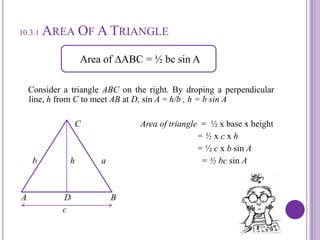
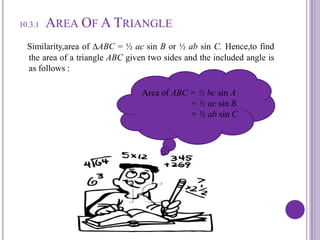
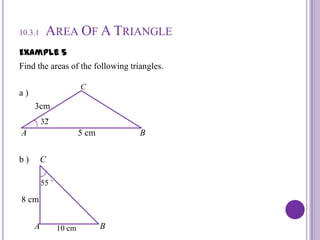
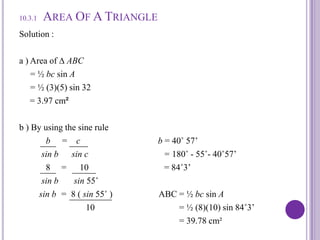
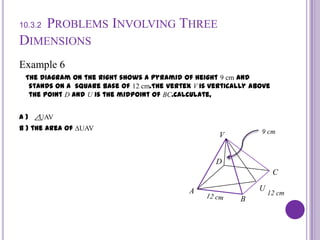
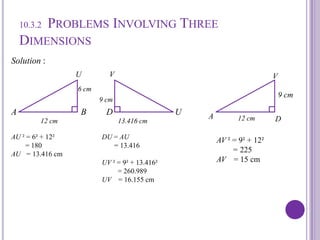
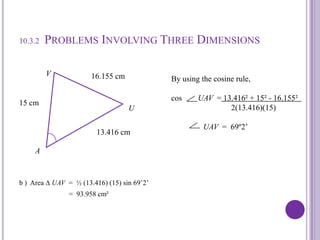
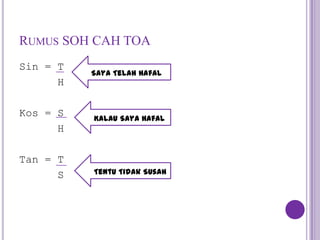
This document discusses calculating the area of triangles. It explains that the area of a triangle is 1/2 * base * height. It provides formulas to calculate the area using two sides and the included angle. Examples are given to demonstrate calculating areas when given side lengths and angles. The document also discusses a problem involving finding the area of a triangle within a three-dimensional pyramid structure. Formulas for trigonometric functions are reviewed.