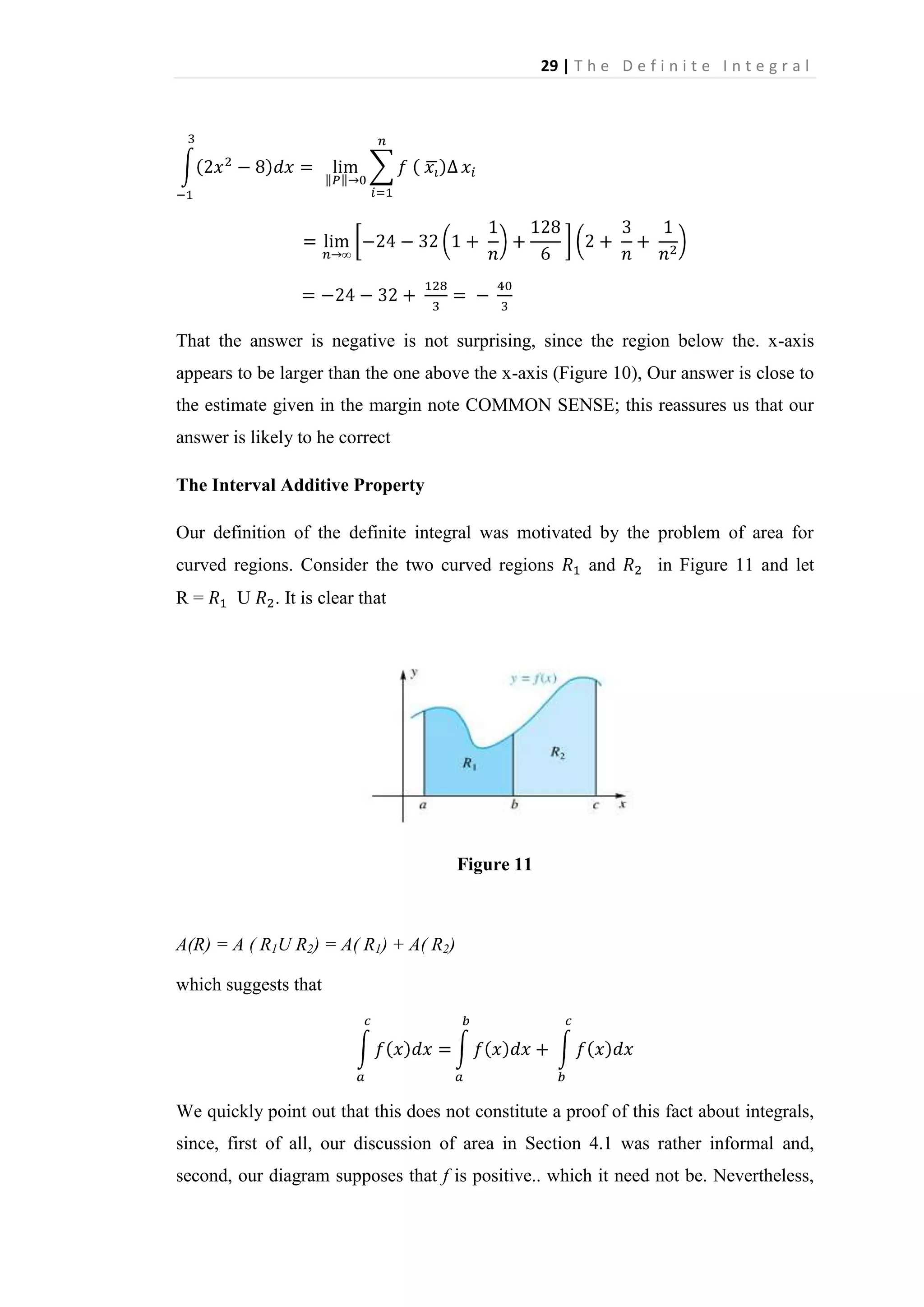
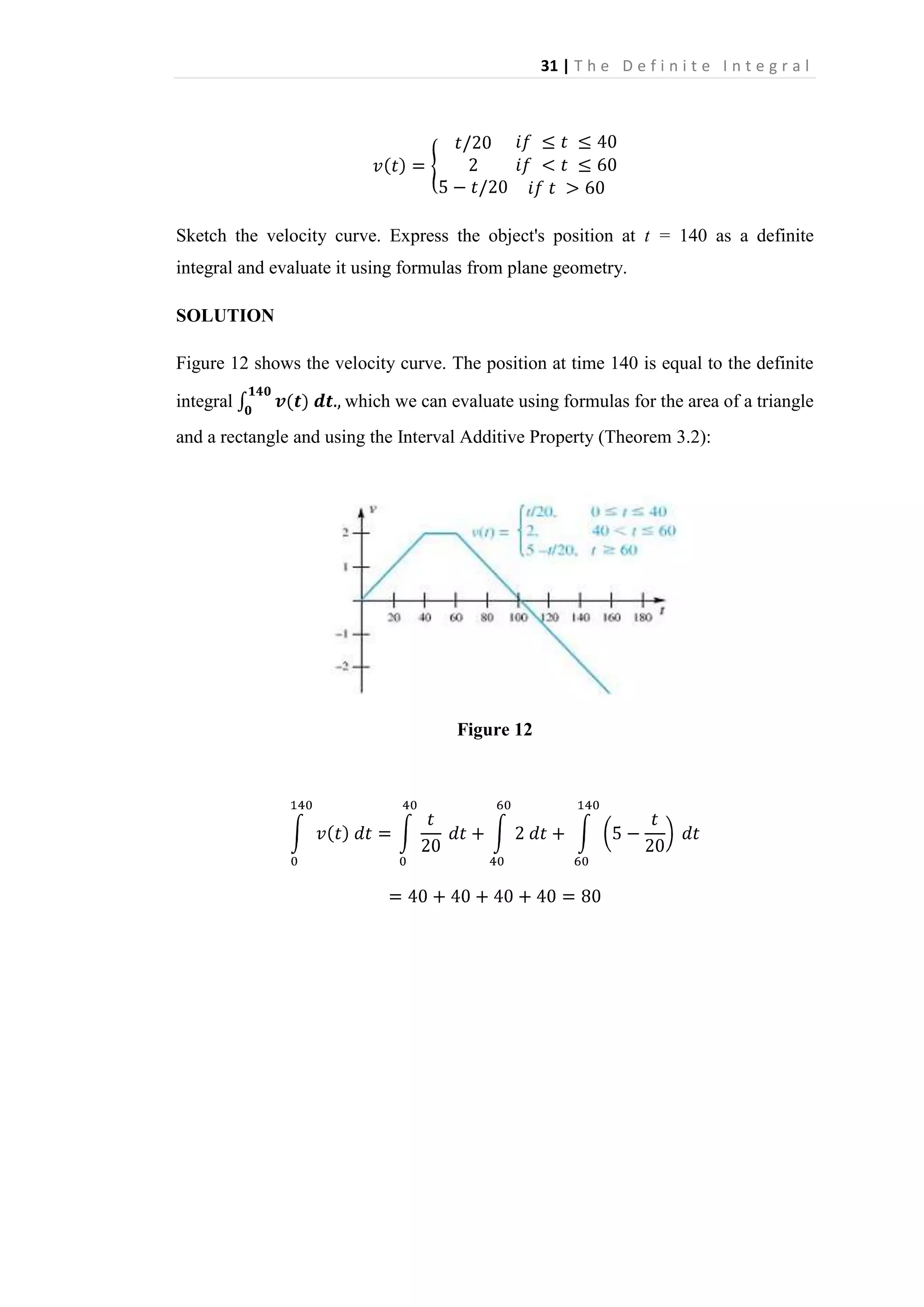
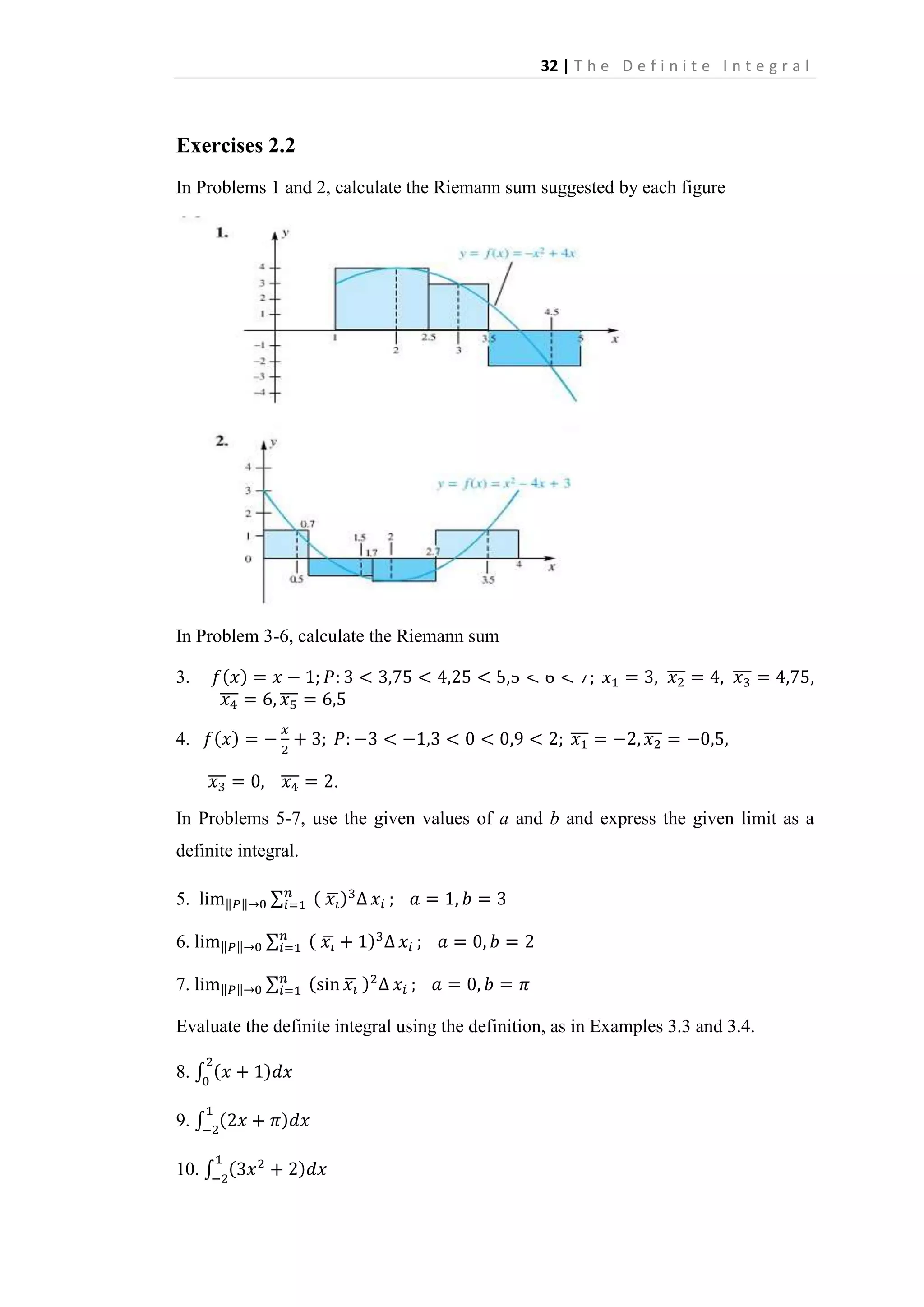
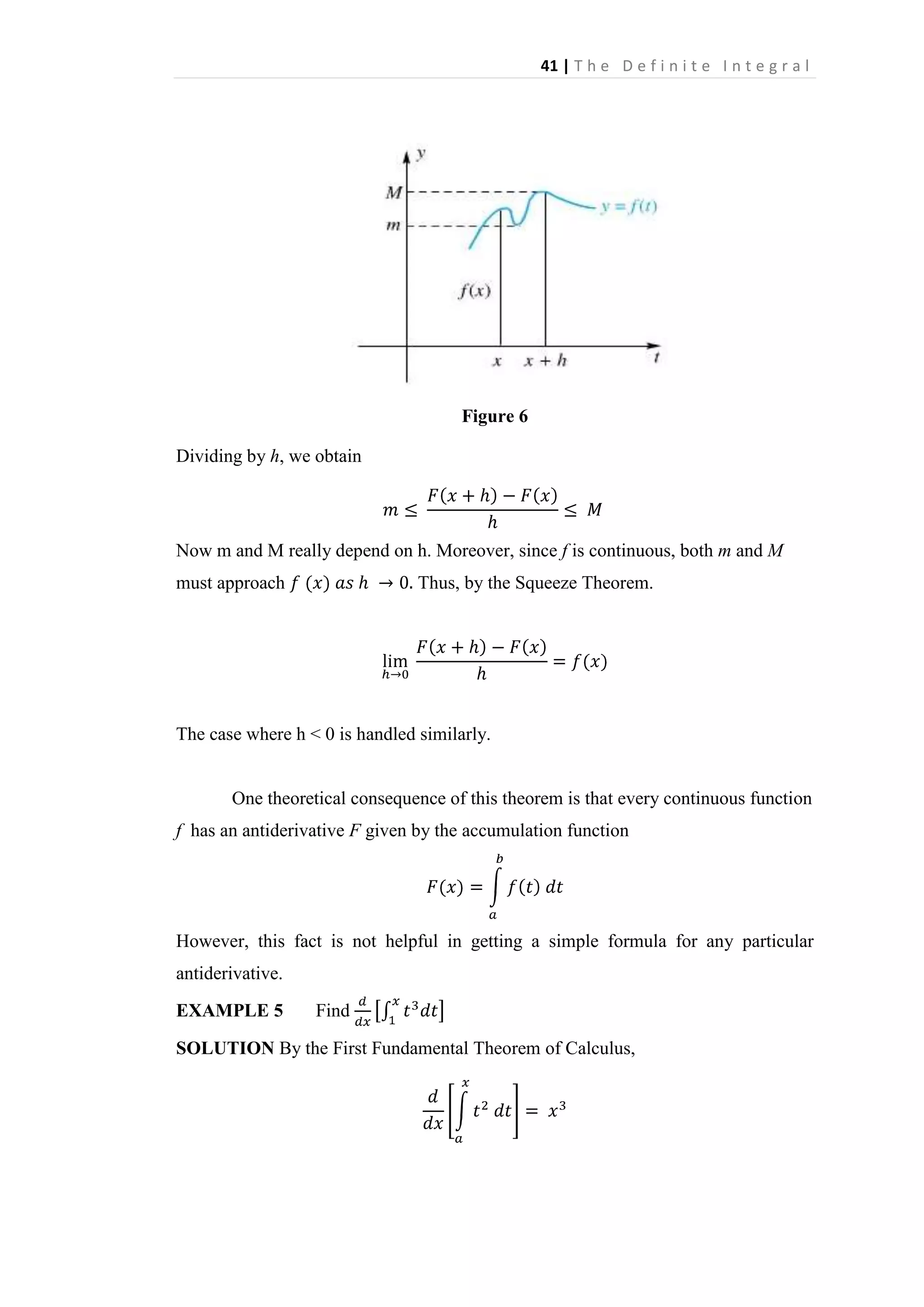
The definite integral is defined as the limit of Riemann sums as the norm of the partition approaches 0. A Riemann sum is the sum of the