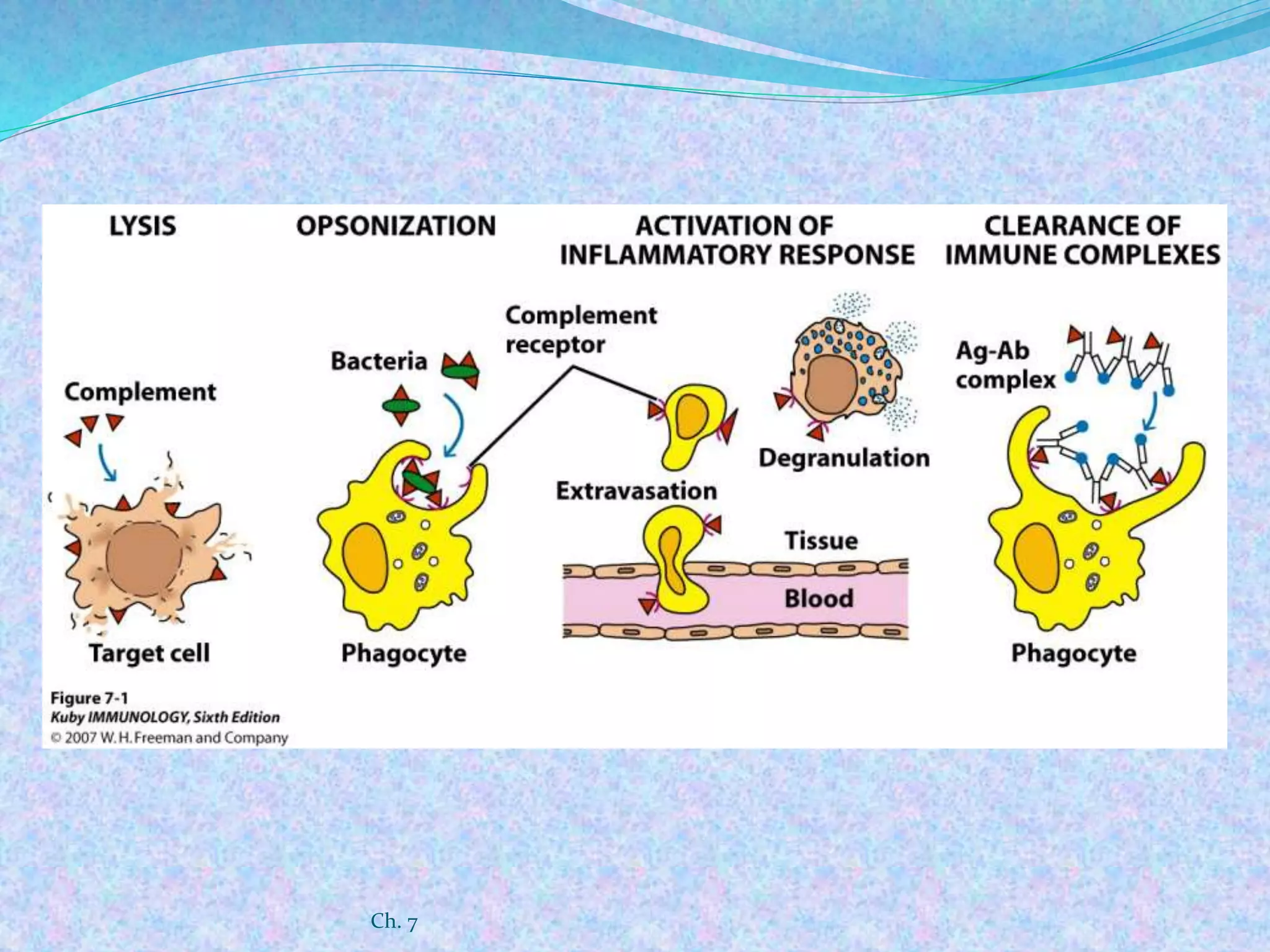
