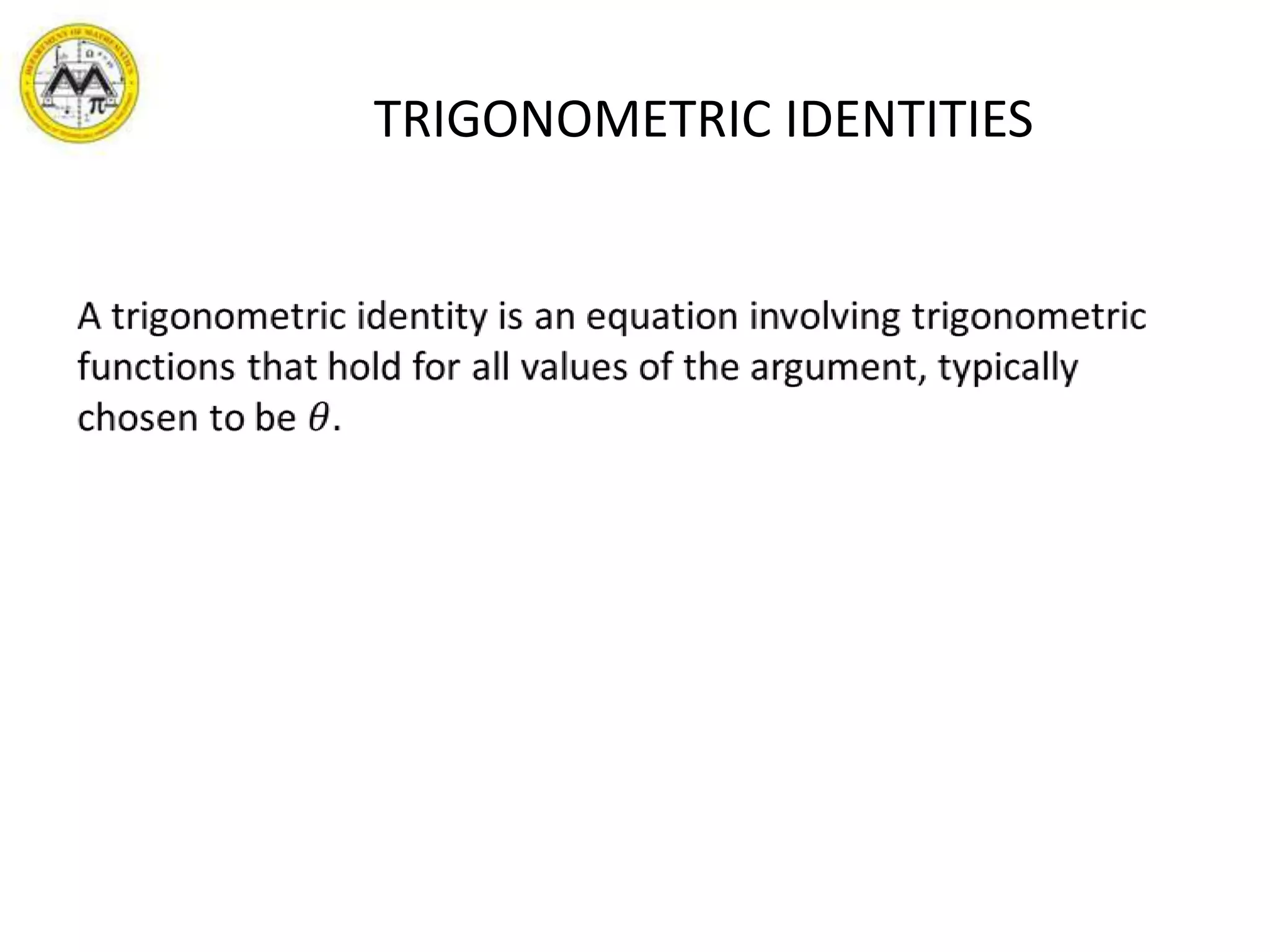
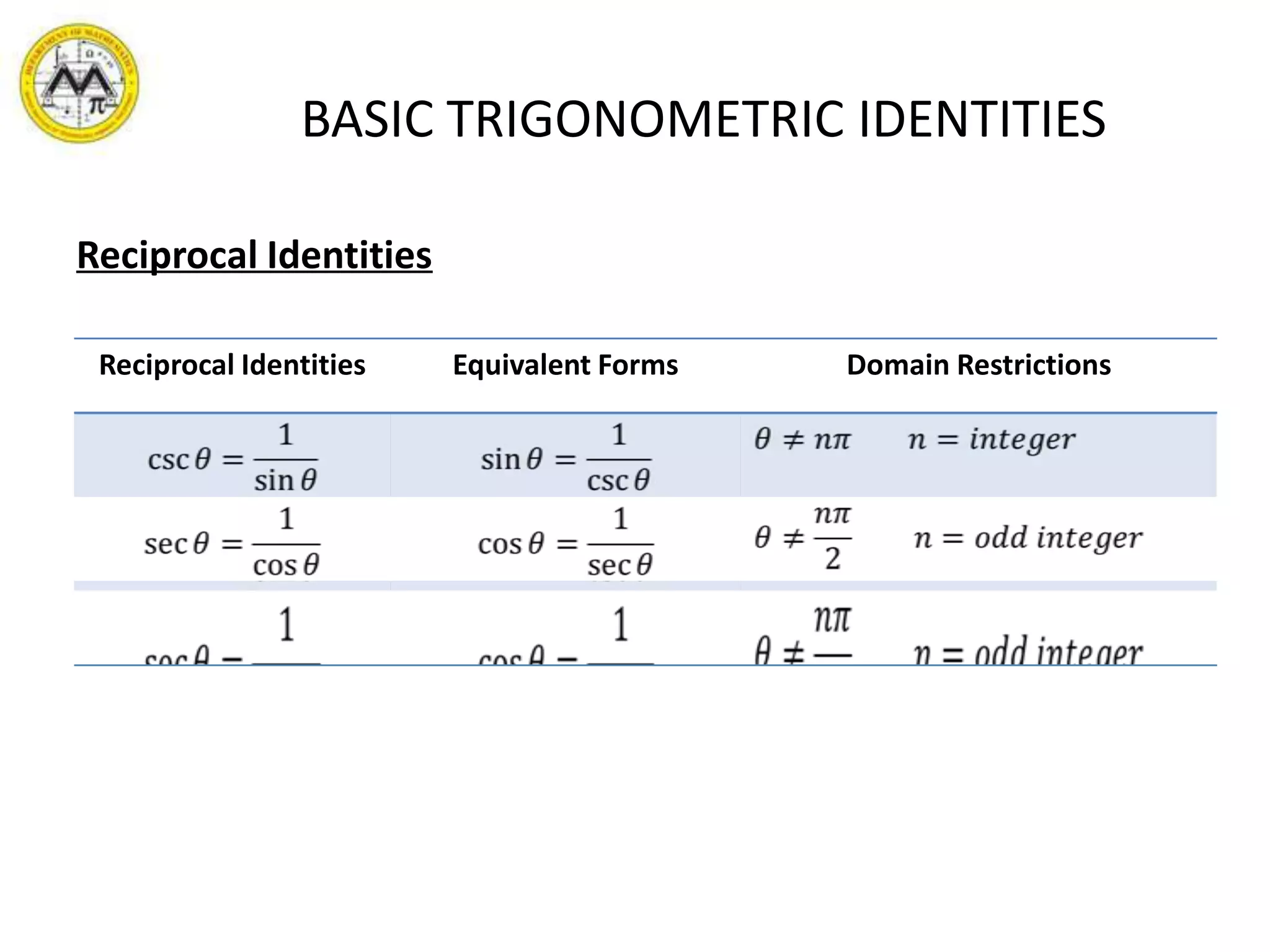
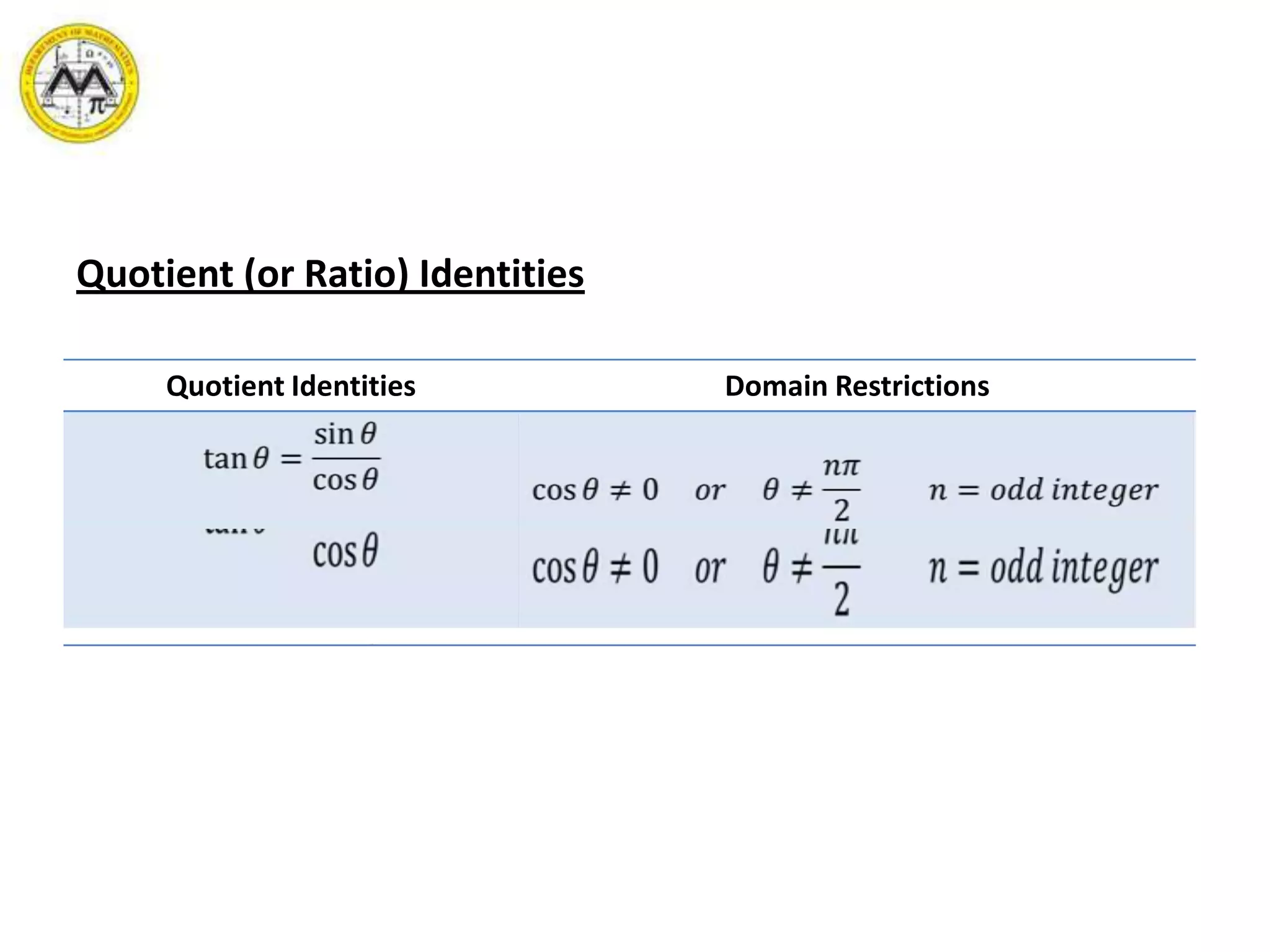