areas of rectangles formed by the function over subintervals of its domain. The definite integral calculates the signed area between the function's graph and the x-axis over an interval. It generalizes the idea of finding the area under a curve to allow for functions that are negative, discontinuous, or unbounded over the interval.
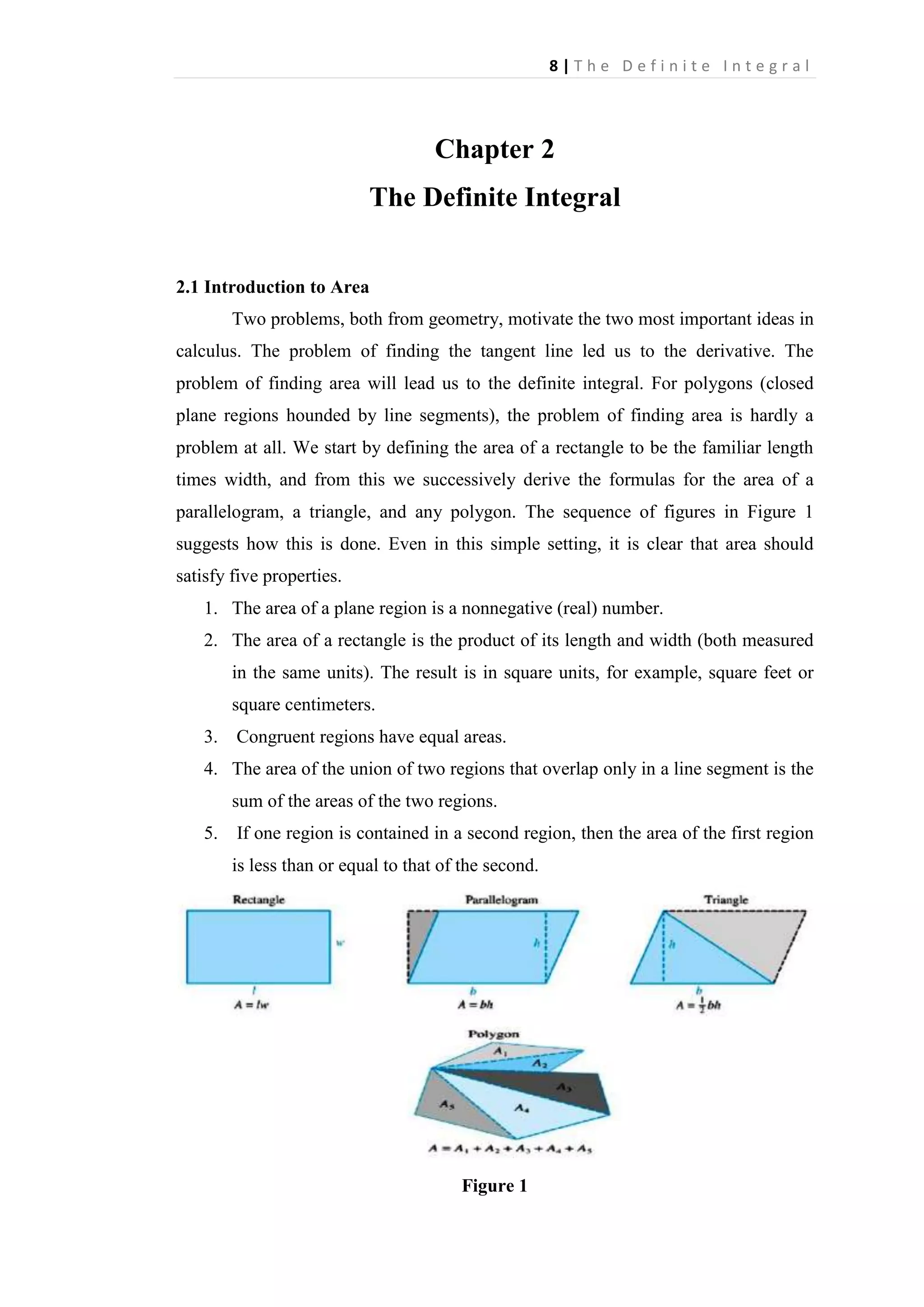


![14 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
Proofs of Special Sum Formulas
To prove Special Sum
—
Formula 1, we
start
with
the identity
, sum both sides, apply Example 2 on the left, and use
linearity on the right.