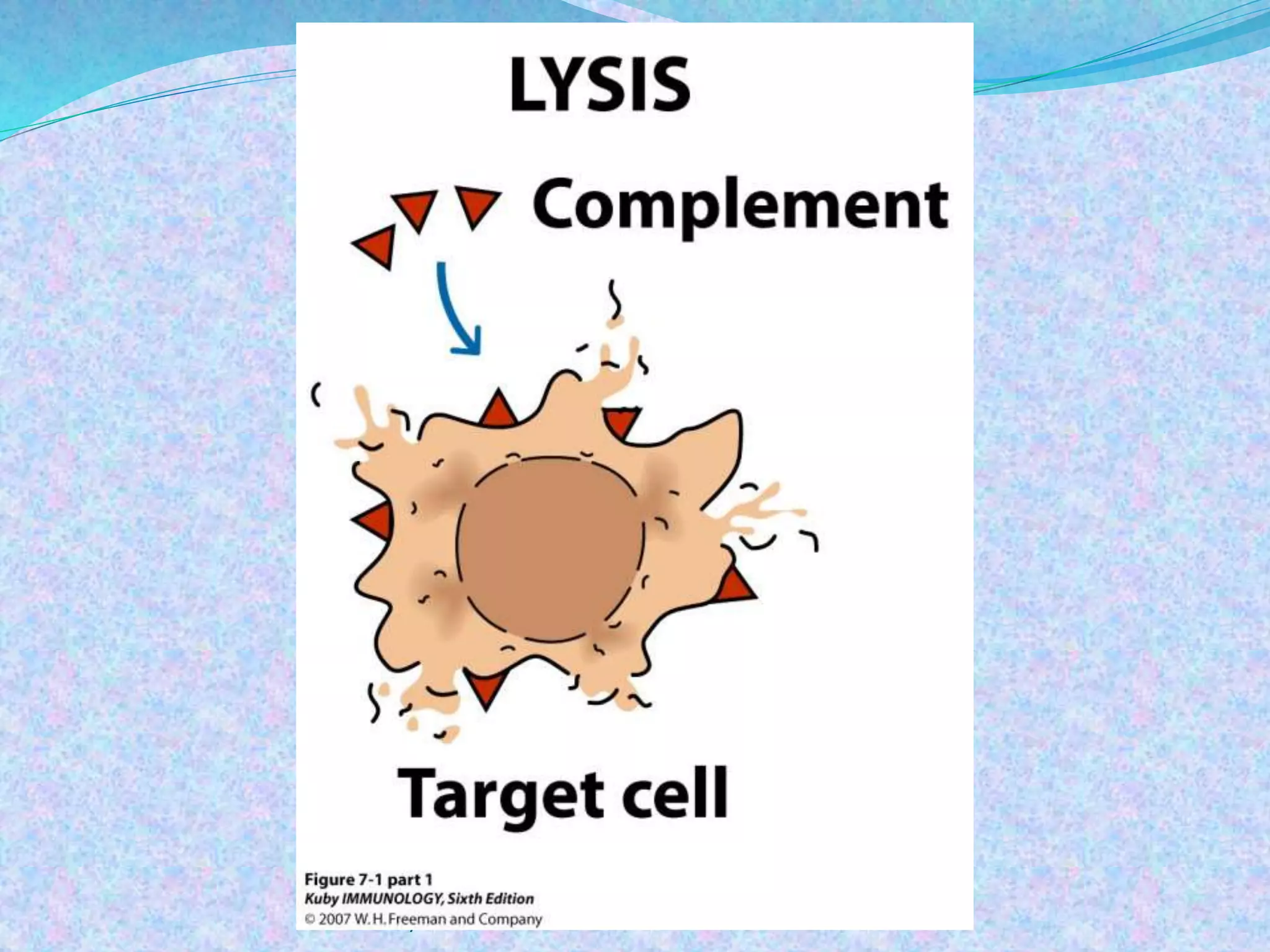