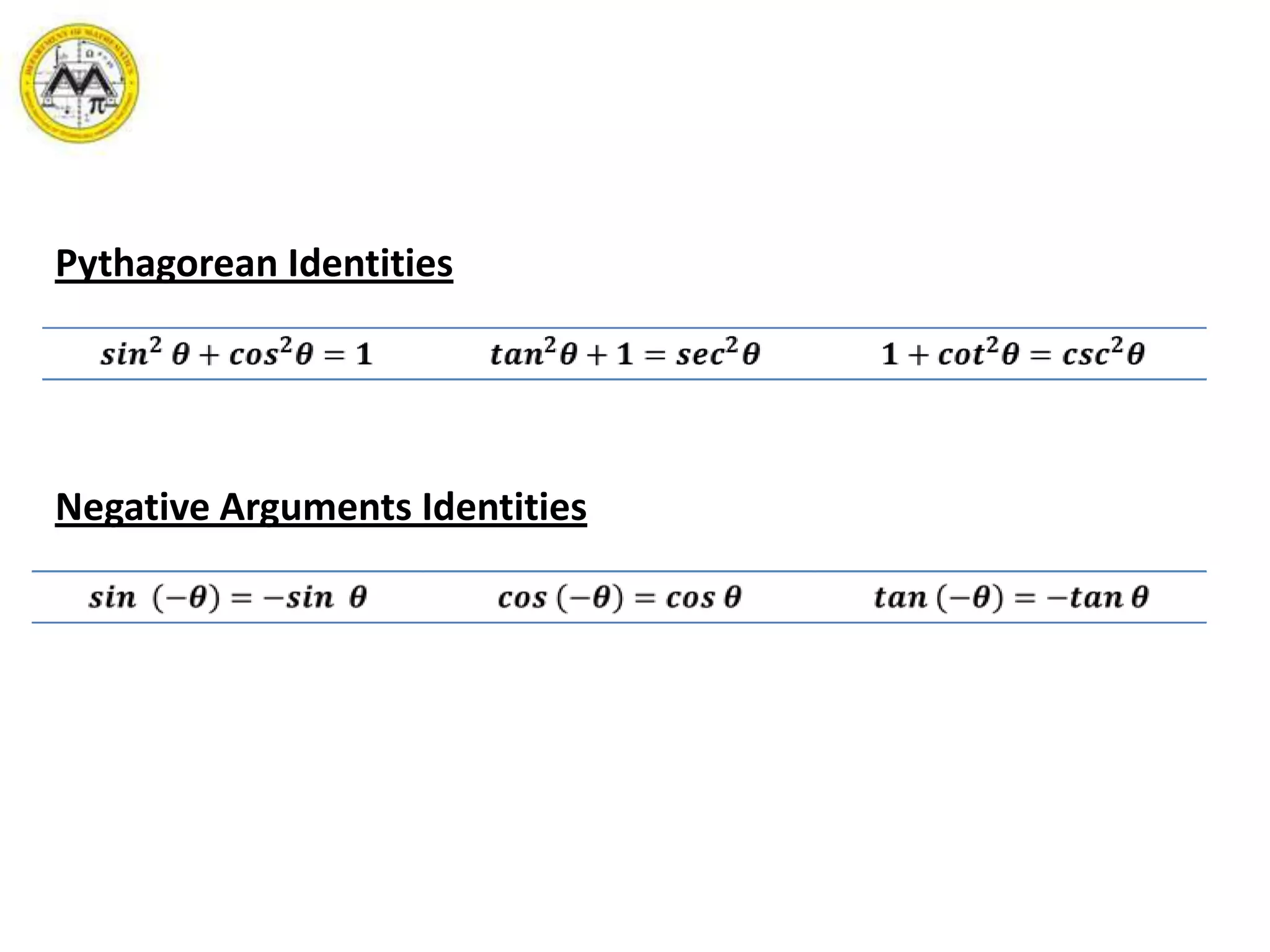
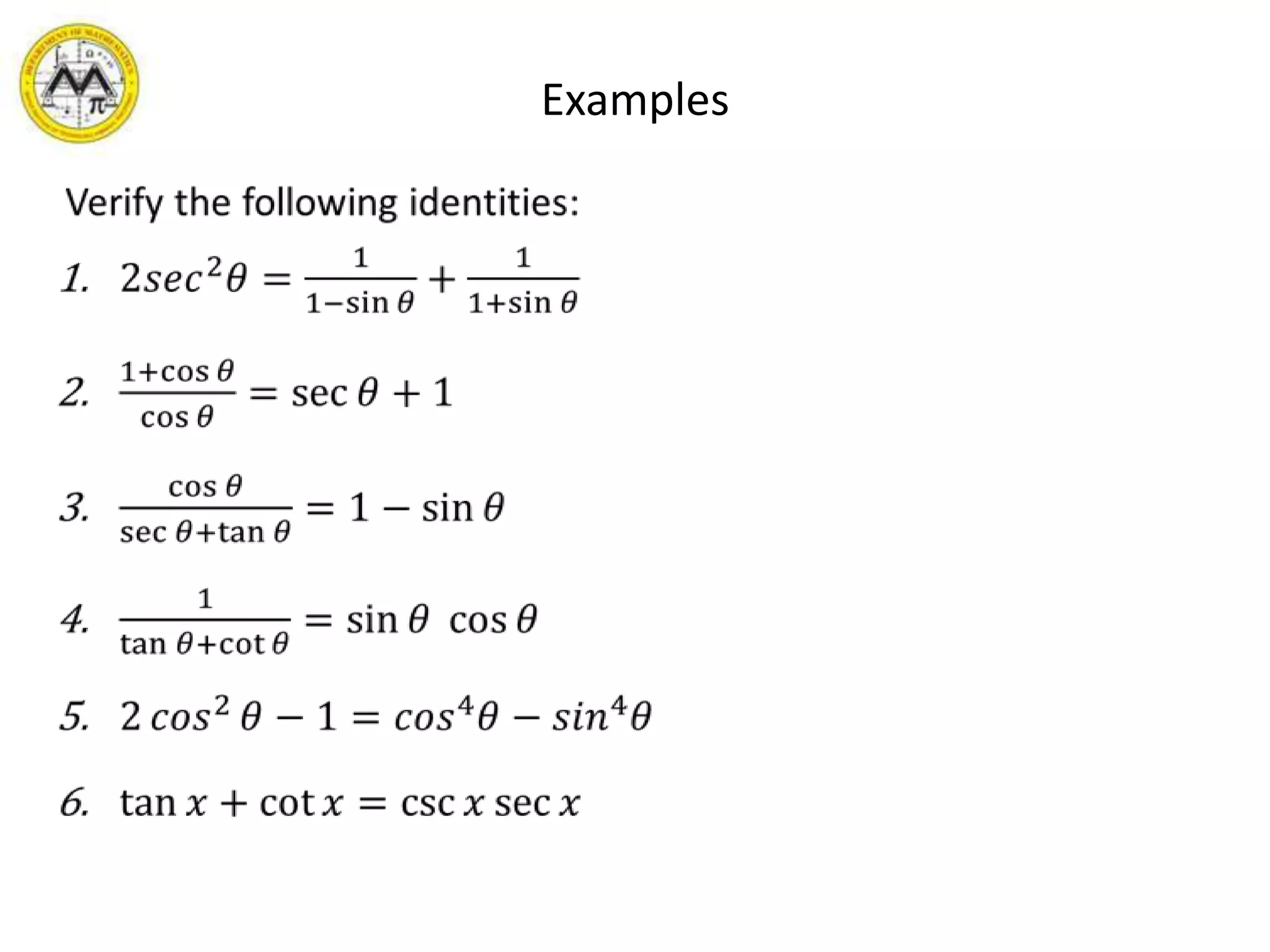
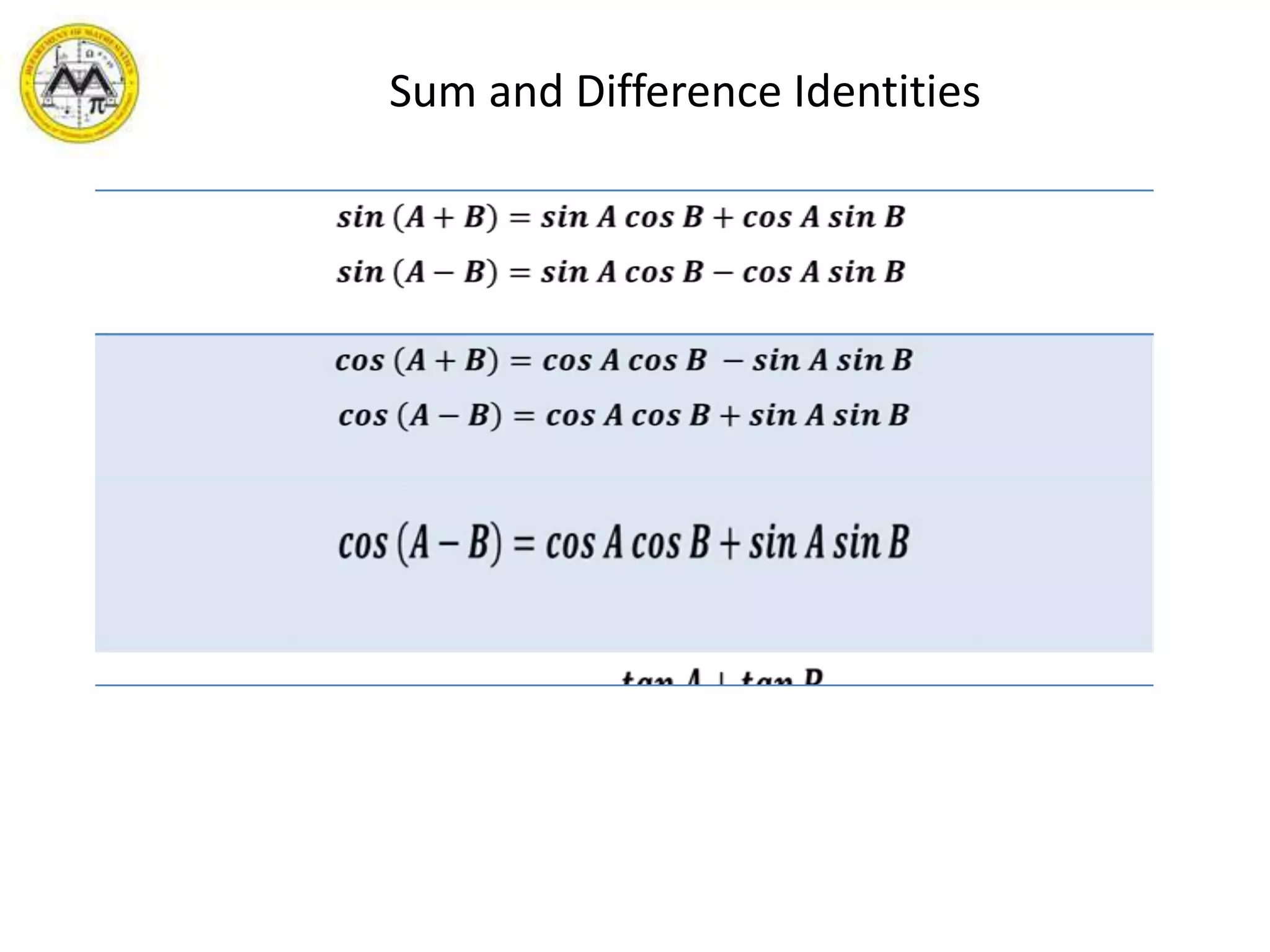
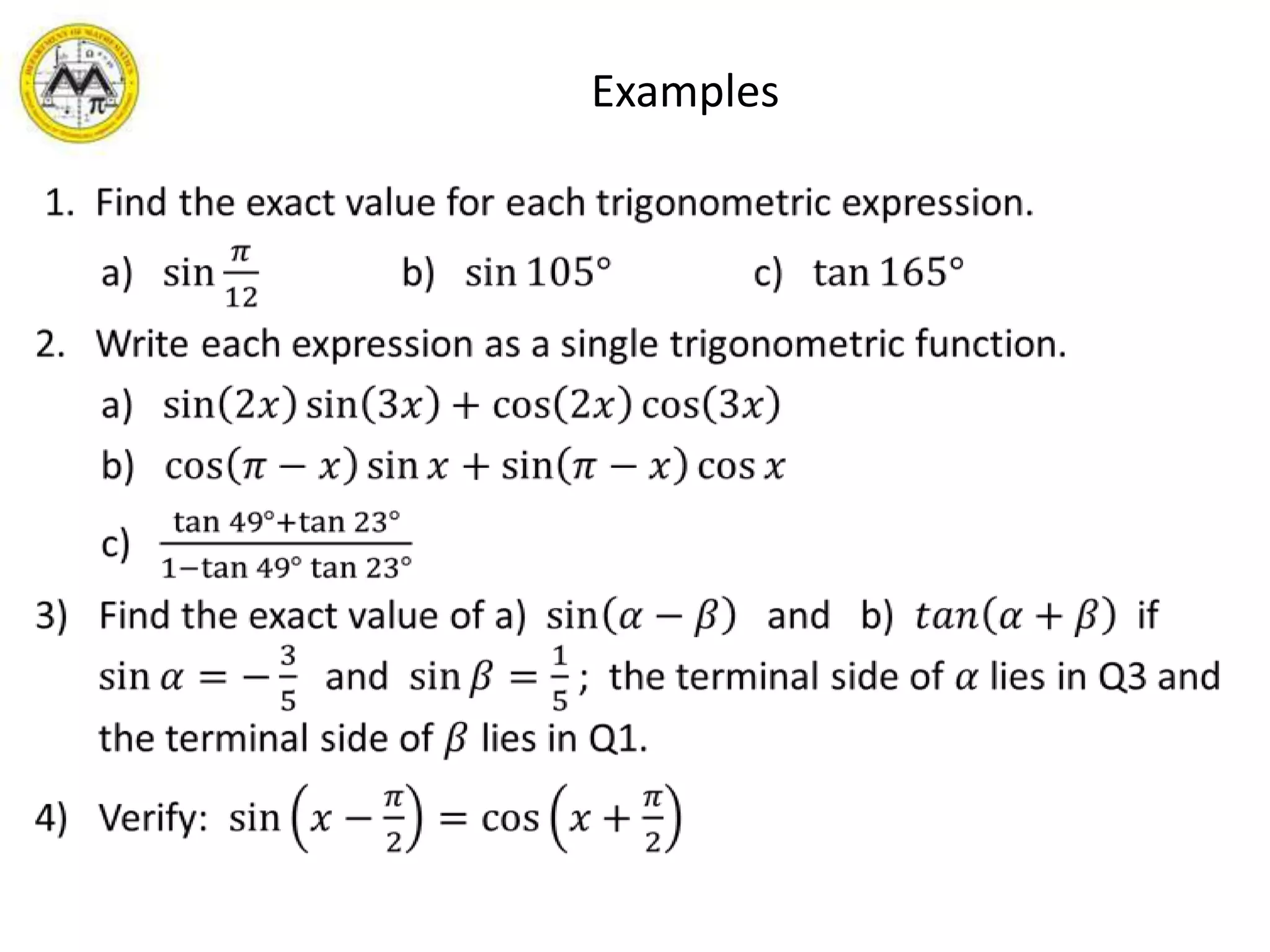