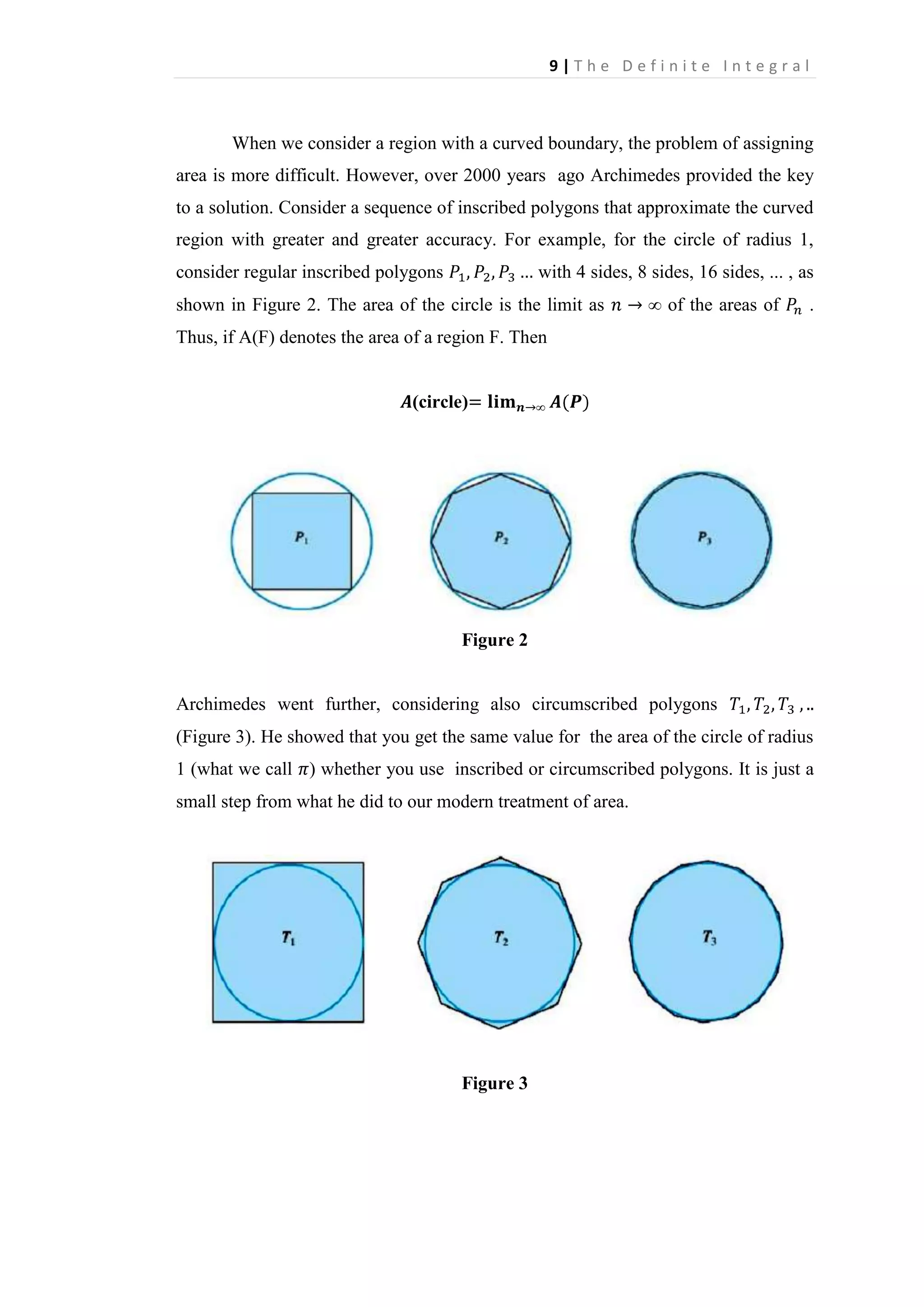
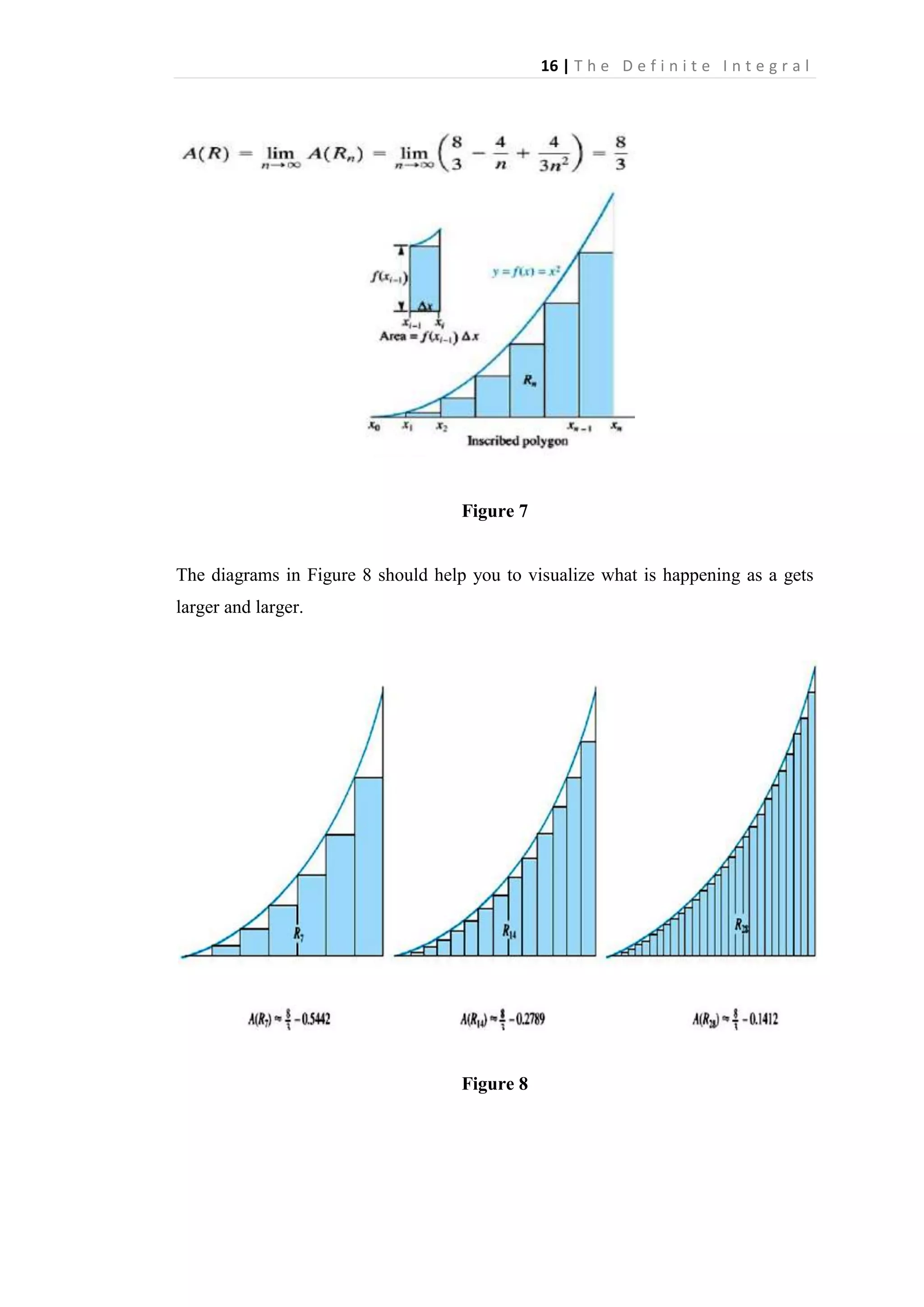
Area by Inscribed Polygons
Consider the region R bounded by the parabola
-axis, and the vertical line
curve
between
, the
(Figure 5). We refer to R as the region under the
and
Figure 5
. Our aim is to calculate its area
Figure 6
Partition (as in Figure 6) the interval [0, 2] into n subintervals, each of length
by means of the
Thus
points](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-7-2048.jpg)


![19 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
2.2 The Definite Integral
All the preparations have been made; we are ready to define the definite integral. The
Definite Integral Both Newton and Leibniz introduced early versions of this concept.
However, it was Georg Friedrich Bernhard Riernann (1826-1866) who gave us the
modern definition. In formulating this definition, we are guided by the ideas we
discussed in the previous section. The first notion is that of a Riemann sum.
Rieffiami Sums
Consider a function f defined on a closed interval [a, b]. It may have both positive
