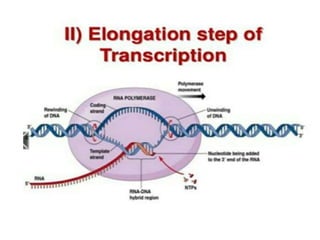
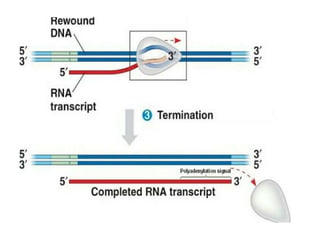
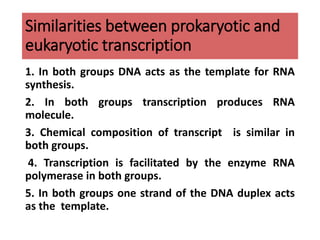
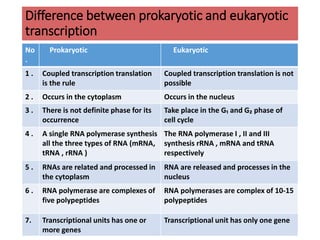
This document discusses transcription in eukaryotes. It begins with definitions of transcription and describes the basic process of RNA being synthesized from a DNA template. It then covers the mechanisms of transcription, including initiation involving RNA polymerase and transcription factors, elongation, and termination. The key similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription are that DNA acts as a template and RNA polymerase facilitates RNA synthesis. Key differences are that eukaryotic transcription occurs in the nucleus, is carried out by three classes of RNA polymerase, and RNAs are processed in the nucleus rather than the cytoplasm.