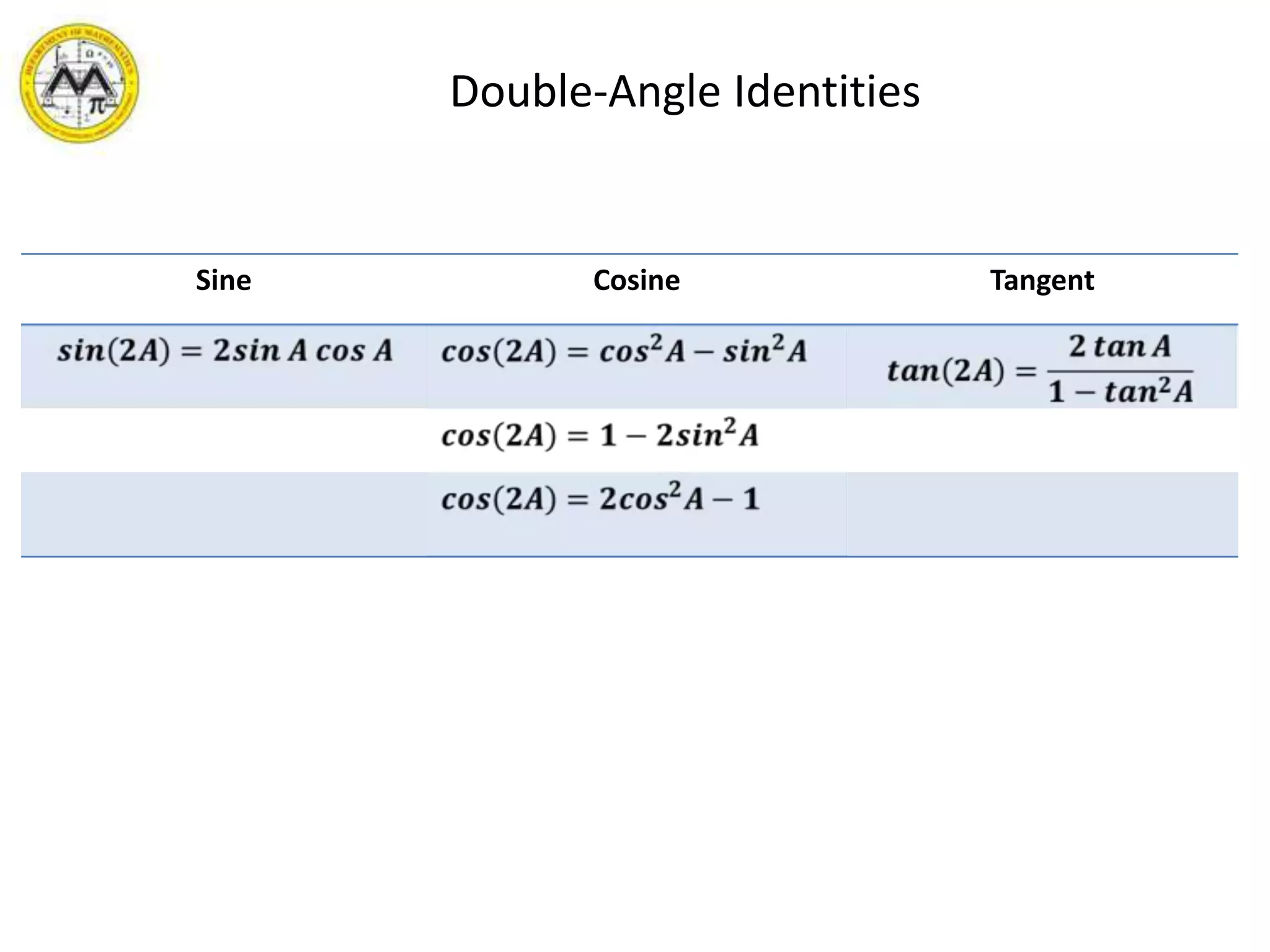
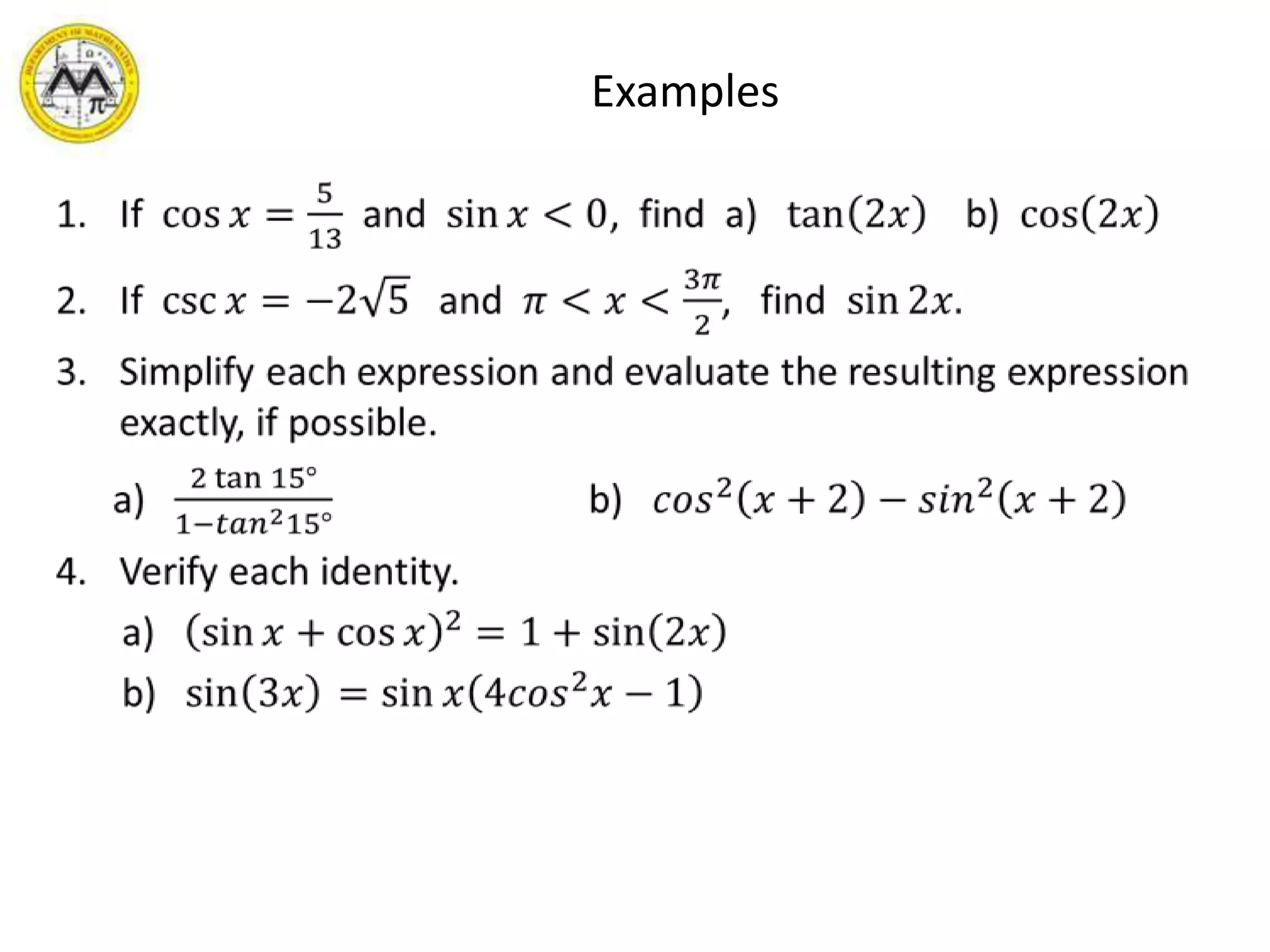
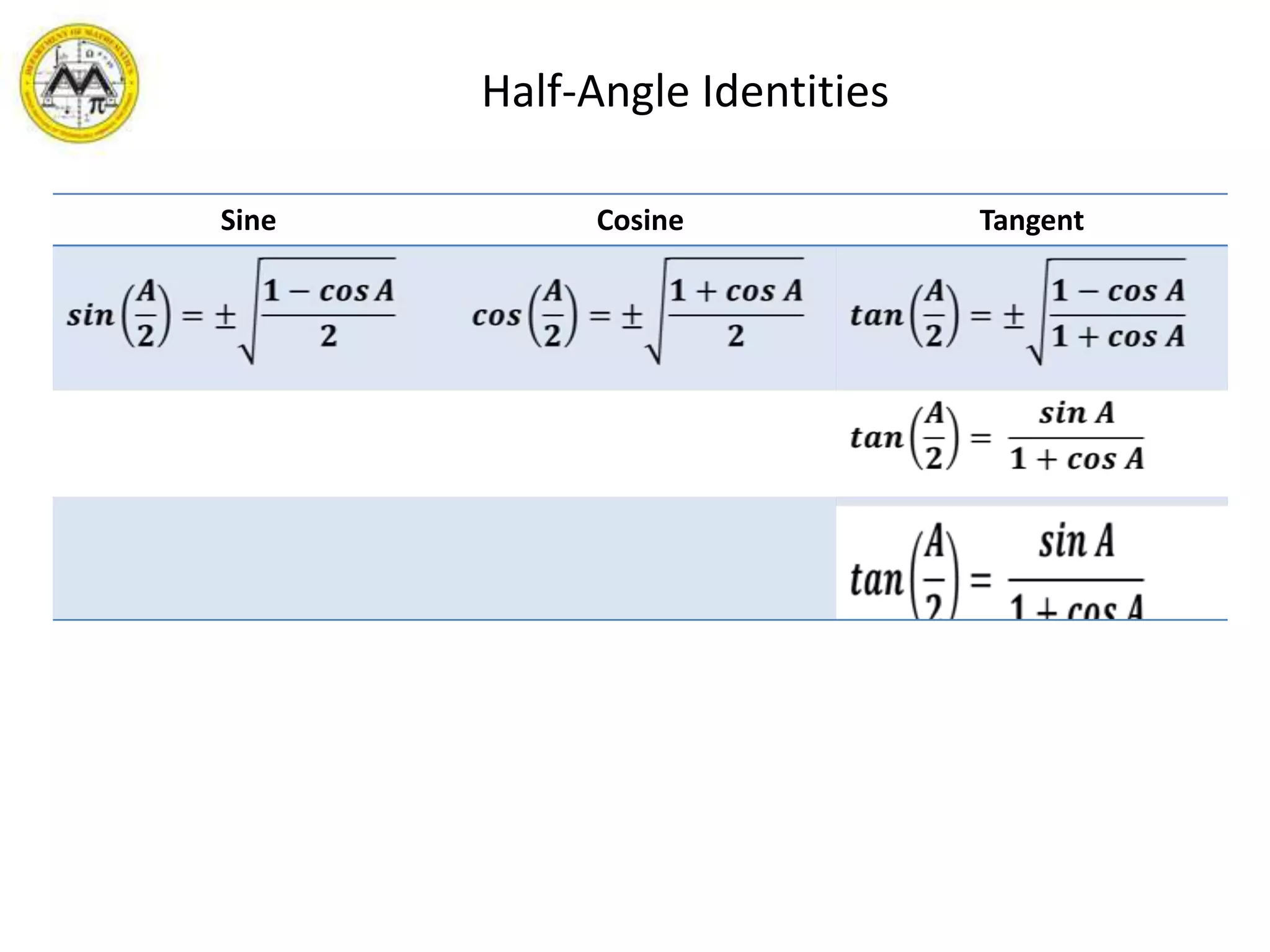