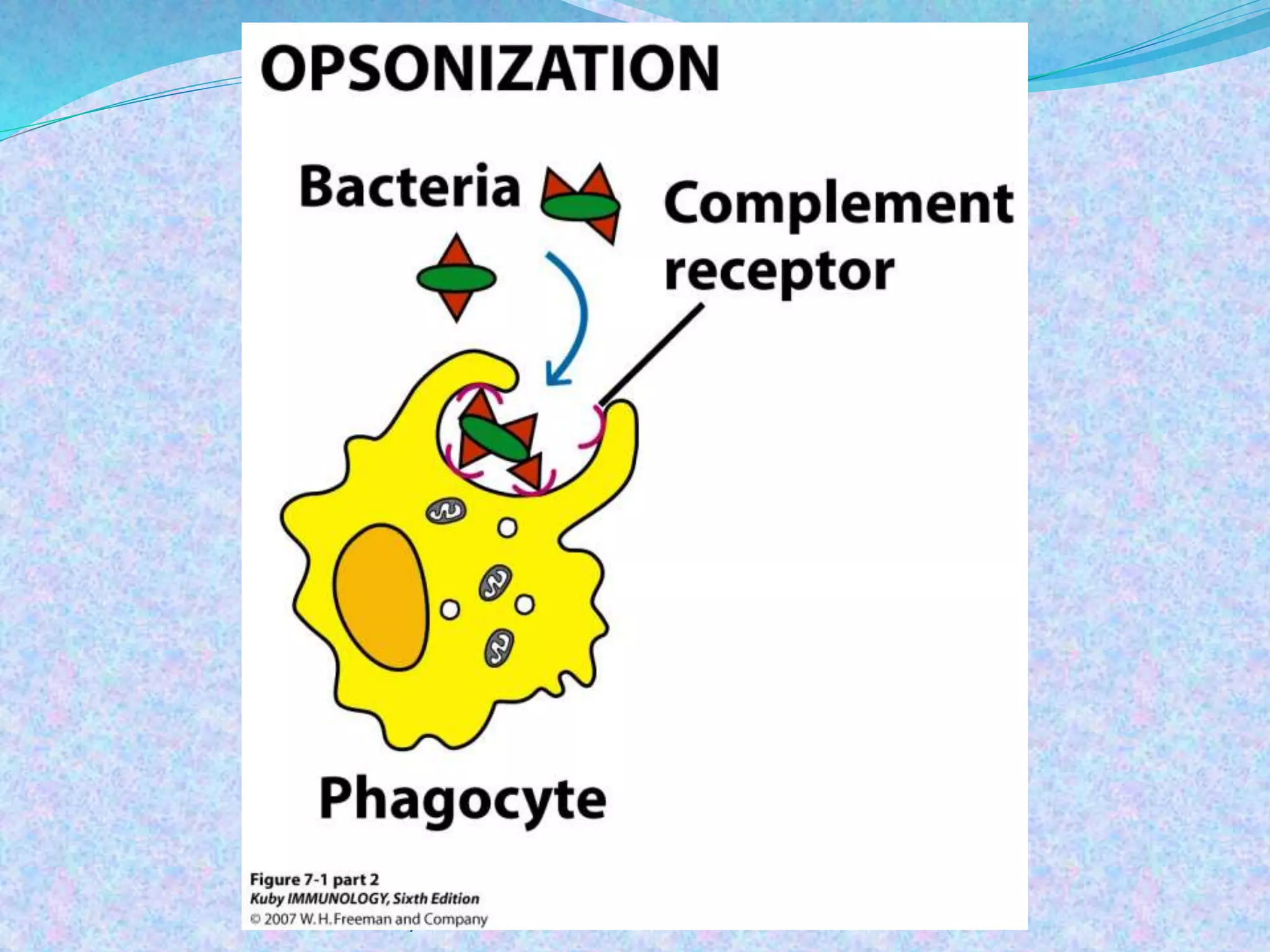