and negative values on the interval, and it does not even need to be continuous. Its
graph might look something like the one in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Consider a partition P of the interval [a, h] into n subintervals (not necessarily
of equal length) by means of points
and let
On each subinterval [
], pick an arbitrary point
(which may be an end point); we call it a sample point for the ith subinterval. An
example of these constructions is shown in Figure 2 for n = 6.
A Partition of [a,b] with Sample points
Figure 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-12-2048.jpg)
![20 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
We call the sum
a Riemann sum for f corresponding to the partition P. Its geometric interpretation
is shown in Figure 3.
A Riemann sum interpreted as an algebraic sum of areas
y
Figure 3
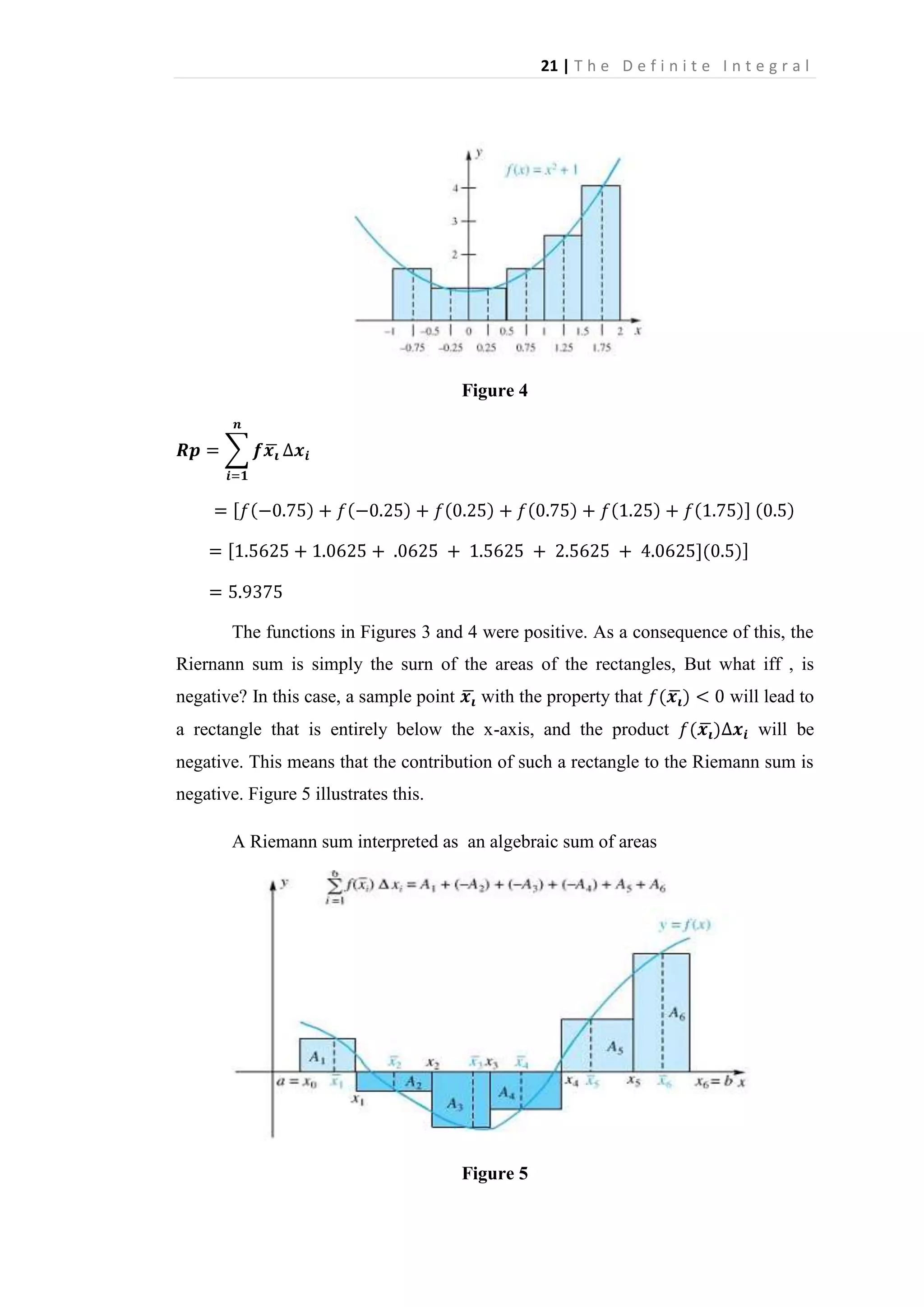
EXAMPLE 3.1
Evaluate the Riemann sum for
on the interval [-1, 2] using the
equally spaced partition points -1 < -0.5 < 0 < 0.5 < 1 < 1.5 < 2, with the sample
point
being the midpoint of the ith subinterval.
