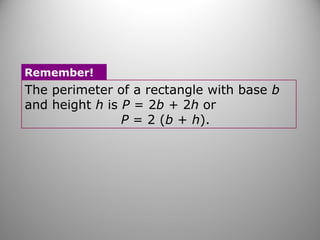
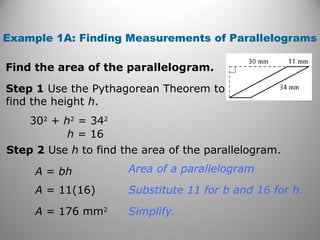
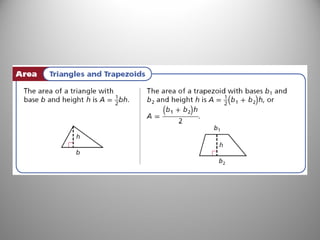
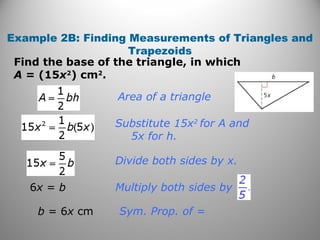
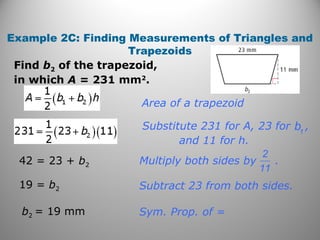
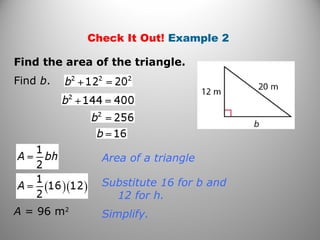
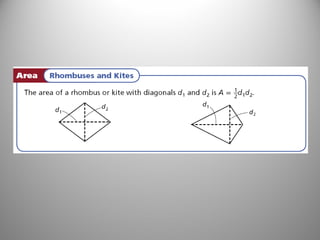
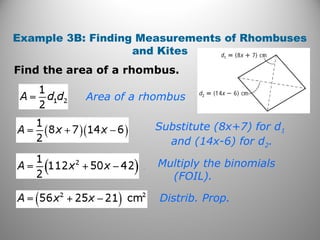
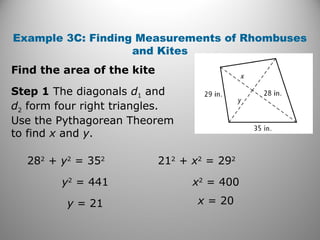
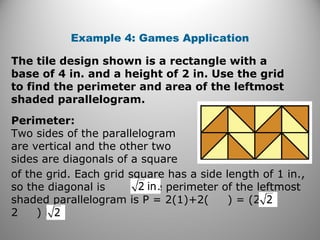
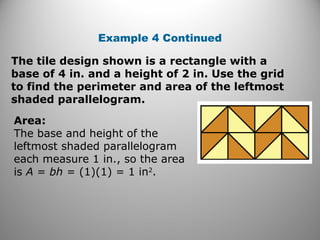
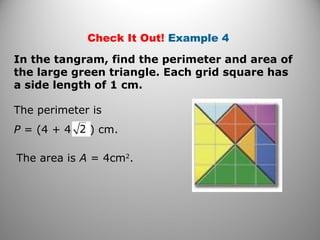
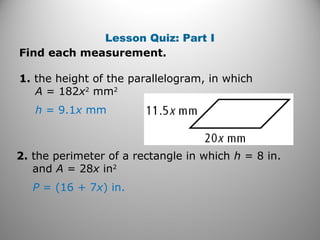
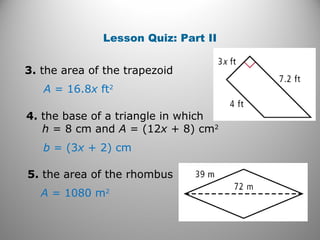
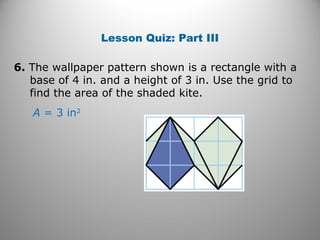
This document discusses formulas and methods for finding the areas and perimeters of parallelograms, triangles, trapezoids, rhombuses, and kites. It provides examples of using these formulas to calculate side lengths, heights, areas, and perimeters when given certain measurements of the shapes. It also includes practice problems for students to solve.