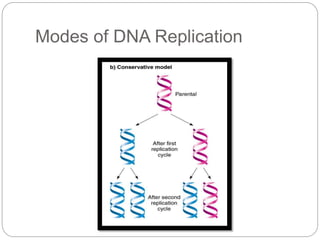
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. It occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle. There are three main modes of DNA replication: semiconservative, conservative, and dispersive. Semiconservative replication, where each new DNA molecule contains one old and one new DNA strand, is the mechanism that occurs in eukaryotic cells. DNA replication begins with initiation at the origin of replication and unwinding of the DNA strands. It then proceeds bidirectionally via elongation, with DNA polymerase adding complementary nucleotides to form new strands. Replication of the lagging strand occurs discontinuously via Okazaki fragments. DNA replication terminates at the end of the DNA strands