SOLUTION
Note the picture in Figure 4.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-13-2048.jpg)
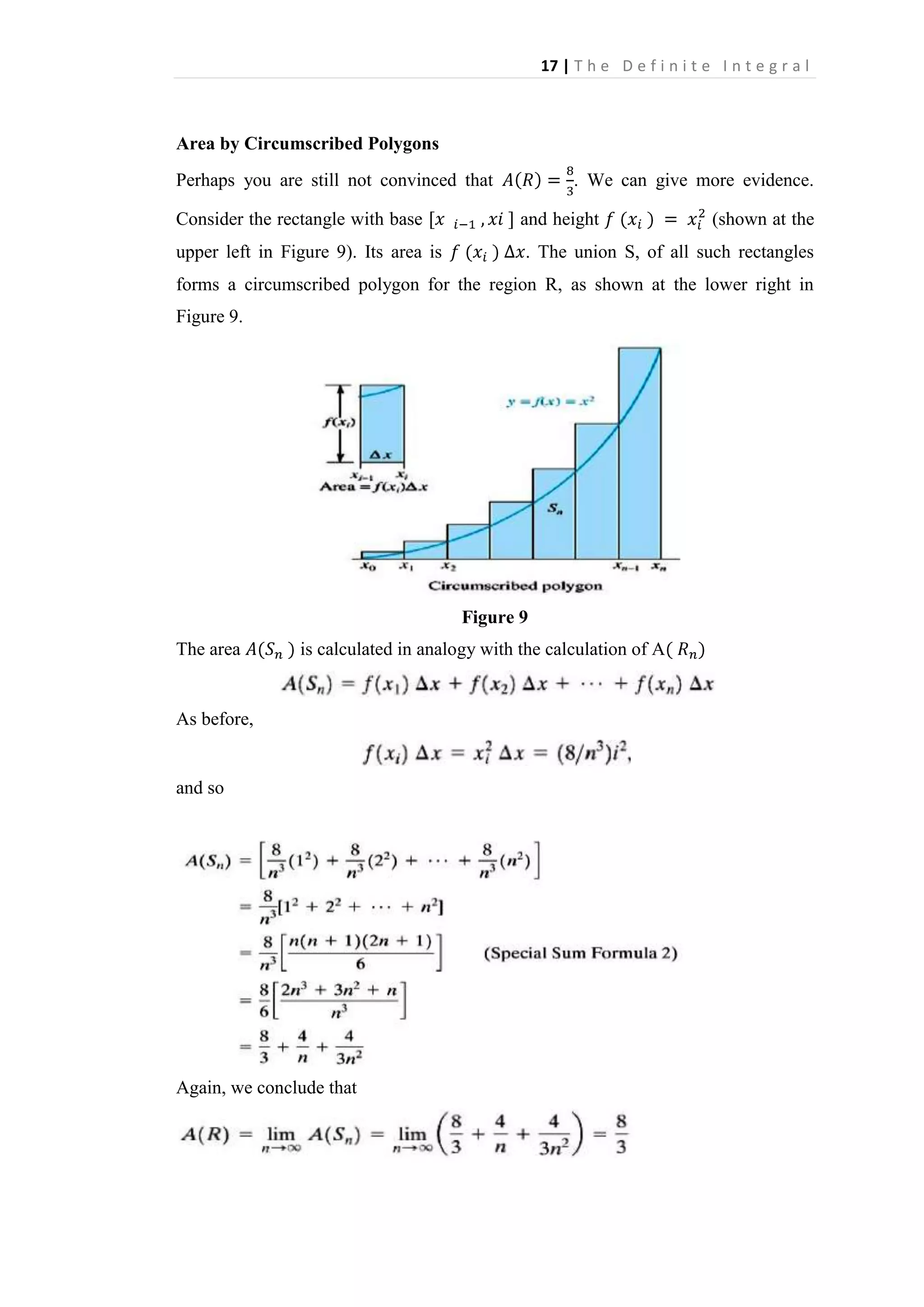
![22 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
EXAMPLE 2.2 Evaluate the Riemann sum Rp for
on the interval [0, 5] using the partition P with partition points 0 < 1.1 < 2 < 3.2 < 4 <
5 and the corresponding sample points
= 1.5,
= 2.5,
=3.6,
SOLUTION
—
—
= (7.875)(1.1) + (3.125)(O.9) + (-2.625)(1.2) + (-2.944)(0.8) + 18(1)
= 23.9698
The corresponding geometric picture appears in Figure 6.
Figure 6
Definition of the Definite Integral
Suppose now that
and
have the meanings discussed above. Also let
,
called the norm of P, denote the length of the longest of the subintervals of the
partition P. For instance, in Example 1,
= 0,5; in Example 2
= 3,2 - 2 = 1,2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-15-2048.jpg)
![23 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
Definition 3.1 Definite Integral
Let f be a function that is defined on the closed interval [a,b]. If
exists, we say f that is iniegrable on [a,b]. Moreover,
, called the definite
integral (or Riemann integral) of f from a to b, is then given by
The heart of the definition is the final line. The concept. captured in that
equation grows out of our discussion of area in the previous section. However, we.
Have considerably modified the notion presented there. For example, we now allow
f to be negative on part or all of [a,b], we use partitions with subintervals that may he
of unequal length, and we allow to be any point on the ith subinterval. Since we have
made these changes, it is important to state precisely how the definite integral relates
to area. In general,
gives the signed area of the region trapped between
the curve y = f(x) and the x-axis on the interval [a, b], meaning that a positive sign is
attached to areas of parts above the x-axis, and a negative sign is attached to areas of
parts below the x-axis. In symbols,
where
and
are as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7
The meaning of the word limit in the definition of the definite integral is
more general than in earlier usage and should be explained. The equality](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-16-2048.jpg)
![24 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
means that corresponding, to each
for all Riernann sums
for
, there is a
> 0 such that
on [a, b] for which the norm
= of the
associated partition is less than 6. In this case, we say that the indicated limit exists
and has the value L.
