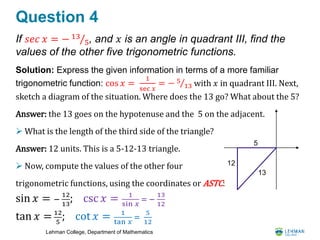
This document contains a 10 question review for a trigonometry midterm examination. It reviews concepts like using trigonometric functions to solve for unknown sides and angles of right triangles, evaluating trig functions for special angles, finding arc lengths and sector areas of circles, graphing trig functions involving amplitude, period and phase shift, and using trigonometric identities. The problems are worked out step-by-step showing the reasoning and math steps to arrive at the solutions, often leaving final answers in radical or pi form.

![Lehman College, Department of Mathematics
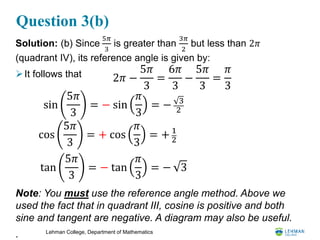
Question 3(a)
Evaluate, without using a calculator, the sine, cosine
and tangent of: (a) 135°[5 points], and (b)
5𝜋
3
[5 points],
Solution: (a) Since 135° is greater than 90° but less
than 180° (quadrant II), its reference angle is given by:
It follows that
Note: You must use the reference angle method.
Above we used the fact that in quadrant II, sine is
positive and both cosine and tangent are negative. A
diagram may also be useful.
sin 135° = + sin 45° = 2
2
180° − 135° = 45°
cos 135° = − cos 45° = − 2
2
tan 135° = − tan 45° = −1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20200317midtermreview-200327155728/85/MAT-108-Trigonometry-Midterm-Review-5-320.jpg)
![Lehman College, Department of Mathematics
Question 5
(a) Find the length of the arc of a circle of radius 3 cm that
subtends a central angle of 150°[5 points]. (b) Determine the
area of the corresponding sector [5 points] (leave all
answers in terms of 𝜋).
Solution: (a) If 𝜃 is given in degrees, then the arc length 𝑙 is
given by the formula:
So,
(a) Area of sector 𝑆 is given by the formula:
It follows that
𝑙 =
𝜃
360°
⋅ 2𝜋𝑟
𝑙 =
150°
360°
⋅ 2𝜋 3 =
5
12
⋅ 6𝜋 =
5𝜋
2
cm
𝑆 =
𝜃
360°
⋅ 𝜋𝑟2
𝑆 =
150°
360°
⋅ 𝜋 3 2
=
5
12
⋅ 9𝜋 =
15𝜋
4
cm2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20200317midtermreview-200327155728/85/MAT-108-Trigonometry-Midterm-Review-8-320.jpg)
![Lehman College, Department of Mathematics
Question 6
(a) Find the length of the arc of a circle of radius 3 cm
that subtends a central angle of
2𝜋
5
[5 points].
(b) Determine the area of the corresponding sector
[5 points] (leave all answers in terms of 𝜋).
Solution: (a) If 𝜃 is given in radians, then the arc length
𝑙 is given by the formula:
So
(a) Area of sector 𝑆 is given by the formula:
It follows that
𝑙 = 3
2𝜋
5
=
6𝜋
5
cm
𝑙 = 𝑟𝜃
𝑆 =
1
2
⋅
2𝜋
5
3 2
=
𝜋
5
9 =
9𝜋
5
cm2
𝑆 =
1
2
𝜃𝑟2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20200317midtermreview-200327155728/85/MAT-108-Trigonometry-Midterm-Review-9-320.jpg)


![Lehman College, Department of Mathematics
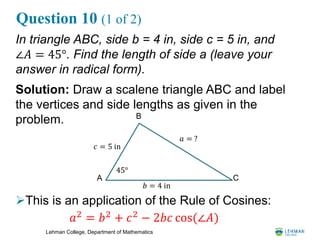
Question 8
In triangle ABC, side a = 7 in, side b = 4 in, and ∠C =
60°. Find the area of the triangle (leave your answer in
radical form) [10 points].
Solution: Draw a scalene triangle ABC and label the
vertices and side lengths as given in the problem.
The formula for the area of an SAS
triangle is
For the given problem: A
B
C
𝑎 = 7 in
𝑏 = 4 in
60°
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 =
1
2
(7)(4) sin 60° = 14 3
2
= 7 3 in2
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 =
1
2
𝑎𝑏 sin(∠C)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20200317midtermreview-200327155728/85/MAT-108-Trigonometry-Midterm-Review-12-320.jpg)
![Lehman College, Department of Mathematics
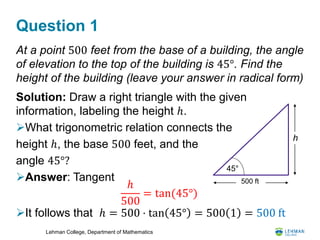
Question 9 (1 of 2)
In triangle ABC, side a = 2 in, ∠𝐴 = 60°, and
∠𝐵 = 45°. Find the length of side b (leave your
answer in radical form) [10 points].
Solution: Draw a scalene triangle ABC and label
the vertices and side lengths as given in the
problem.
This is an application of the Rule of Sines:
A
B
C
𝑎 = 2 in
𝑏 = ?
60°
45°
𝑏
sin(∠𝐵)
=
𝑎
sin(∠𝐴)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20200317midtermreview-200327155728/85/MAT-108-Trigonometry-Midterm-Review-13-320.jpg)