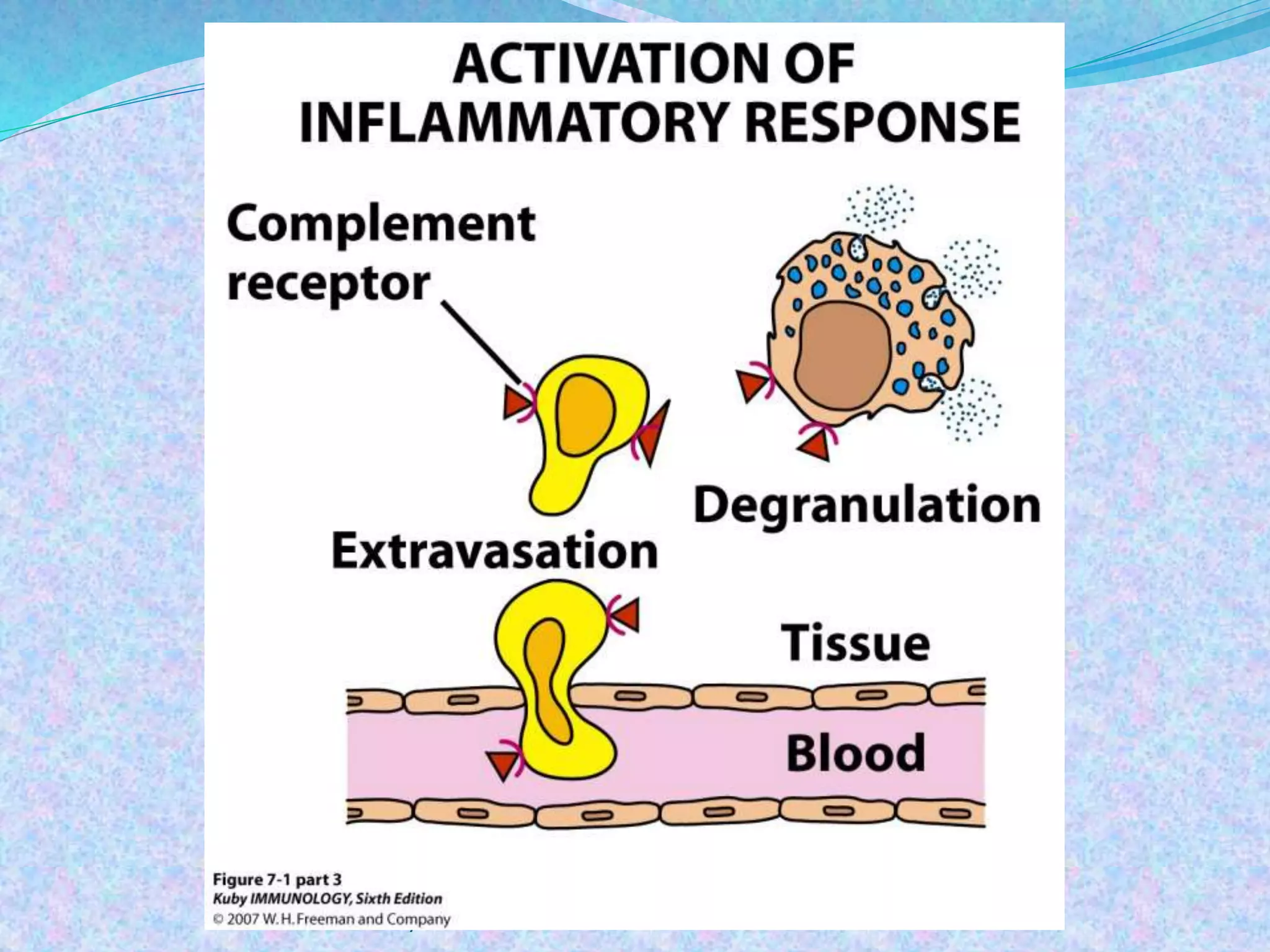
