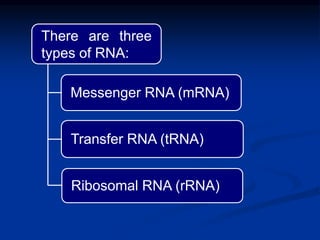
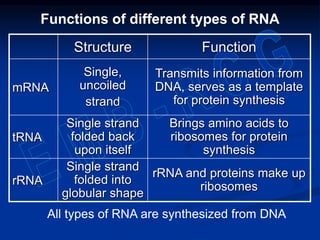
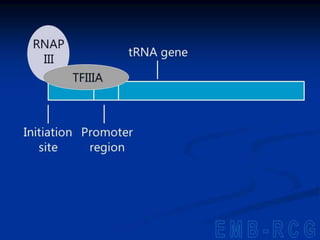
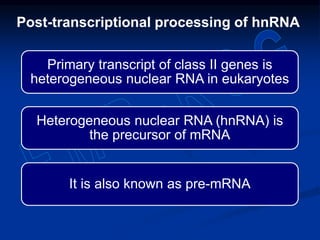
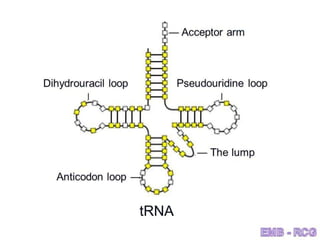
1. DNA contains genes that encode the information for synthesizing proteins. The genes contain base sequences that are transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA), which then directs protein synthesis.
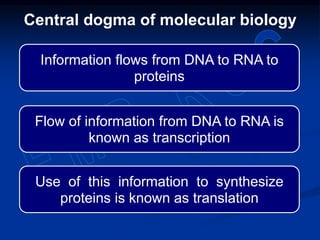
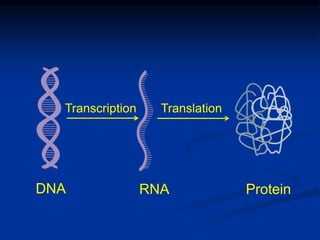
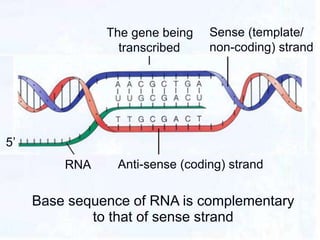
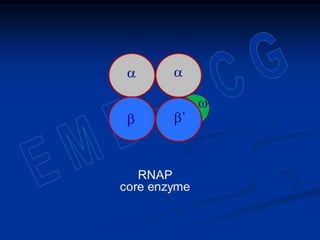
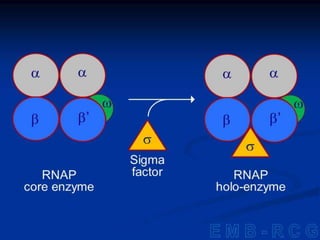
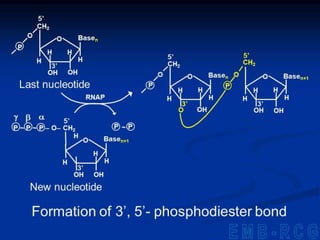
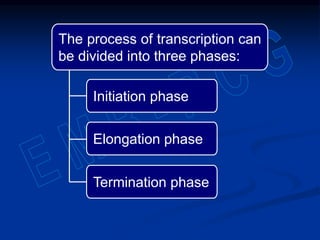
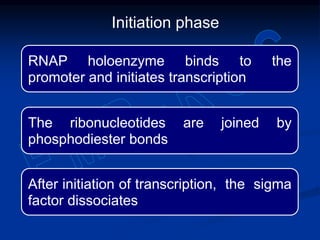
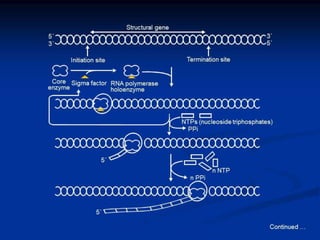
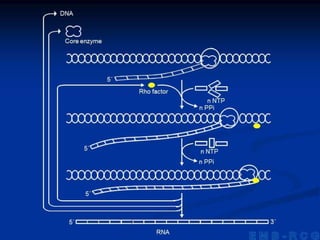
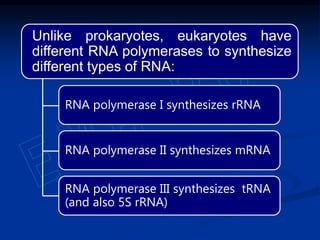
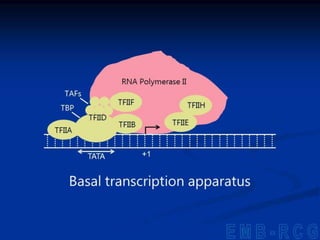
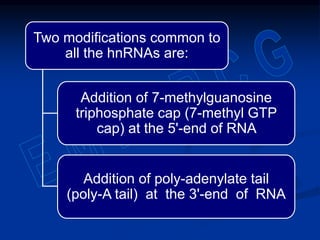
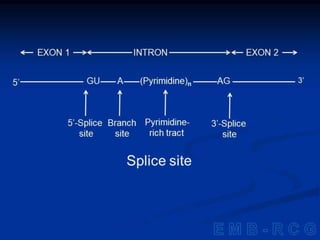
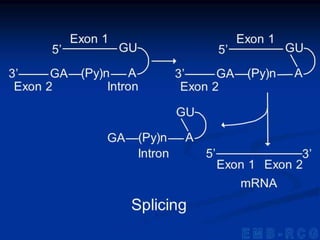
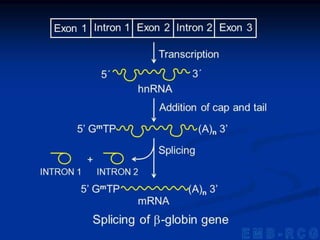
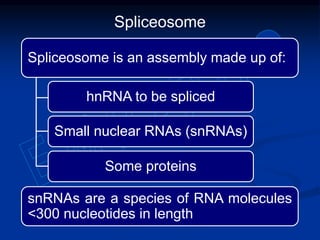
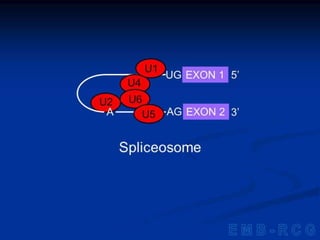
2. During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to promoter regions on DNA and synthesizes mRNA complementary to the template DNA strand. The mRNA is then processed and modified before being translated into protein.
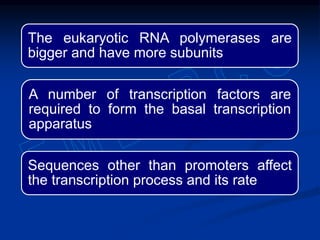
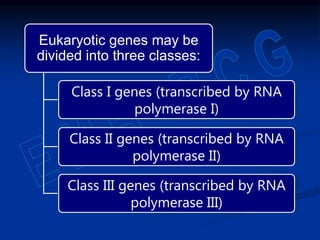
3. Transcription is regulated through control regions in DNA that bind transcription factors, inducing or repressing transcription depending on the factor. This regulates the expression of genes and allows control of protein synthesis.