That was a mouthful, and we are not going to digest it just now. We simply
assert that the usual limit theorems also hold for this kind of limit.
Returning to the symbol
, we might call a the lower end point and
b' the upper end point for the integral. However, most authors use the terminology
lower limit of integration and upper limit of integration, which is tine provided we
realize that this usage of the word limit has nothing to do with its more technical
meaning.
In our definition of
, we implicitly assumed that a < b. We
remove that restriction with the following definitions.
Thus.
Finally, we point out that x is a dummy variable in the symbol
.
By this lyre mean that x can be replaced by any other letter (provided, of course, that
it is replaced in each place where. it occurs). Thus,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-17-2048.jpg)
![25 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
What Functions Are Integrable? Not every function is integrable on a closed
interval [a1 b]. For example., the unbounded function
which is graphed in Figure 8, is not integrable on [-2, 2], It can be shown that for
this unbounded function, the Riemann sum can be made arbitrarily large. Therefore,
the limit of the Riemann sum over [-2, 2] does not exist.
Figure 8
Even some bounded functions can fail to be integrable, but they have to be pretty
complicated (see Problem 39 for one example). Theorem 3.1 (below) is the most
important theorem about integrability. Unfortunately.. it is too difficult to prove here:
we leave that for advanced calculus books.
Theorem 3.1 Integrability Theorem
If f is bounded on[a,b] and if it is continuous there except at a finite number of
points, then f is integrable on [a,b]. In particular, if f is continuous on the whole
interval [a,b], it is integrable on [a,b].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-18-2048.jpg)
![26 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
As a consequence of this theorem, the following functions are integrable on
every closed interval [a, b].
1. Polynomial functions
2. Sine and cosine functions
3. Rational functions, provided that the interval [a, b ] contains no points where the.
denominator is 0.
Calculating Definite Integrals
Knowing that a function is integrable allows us to calcalte its integral by using a
regular partition (i.e., a partition with equal-length subintervals) and by picking the
sample points 1 in any way that is convenient for us. Examples 3 and 4 involve
polynomials, which we just learned are integrable.
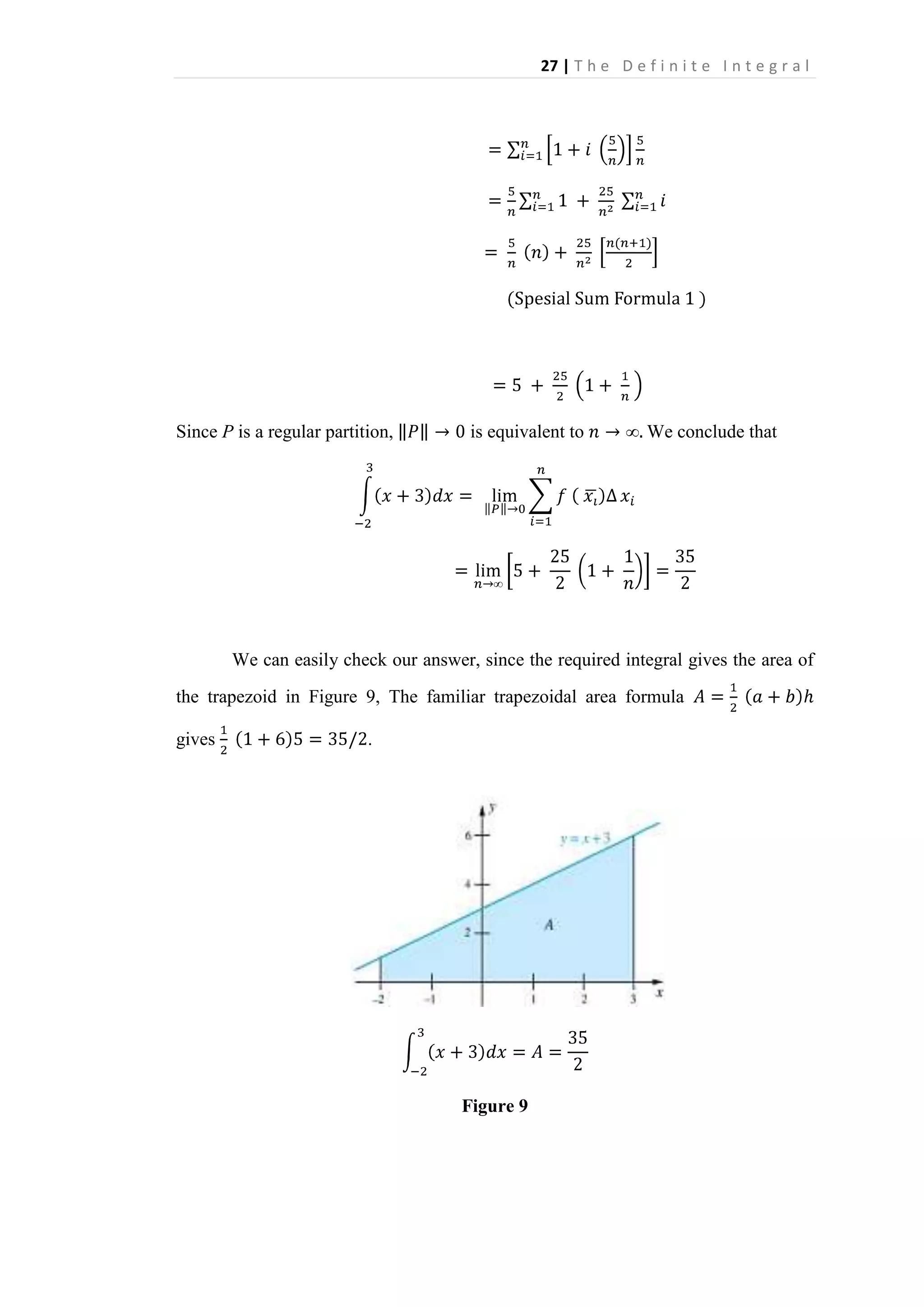
EXAMPLE 3 Evaluate
SOLUTION Partition the interval [-2,3] into n equal subintervals, each of length
In each subinterval [xi _ j, xj. use ,Ti = xi as the sample point.
Then
Thus,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-19-2048.jpg)
![28 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
EXAMPLE 4 Evaluate
SOLUTION No formulas from elementary geometry will help here. Figure 10
suggests that the integral is equal to
, where
and
are the areas of the
regions below and above the x-axis.
