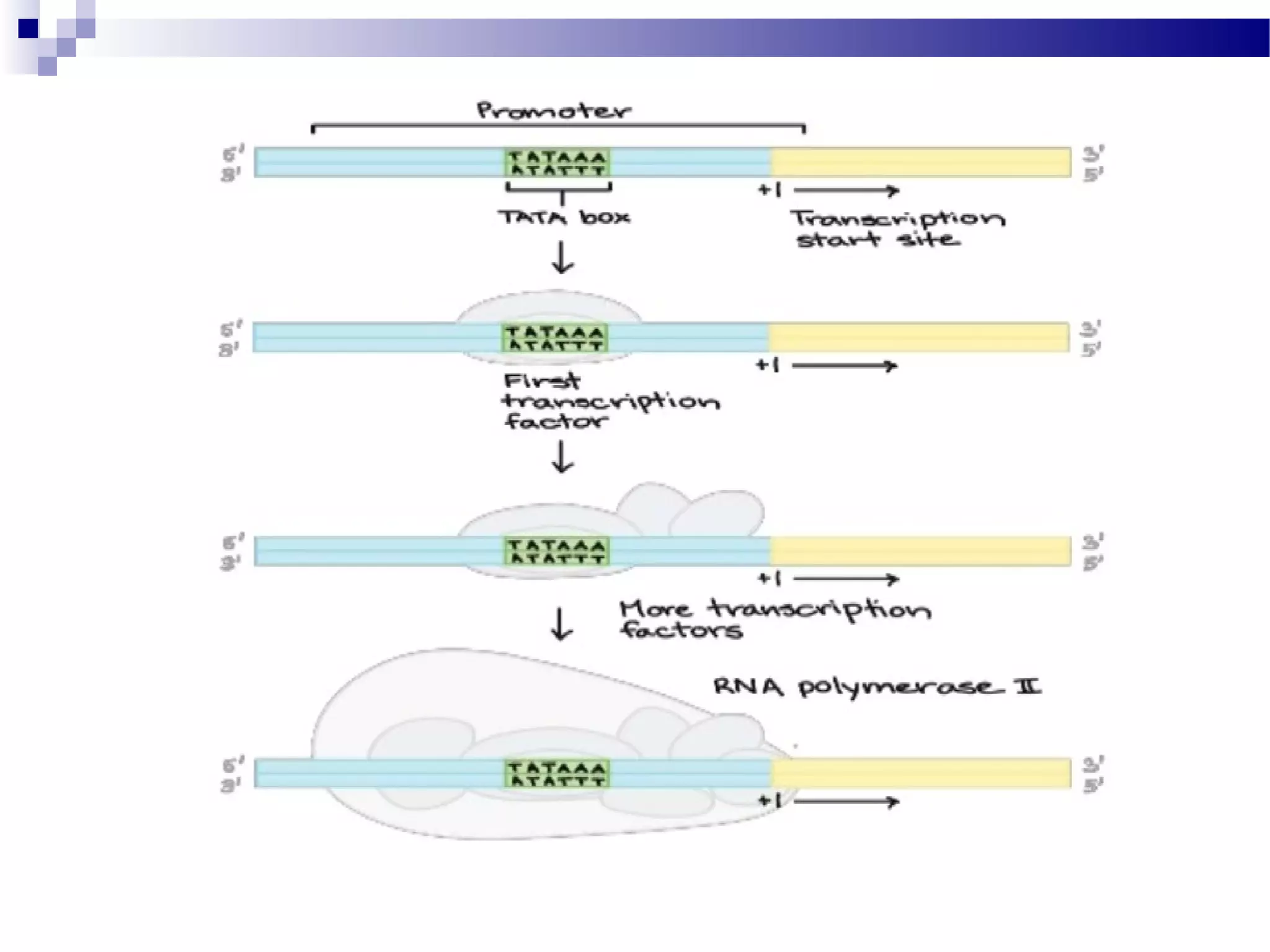
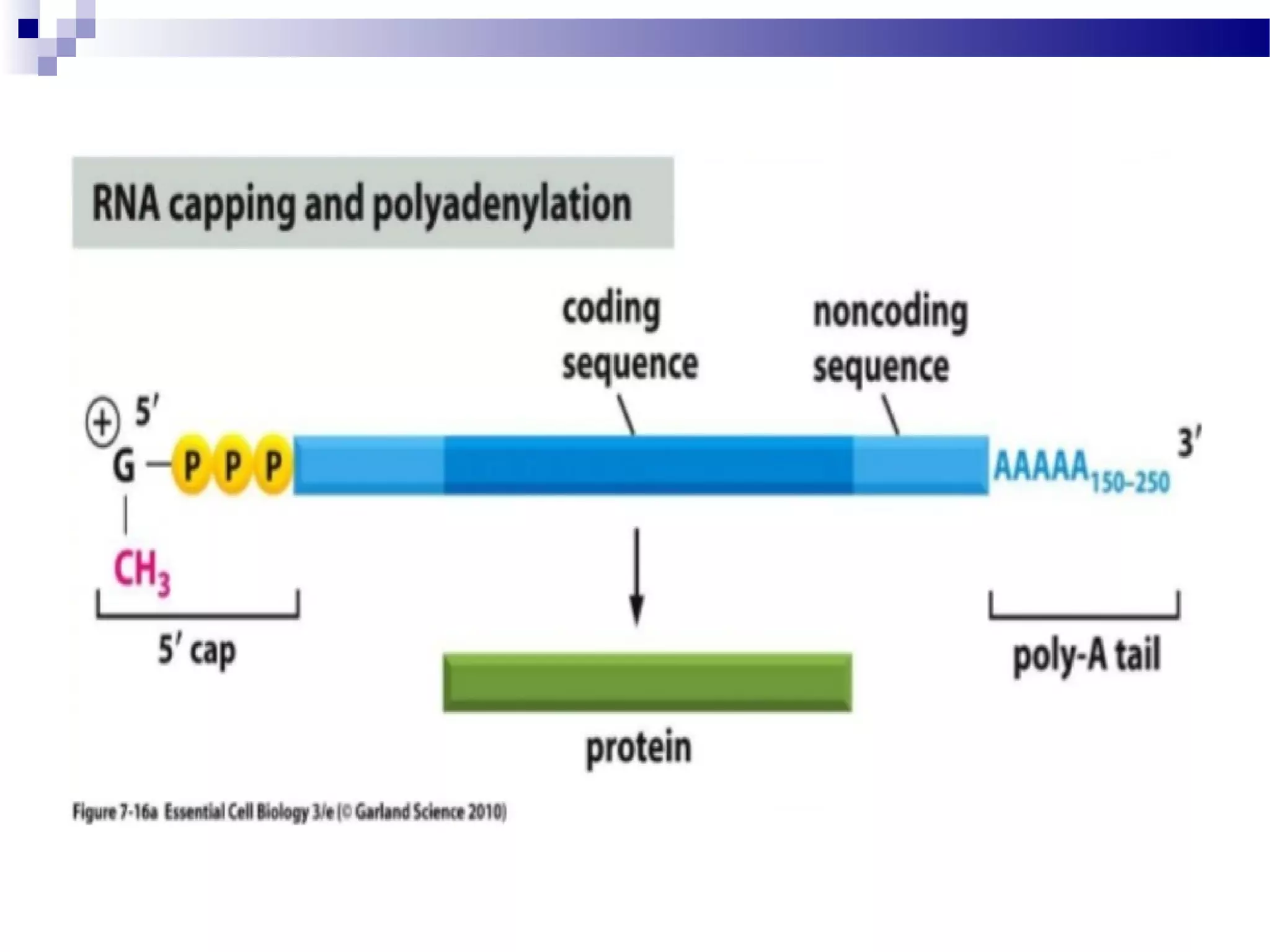
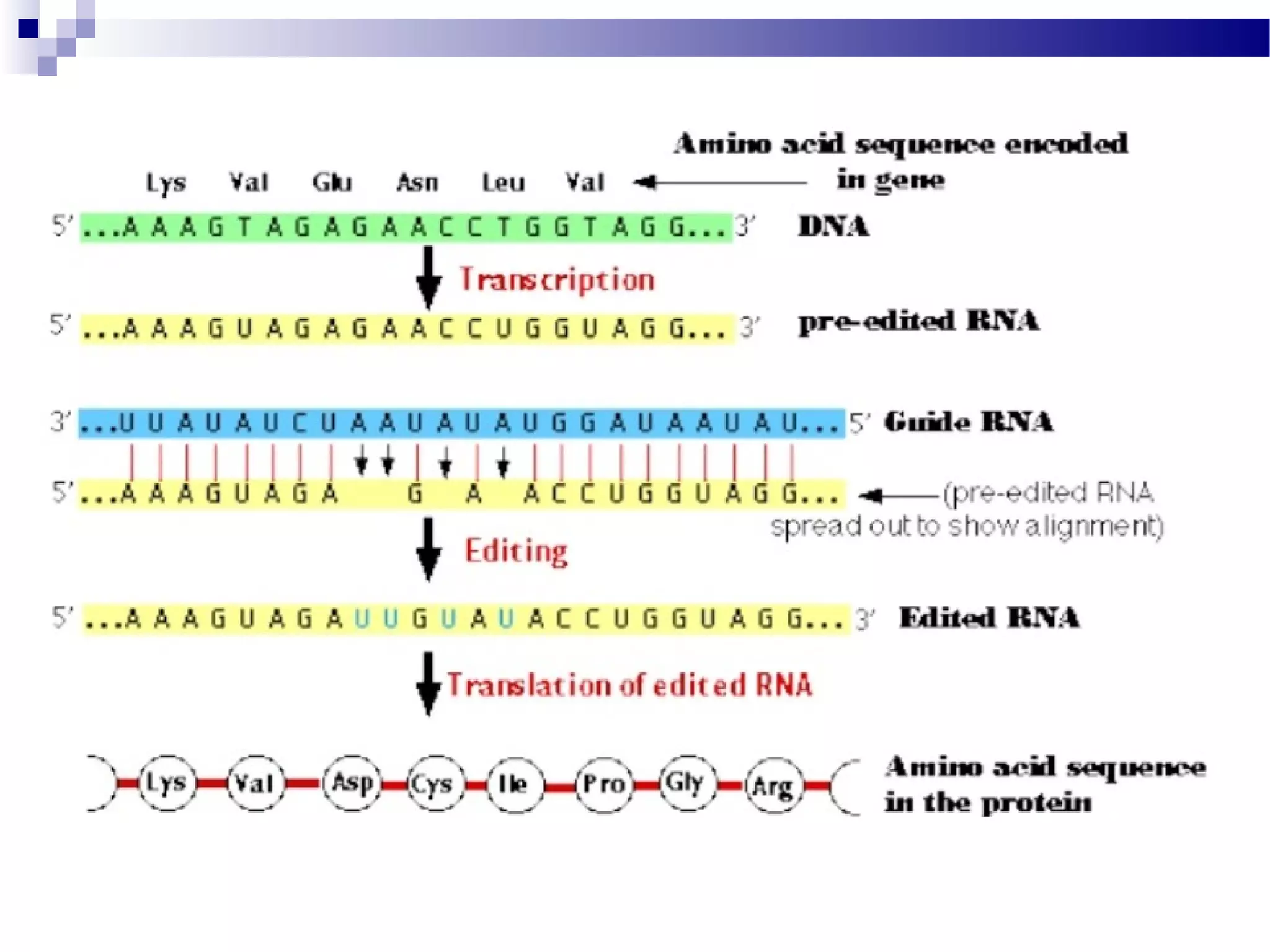
DNA is transcribed into RNA through the process of transcription. In eukaryotes, transcription is initiated when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter region near a gene. It then elongates the RNA molecule using the DNA as a template. Transcription ends when the polymerase reaches a termination sequence. The primary RNA transcript often undergoes processing like splicing, capping, polyadenylation, and editing to become a functional mRNA, tRNA, or rRNA molecule. These post-transcriptional modifications are required for gene expression.