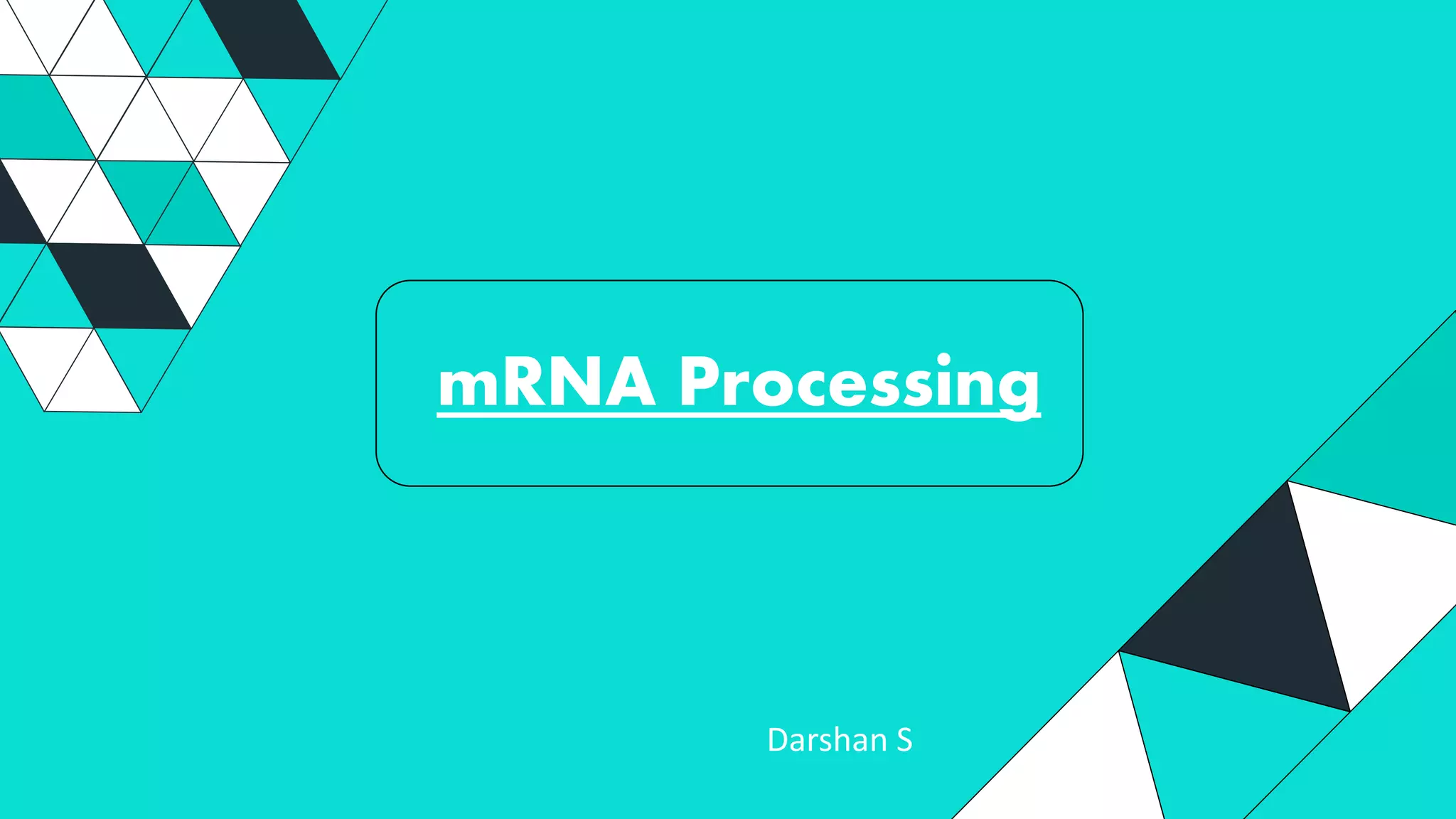
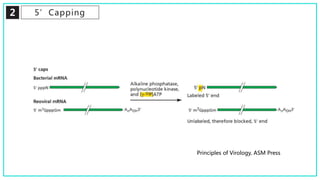
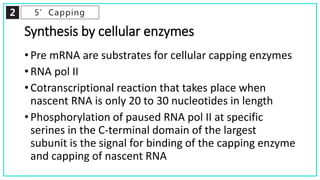
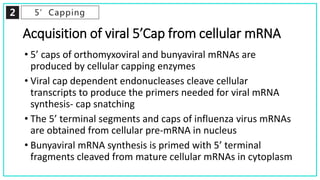
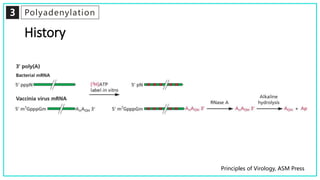
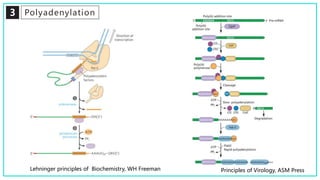
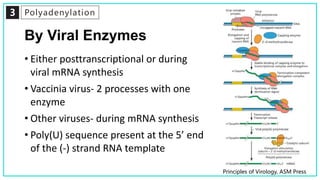
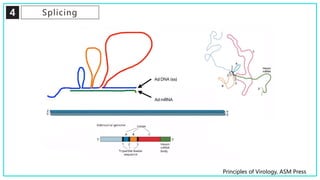
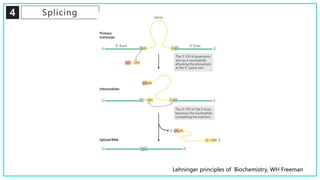
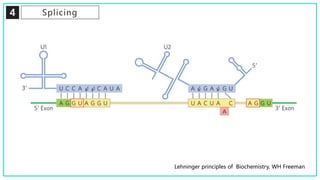
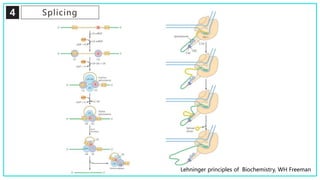
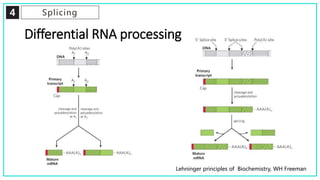
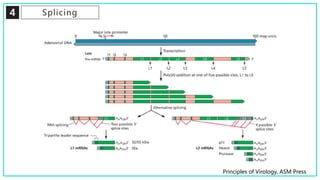
mRNA processing involves several key steps after transcription. These include 5' capping, which protects mRNA from degradation and aids in translation. Polyadenylation adds a poly-A tail to the 3' end, increasing stability and translation efficiency. Splicing removes non-coding introns and joins exons, which can produce different mRNAs and proteins from the same initial transcript. These processing steps are carried out by cellular enzymes for most eukaryotic mRNAs, but some viruses encode their own enzymes or acquire cellular mRNA caps to modify their own transcripts.