Figure 10
Let P be a regular partition of [-1, 3] into n equal subintervals, each of length
In each subinterval
],choose
. Then
and
Consequently,
=
We conclude that
to be the. right end point, so](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-21-2048.jpg)



![35 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
In this case we can evaluate this definite integral using a geometrical argument; A(x)
is just the area of a trapezoid, so
With this done, we see that the derivative of A is
In other words,
Let's define another accumulation function B as the area under the curve
, above the t-axis, to the right of the origin, and to the left of the line
.
Figure 2
where
see Figure 2). This area is given by the definite integral
. To
find this area, we first construct a Rie.mann sum. We use a regular partition of [0,x]
and evaluate the. function at the right end point of each subinterval. Then
the right end point of the ith interval is
therefore
and
= ix/n. The Riemann sum is](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-28-2048.jpg)

![37 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
which paint is being applied is equal to the width of the brush.. in effect, the height
of the function. We can restate this result as follows,
The rate of accumulation at t = x is equal to the value of the function being
accumulated at t = x.
Figure 3
This, in a nu[shell, is the First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus it is fUndamental
because it links the derivative and the definite integral, the most important kinds
of limits you have studied so far.
Theorem 3.3 First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Let f be continuous on the closed interval [a,b] and let x be a (variable) point in
(a,b). Then
Sketch or Proof For now. we present a sketch of the proof. This sketch shows the
important features of the proof, but a complete proof must wait until after we have
established a few other results. For x in [a, b], define
. Then for x
in (a ,b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-30-2048.jpg)
![38 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
The last line follows from the Interval Additive Property (Theorem 4.2B). Now,
when h is small., f does not change. much over the interval [x, x + h]. On this
interval, f is roughly equal to ,f( x) the value of f evaluated at the left end point of the
interval (see Figure 4). The area under the curve
from x to x + h is
approximately equal to the area of the rectangle with width h and height f(x);
that is
Of course, the flaw in this argument is that h is never 0, so we cannot claim
that f does riot change over the interval [x, x + h].. We will give a complete proof
later in this section.
Comparison Properties Consideration of the areas of the regions
and
in
Figure 5 suggests another property of definite integrals.
Theorem 3.4 Comparison Property
If f and g are integrable on [a,b] and if
for all x in [a,b], then
In informal but descriptive language, we say that the definite integral preserves
inequalities.
Proof
Let
for each
be an arbitrary partition of [a,b], and
be any sample point on the ith subinterval [
conclude successively that
,
]. We may](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-31-2048.jpg)
![39 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
Theorem 3.5 Boundedness Property
If f is integrable on [a,b] and
for all x in [a,b], then
Proof
The picture in Figure 6 helps us to understand the theorem. Note that m(b — a) is the
area of the lower, small rectangle. M (b — a) is the area of the large rectangle, and
is the area under the curve.
To prove the right-hand inequality, let
for all x in [a,b]. Then, by
Theorem 3.4,
However,
is aqual to the area of a rectangle with wideth b-a and height
M. Thus.
The left-hand inequality is handled similarly.
The Definite Integral is a Linear Operator
Earlier we learned that
and
linear operators. You can add
to the list.
Theorem 3.5 Linearity of the Definite Integral
Suppose that f and g are integrable on [a,b] and that k is a constant. Then kf
f + g are integrable and
and](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-32-2048.jpg)
![40 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
Proof The proofs of (i) and (ii) depend on the linearity of and the properties of limits.
We show (ii).
Part (iii) follows from (i) and (ii) on writing
Proof of the First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus With these results in hand,
we are now ready to prove the First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
Proof In the sketch of the proof presented earlier. we defined
and we established the fact that
Assume. for the moment that h > 0 and let m and M be the minimum value
and maximum value., respectively, of f on the interval [x,x + h] (Figure 6). By
Theorem 3.5 ,
or](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-33-2048.jpg)

![43 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
Another way to find this derivative is to evaluate the definite integral first and
then use our rules for derivatives. The definite integral
below the tine y = 3t – 1 between t = 1 and t =
–
is the area
(see. Figure 7). Since. the area of
this trapezoid is
Thua ,
Position as Accumulated Velocity In the last section we saw how the position of an
object, initially at the origin, is equa[ to the definite integral of the velocity function,
This often leads to accumulation functions, as the next example illustrates.
2.4 The Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and Method of Subtitution
The First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, given in the previous section, gives the
inverse relationship between definite integrals and derivatives. Although it is not yet
apparent, this relationship gives us a powerful tool for evaluating definite integrals.
This tool is called the Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, and we will apply
it much more often than the First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
Theorem 3.6 Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Let f be continuous (hence integrable) on [a, b], and let F be any antiderivative of f
on [a, b]. Then
Proof For x in the interval [a, b] define
. Then, by the First
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, G' (x) = f(x) for all in (a, b). Thus. G is an
antiderivative off; but F is also an antiderivative of f, we conclude that since F'(x)=
G'(x), the functions F and G differ by a constant. Thus, for all x in (a, b)
F(x) = G(x) + C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-36-2048.jpg)
![44 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
Since the function F and G are continuous on the closed interval [a,b], we have F(a)
= G(a) + C and F(b)=G(b) + C. Thus, F(x) = G(x) + C on the closed interval [a,b].
Since
, we have
Therefore,
EXAMPLE 9 Show that
SOLUTION
, where k is a constant.
is an antiderivative of f (x) = k. Thus, by the Second
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus,
.
EXAMPLE 10 Show that
SOLUTION
.
is an antiderivative
. Therefore,
.
EXAMPLE 11 Show that if r is a rational number different from -1. Then
SOLUTION
is an antiderivative of
. Thus, by the Second
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
If r < 0, we require that 0 not be in [a, b]. Why?
It is convenient to introduce a special symbol for F(b) - F (a). We write
With this notation,
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-37-2048.jpg)

![46 | T h e D e f i n i t e I n t e g r a l
Notice how we had to multiply by . 3 in order to have the expression 3dx = du in
the integral.
EXAMPLE 14 Evaluate
SOLUTION
.
Here the appropriate substitution is
. This gives us
in the integrand, but more importantly, the extra x in the integrand can be put
with the differential, because du = 2x dx. Thus
.
EXAMPLE 15 Evaluate
SOLUTION
Let
.
; then
. Thus,
Therefore, by the Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus,
Theorem 3.7 Substitution Rule for Definite Integrals
Let g have a continuous derivative on [a, b], and let f be continuous on the range of
g. Then
where
.
Proof Let F be an antiderivative of f . Then, by the Second Fundamental Theorem
of Calculus,
On the other hand, by the Substitution Rule for Indefinite Integrals](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter2-140211090653-phpapp01/75/Chapter-2-39-2048.jpg)

