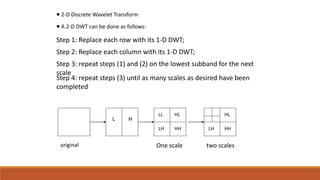
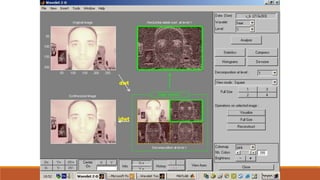
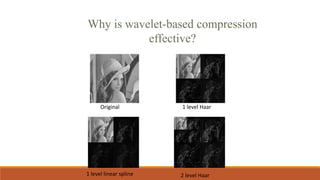
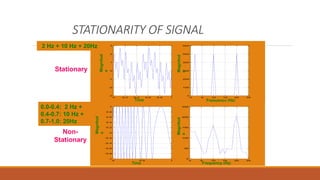
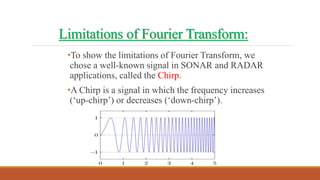
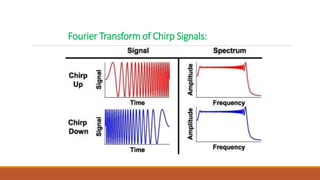
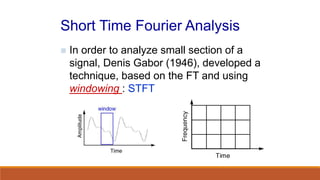
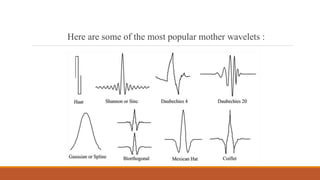
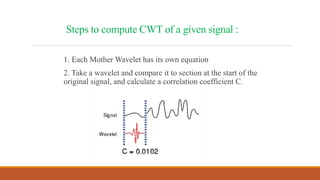
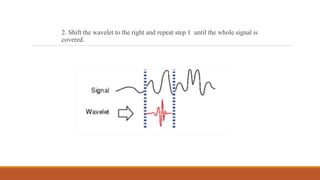
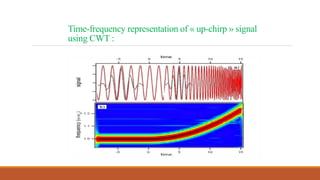
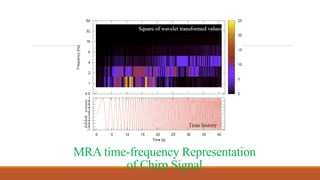
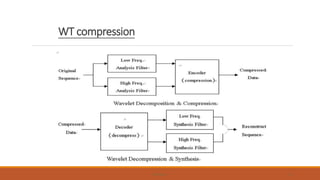
This document provides an introduction to wavelet transforms. It begins with an outline of topics to be covered, including an overview of wavelet transforms, the limitations of Fourier transforms, the historical development of wavelets, the principle of wavelet transforms, examples of applications, and references. It then discusses the stationarity of signals and how Fourier transforms cannot show when frequency components occur over time. Short-time Fourier analysis is introduced as a solution, but it is noted that wavelet transforms provide a more flexible approach by allowing the window size to vary. The document proceeds to define what a wavelet is, discuss the historical development of wavelet theory, provide examples of popular mother wavelets, and explain the steps to compute a continuous wave



















![SUBBABD CODING ALGORITHM
0-1000 Hz
D2: 250-500 Hz
D3: 125-250 Hz
Filter 1
Filter 2
Filter 3
D1: 500-1000 Hz
A3: 0-125 Hz
A1
A2
X[n]
512
256
128
64
64
128
256
SS
A1
A2 D2
A3 D3
D1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt-150811145611-lva1-app6892/85/Introduction-to-wavelet-transform-32-320.jpg)