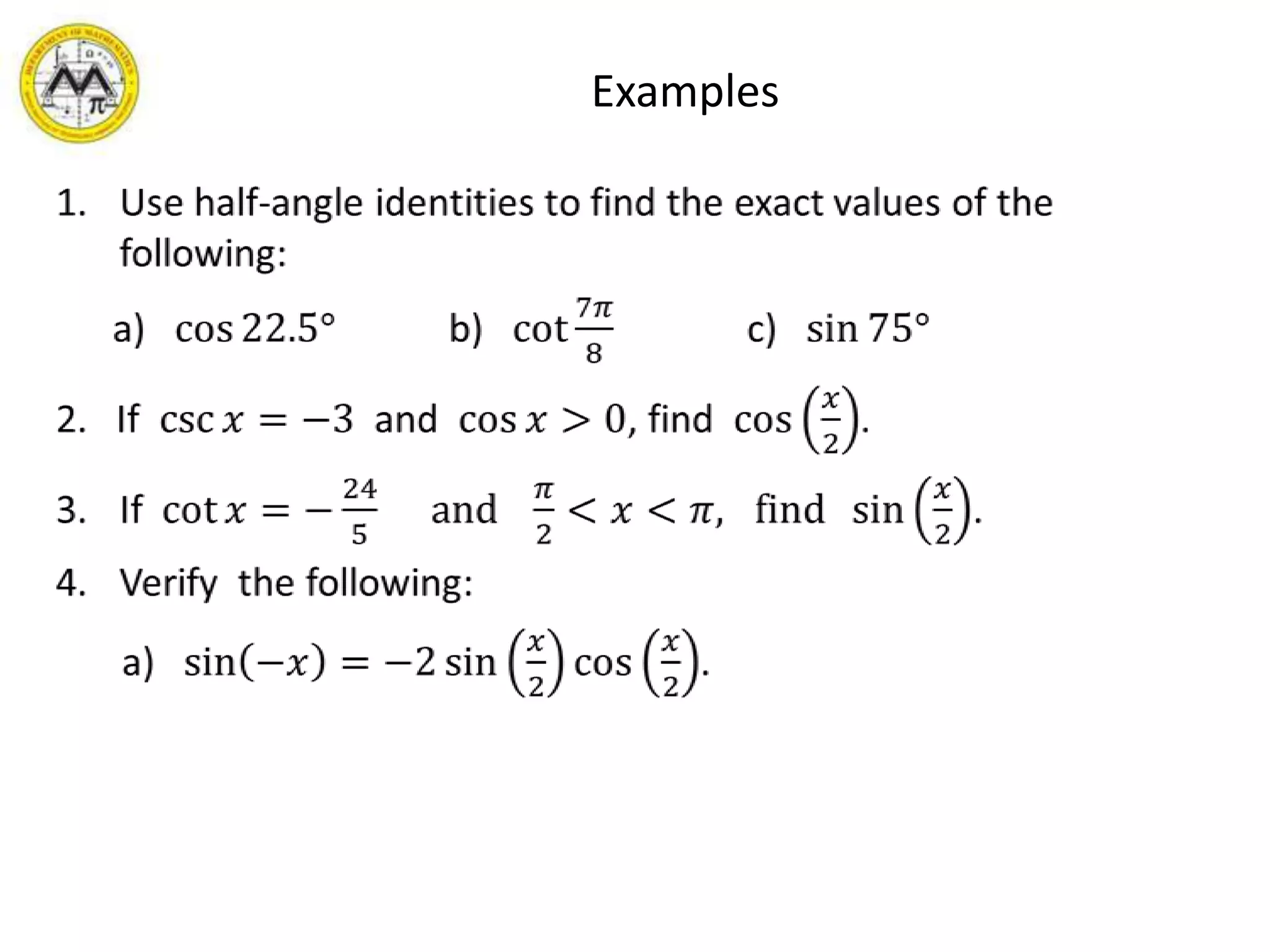
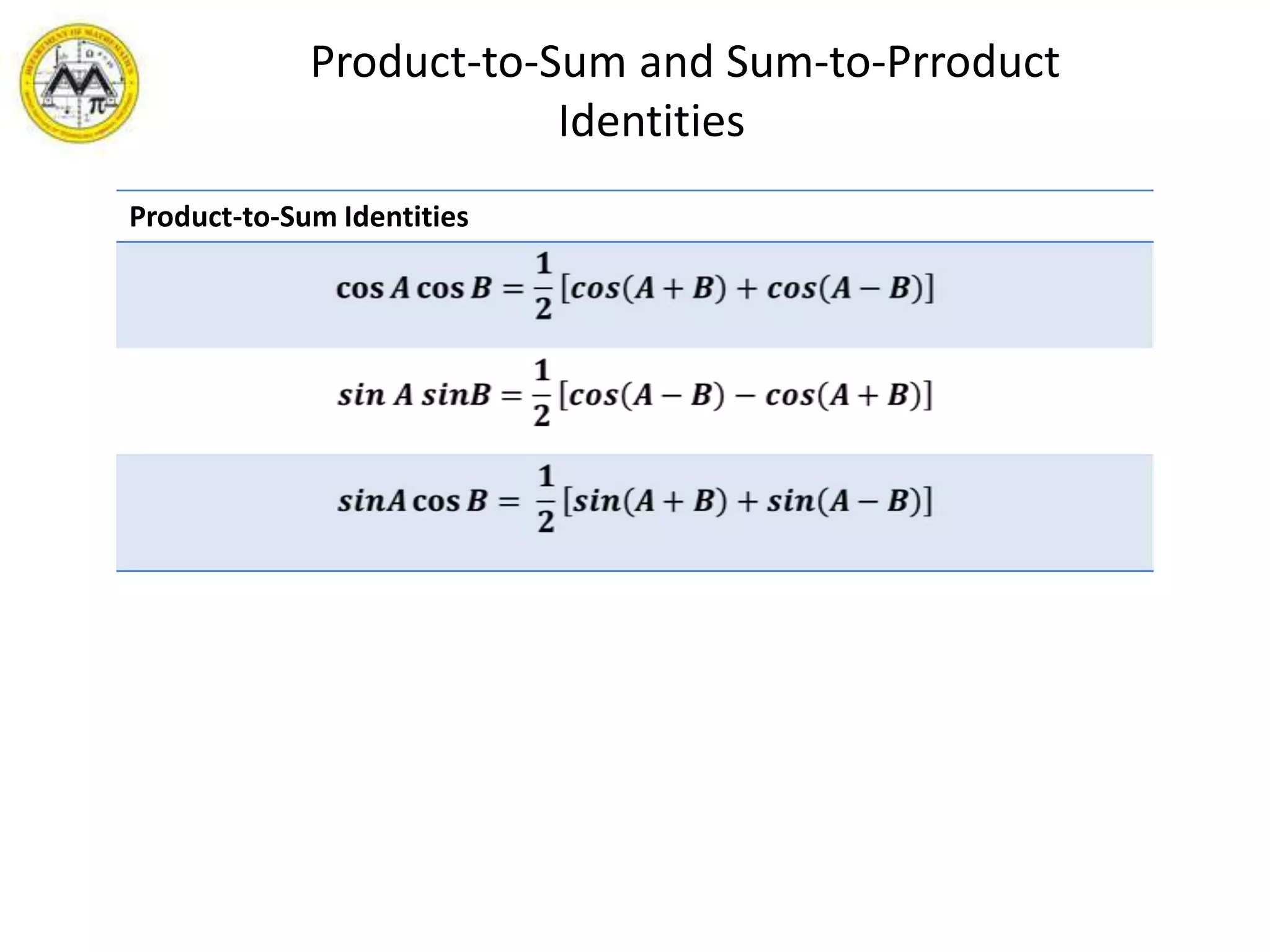
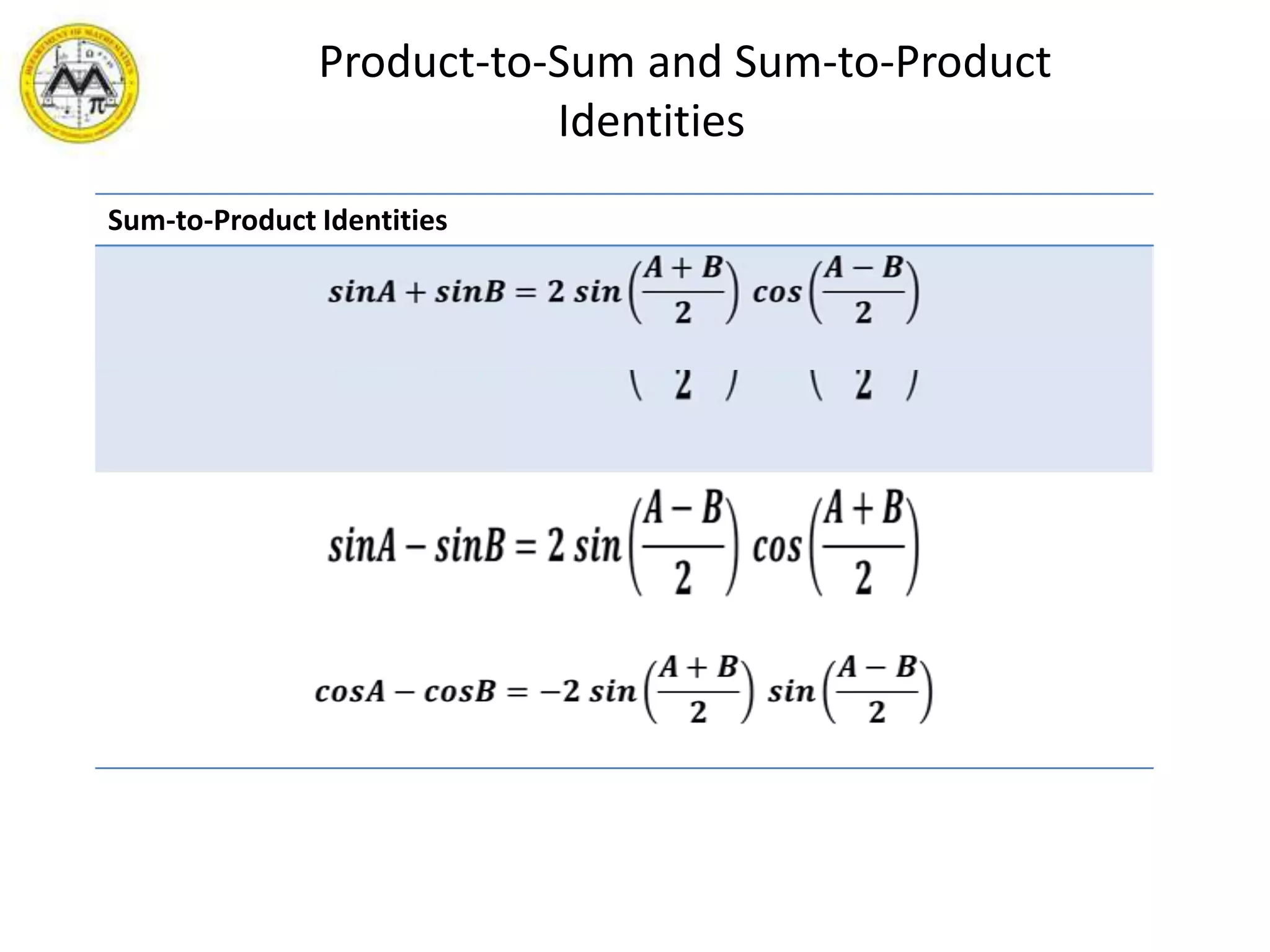
