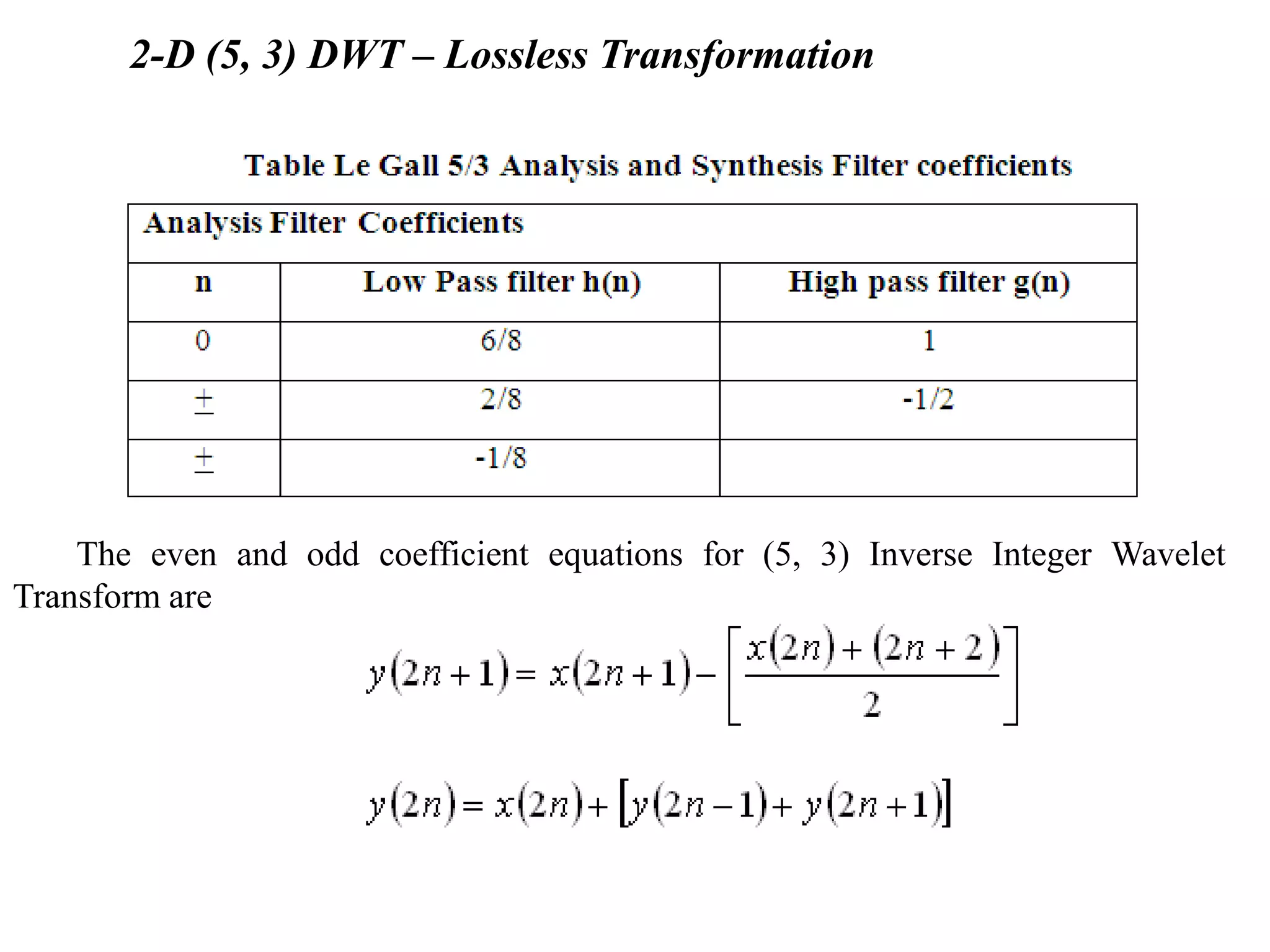
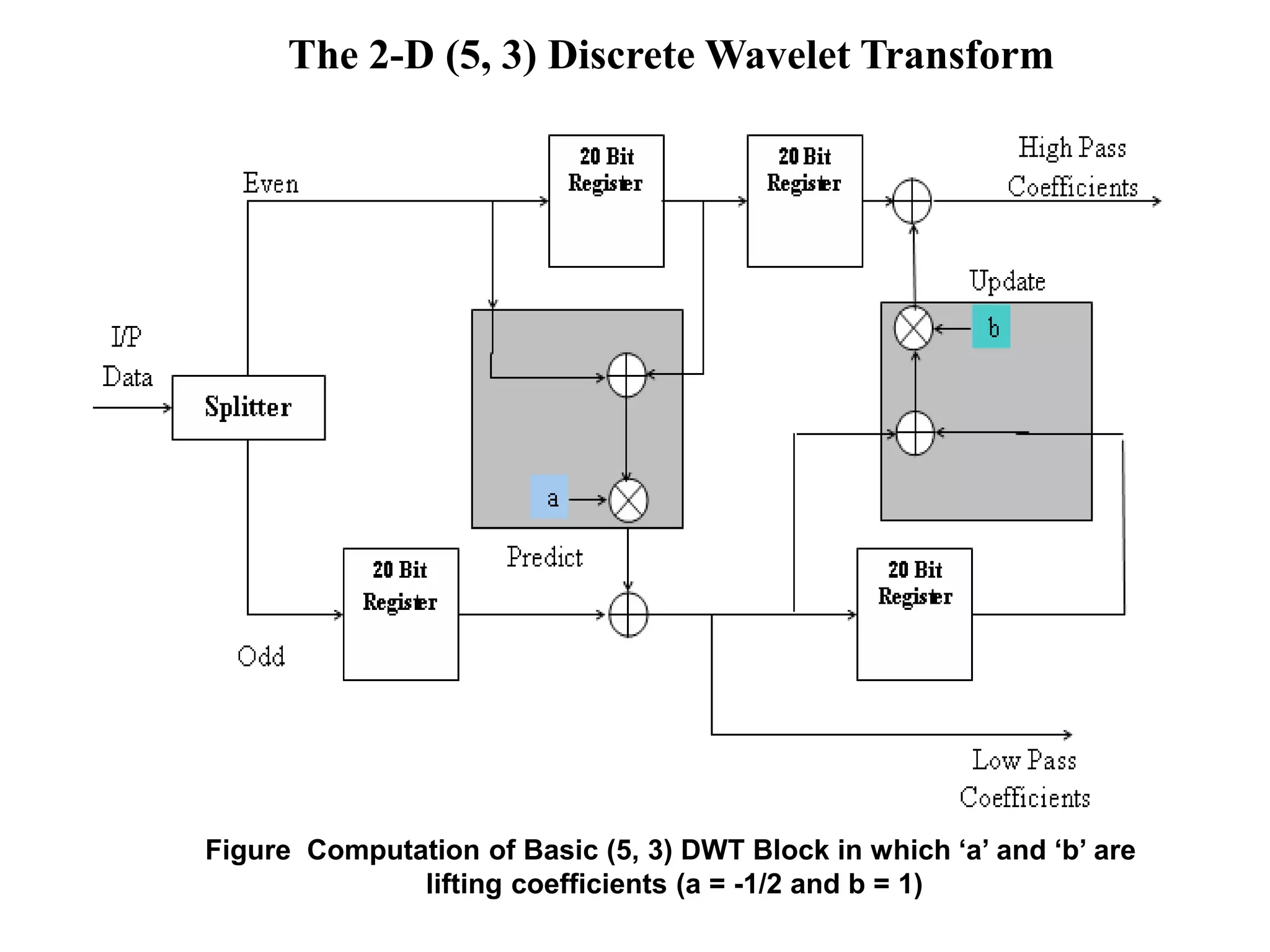
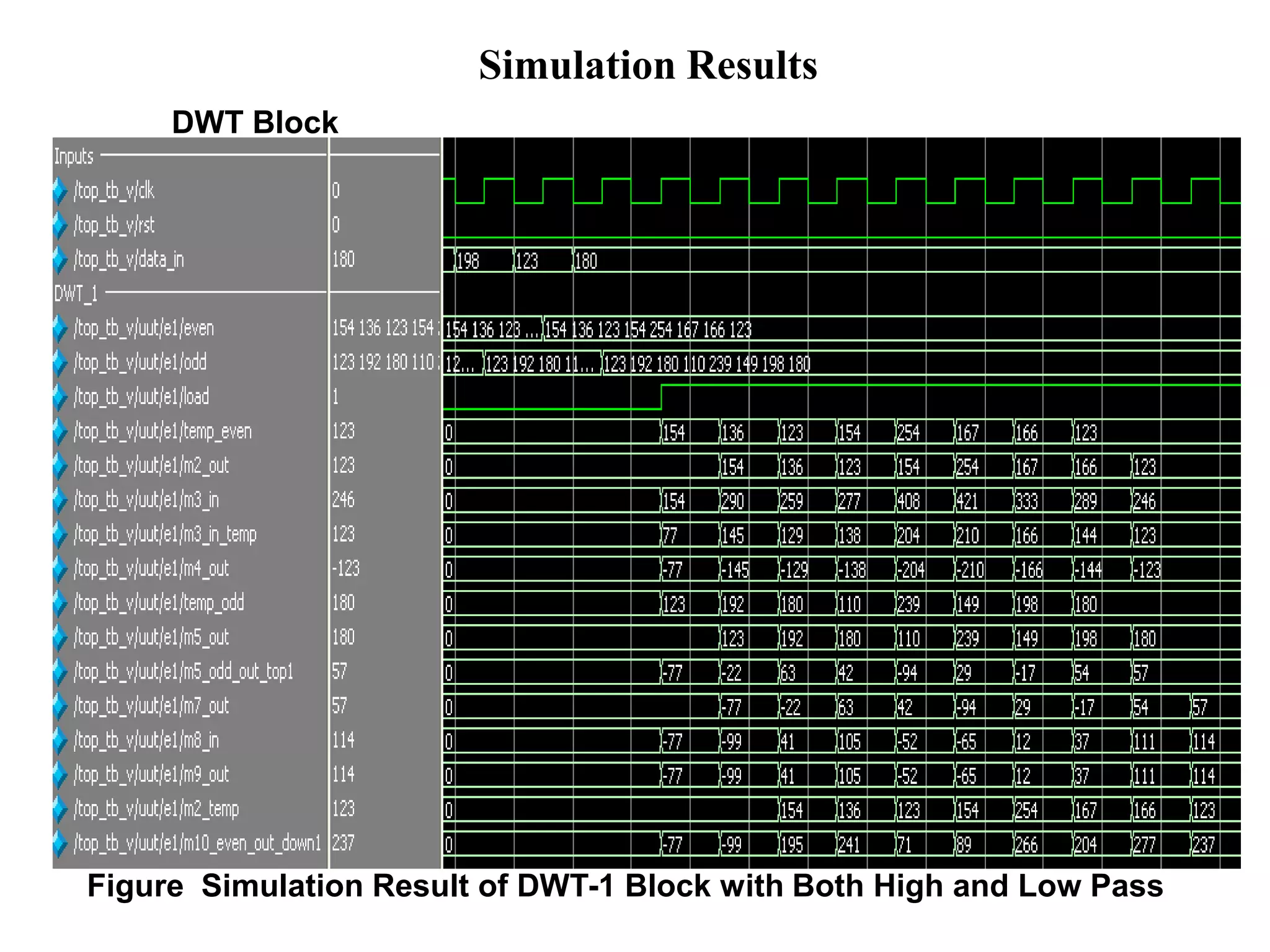
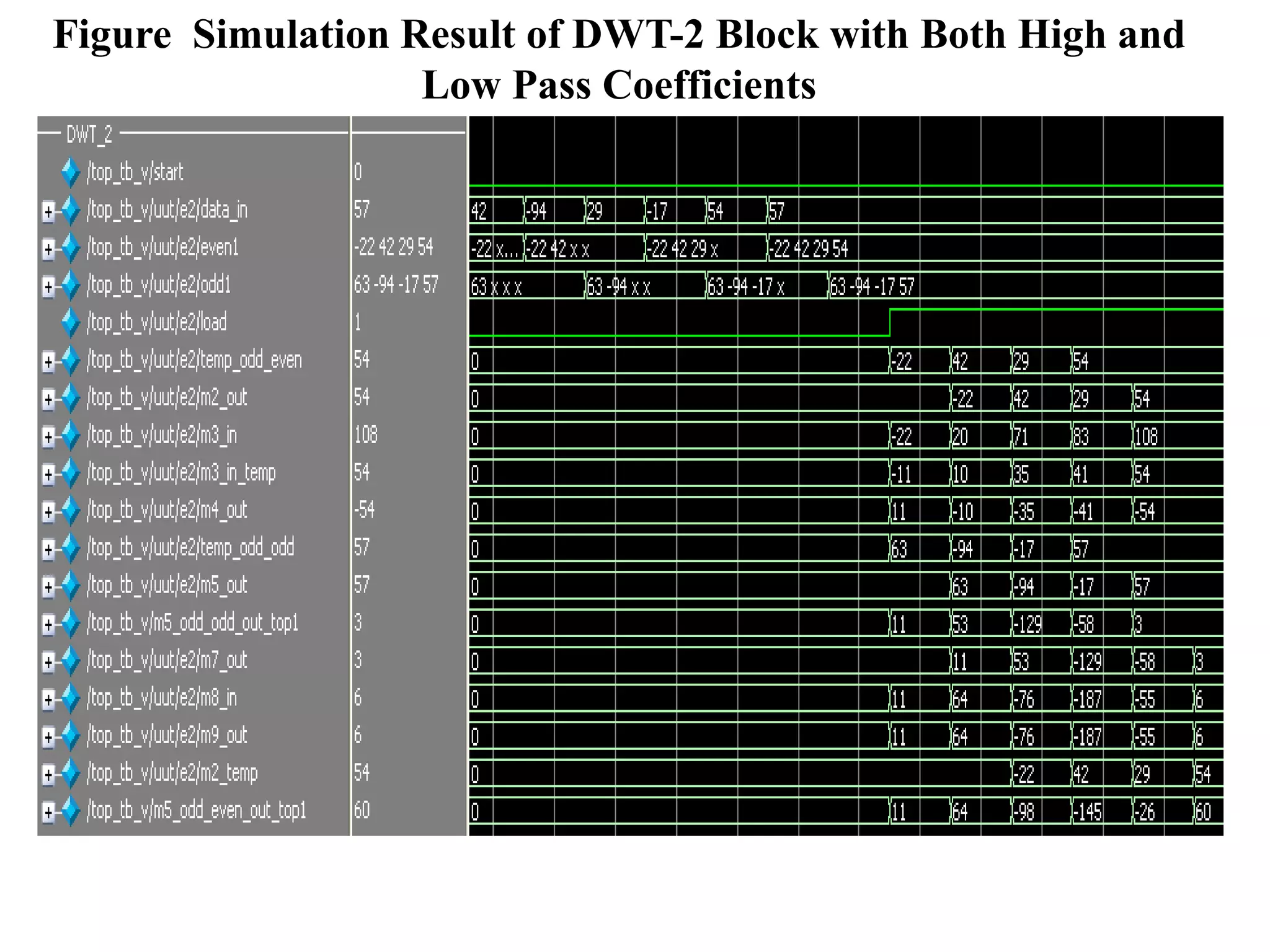
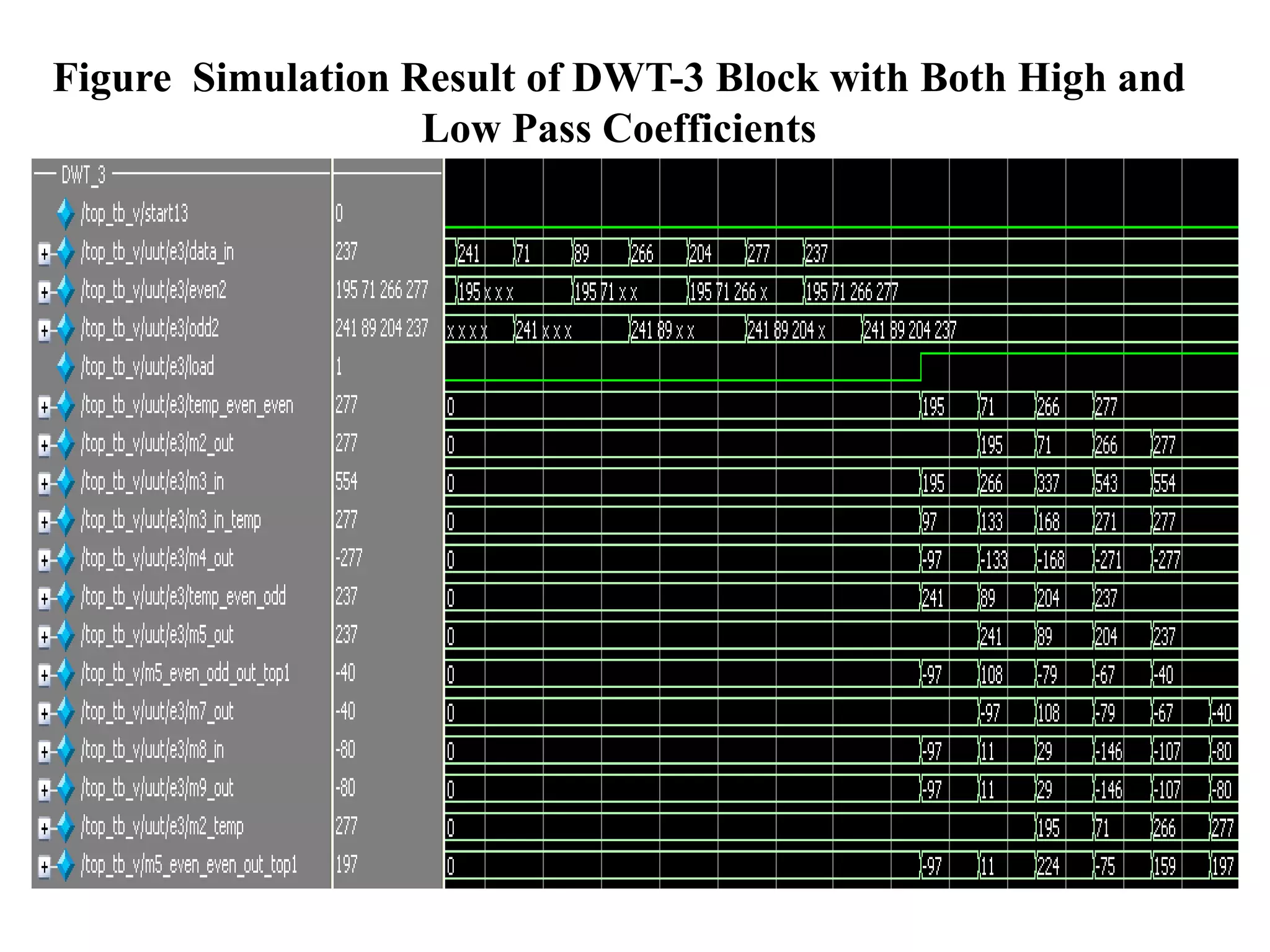
This document summarizes a student project on implementing lossless discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and inverse discrete wavelet transform (IDWT). It provides an overview of the project, which includes introducing DWT, reviewing literature on lifting schemes for faster DWT computation, and simulating a 2D (5,3) DWT. The results show DWT blocks decomposing signals into high and low pass coefficients. Applications mentioned are in medical imaging, signal denoising, data compression and image processing. The conclusion discusses the need for lossless transforms in medical imaging. Future work could extend this to higher level transforms and applications like compression and watermarking.