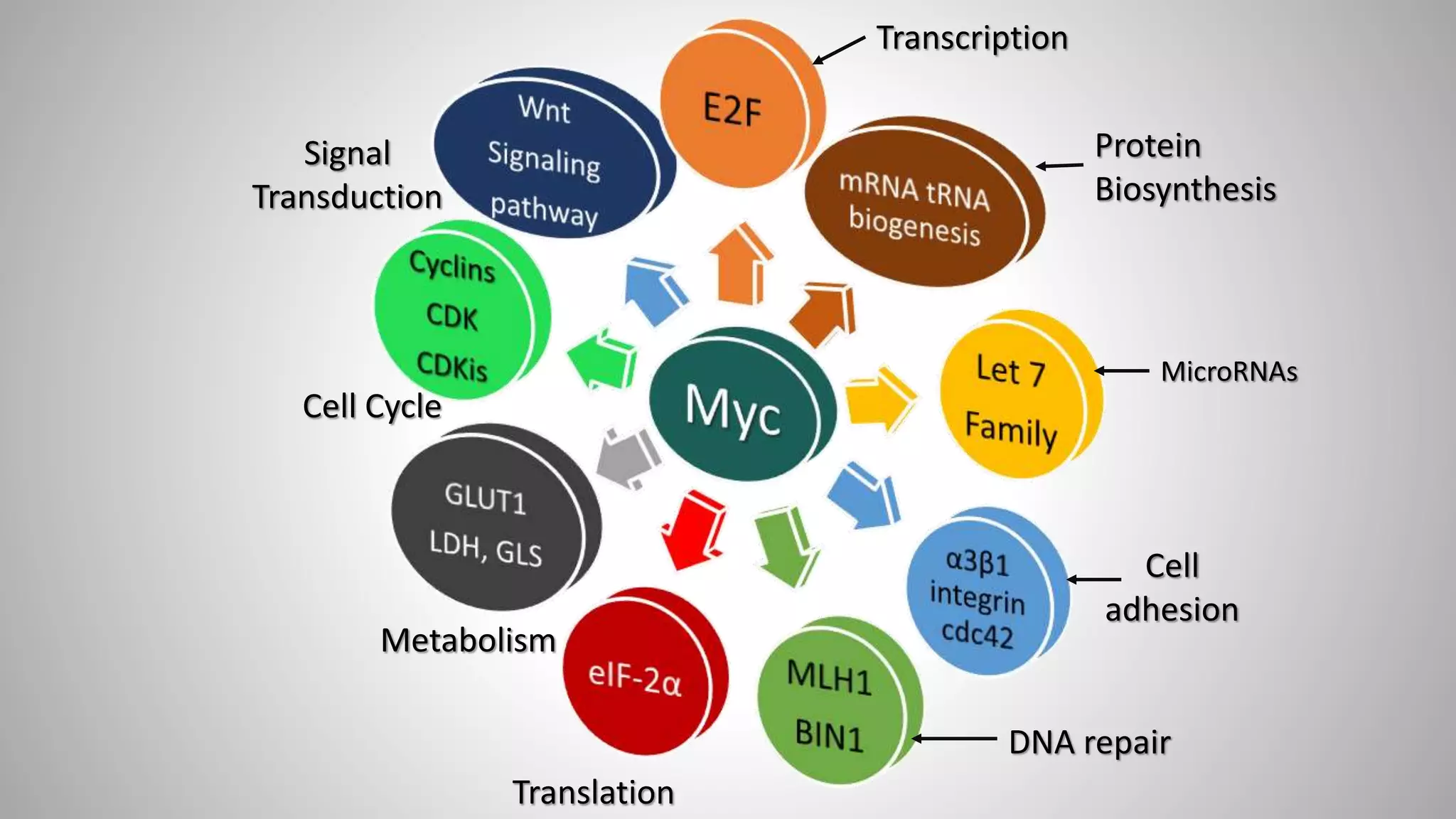
Proto-oncogenes are normal genes that can become oncogenes following mutations. They encode proteins involved in cell growth, proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis. Examples include HER2, Wnt, Myc, Ras and genes in the Ras signaling pathway. Mutations in proto-oncogenes convert them into oncogenes, driving uncontrolled cell growth and tumor development. Common mutations are point mutations, which result in overactive gene products by altering transcription or protein function. For example, point mutations in Ras genes are found in many cancers and keep the Ras protein constantly active.