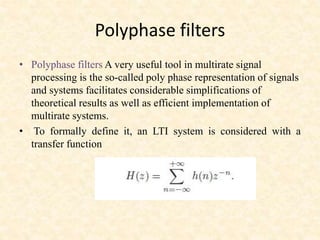
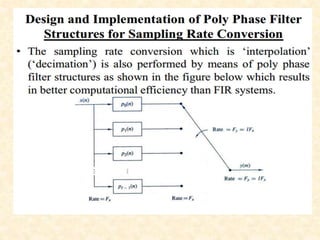
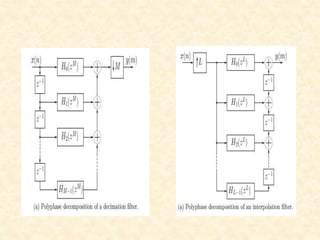
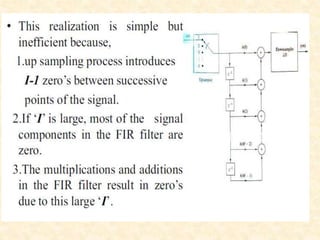
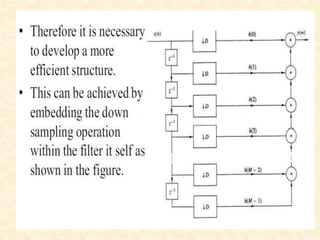
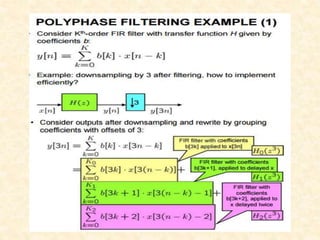
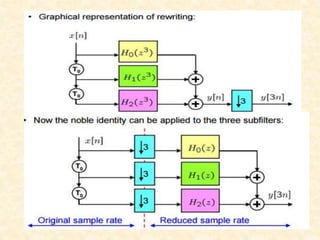
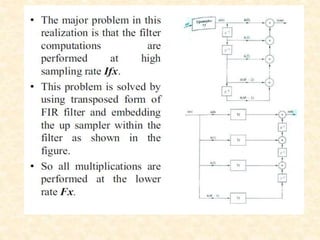
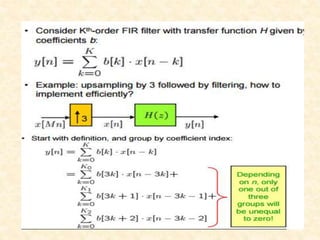
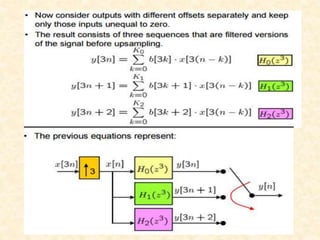
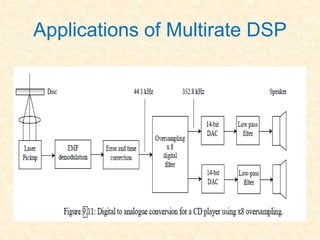
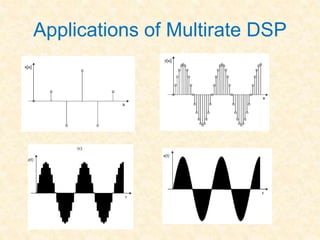
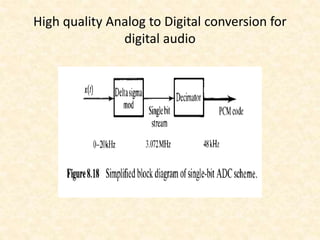
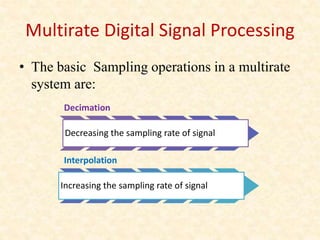
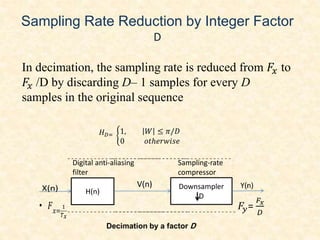
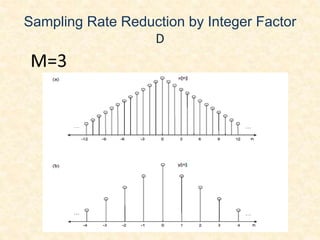
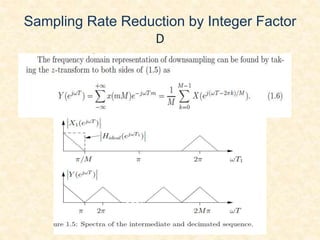
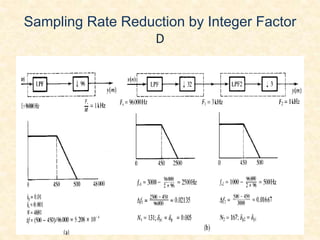
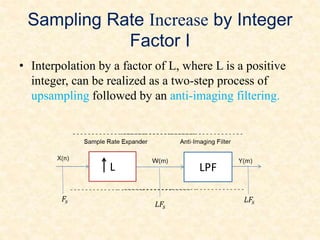
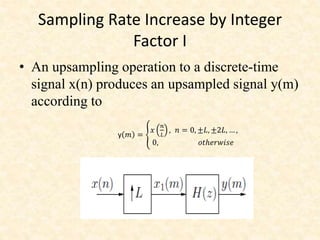
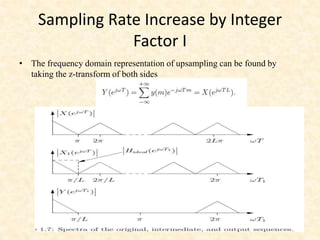
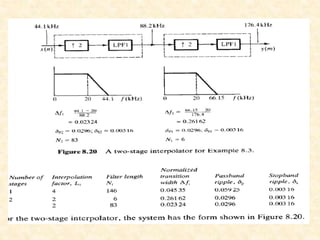
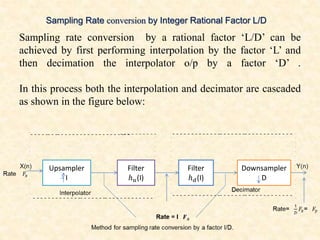
This document discusses multirate digital signal processing. It explains that multirate systems use multiple sampling rates to process digital signals. Common operations in multirate systems are decimation, which decreases the sampling rate, and interpolation, which increases it. Decimation and interpolation can be realized through filtering and downsampling/upsampling. The document also provides examples of multirate applications like digital audio conversion and discusses tools like polyphase filters used in multirate signal processing.






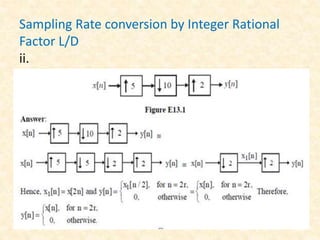
![• Example:
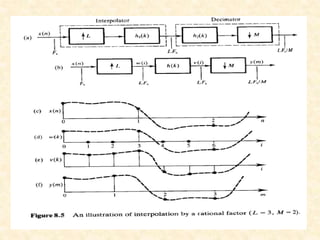
Consider a multirate signal processing problem:
i. State with the aid of block diagrams the process
of changing sampling rate by a non-integer
factor.
ii. Develop an expression for the output y[n] and
g[n] as a function of input x[n] for the multirate
structure of fig .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assignment-151118155857-lva1-app6891/85/Multirate-DSP-18-320.jpg)