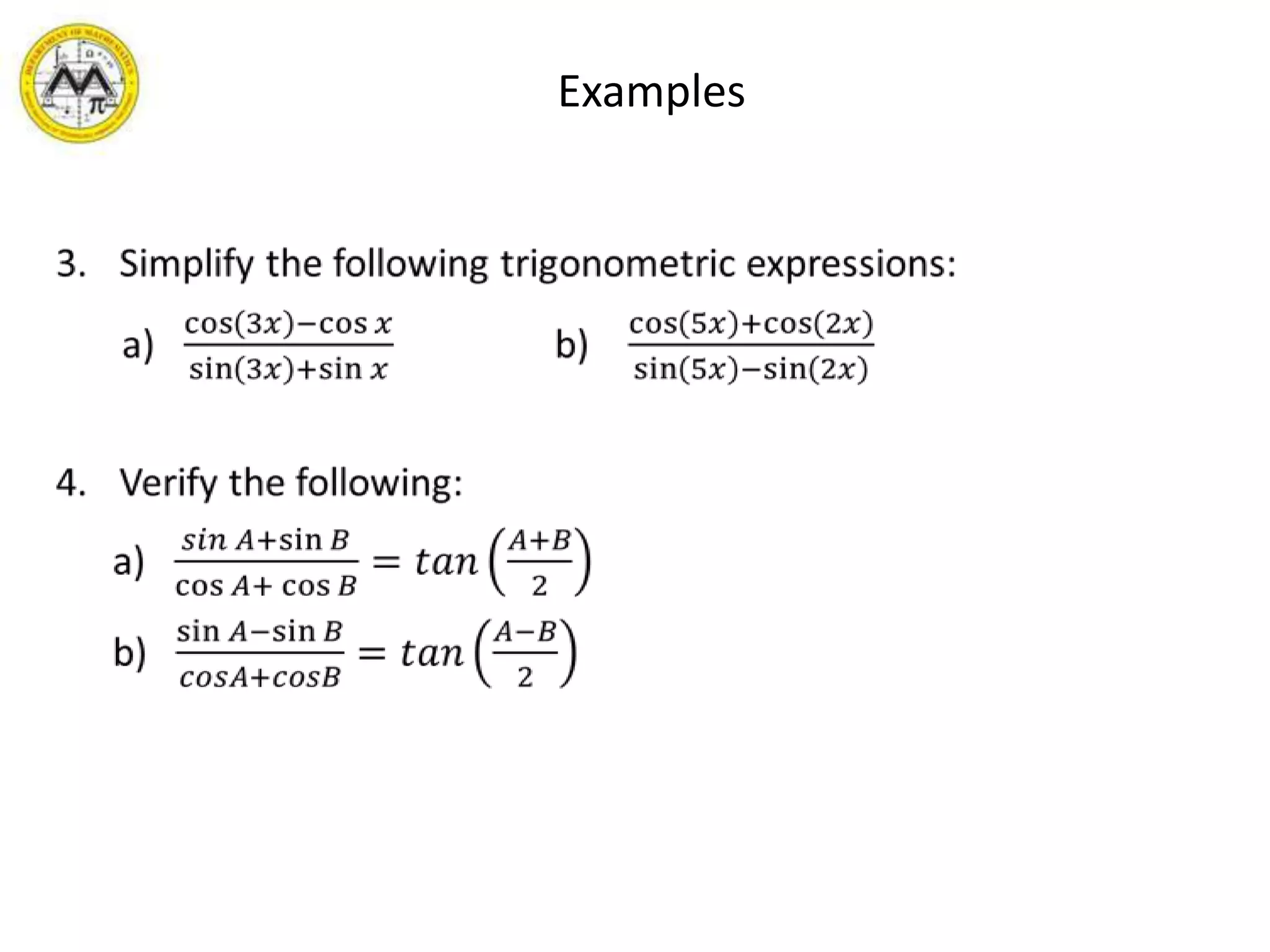
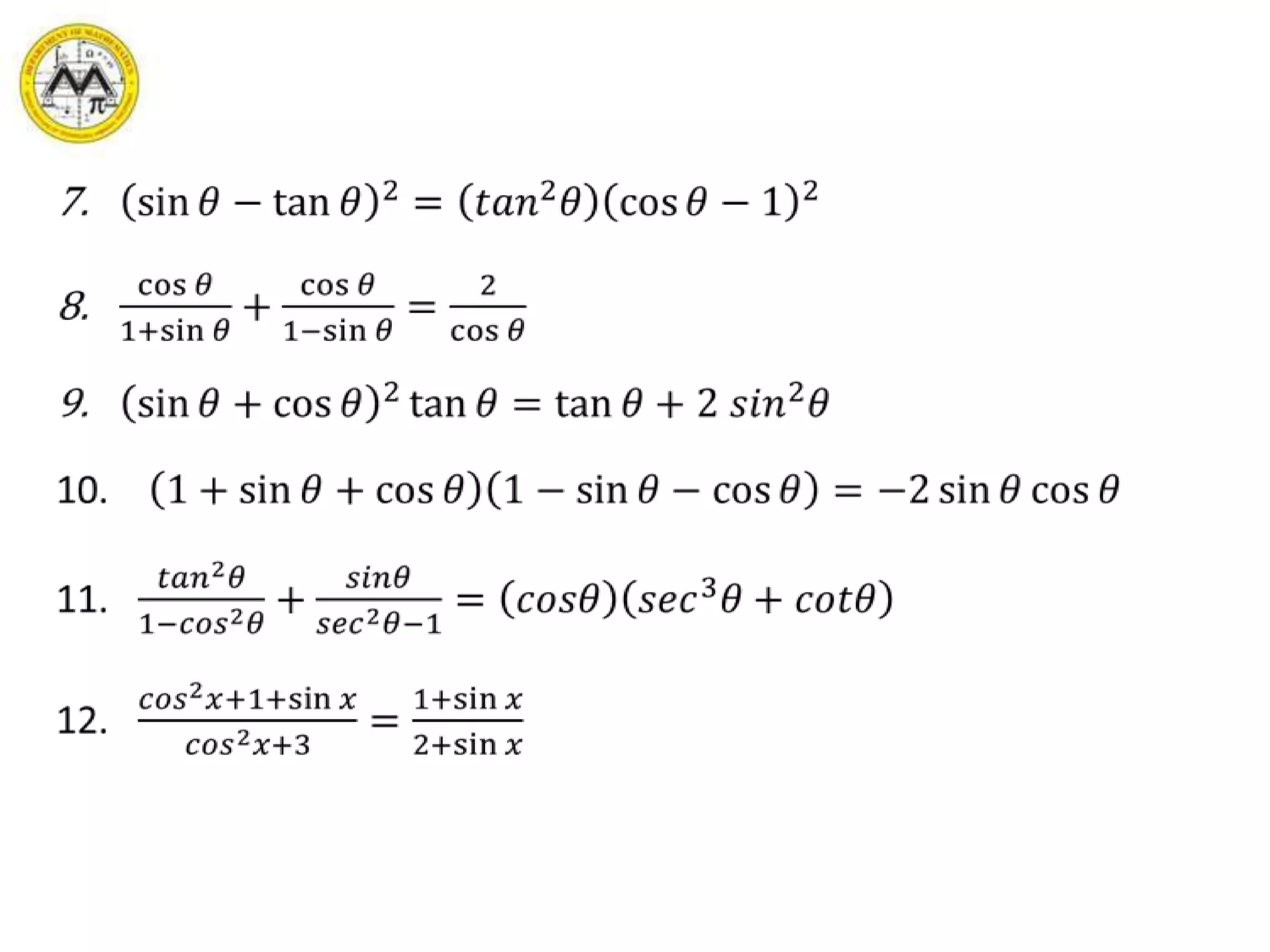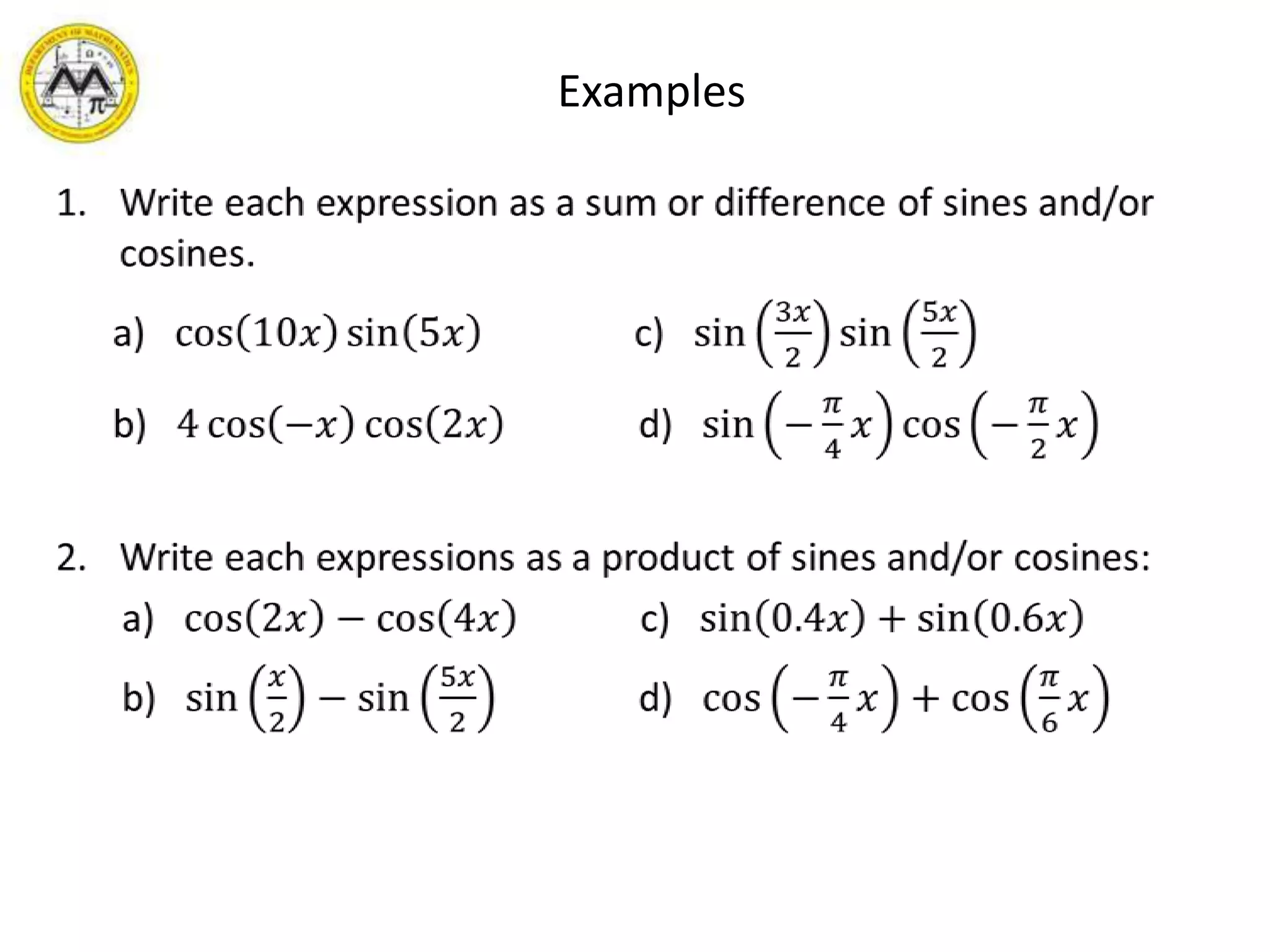This document provides an overview of trigonometric identities and examples of their applications. It discusses basic identities, verifying identities, and advanced identities involving sums, differences, doubles angles, and half angles. Examples are provided for applying product-to-sum and sum-to-product identities. The objectives are to review and apply various trigonometric identities to simplify expressions and evaluate functions.