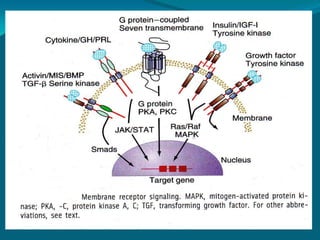
TGF-β signals from the cell membrane to the nucleus through SMAD proteins. Pathway-restricted SMADs are phosphorylated by cell surface receptors with kinase activity, then oligomerize with Smad4 and translocate to the nucleus to direct transcription in response to TGF-β. Inhibitory SMADs block the activation of pathway-restricted SMADs.