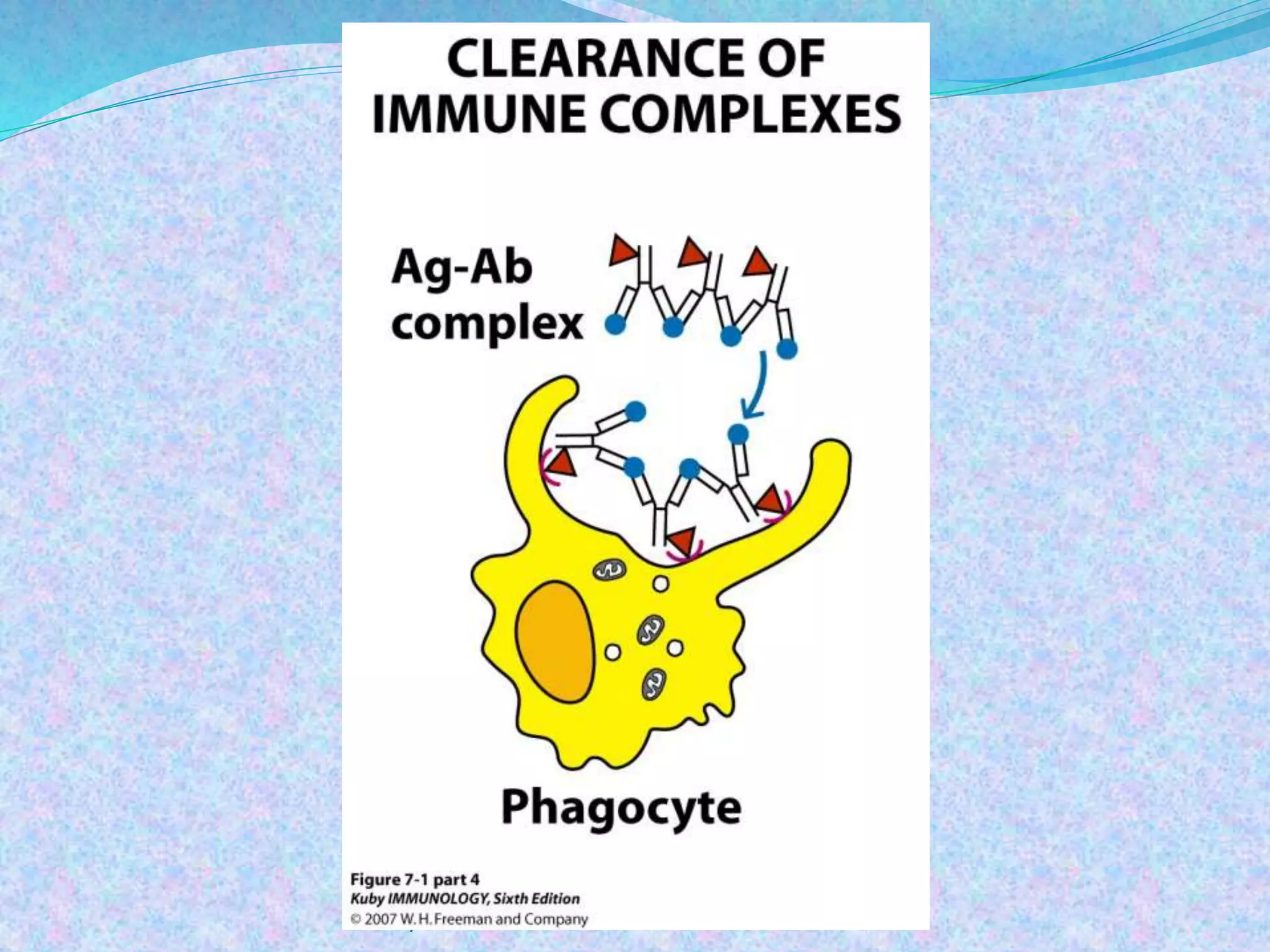
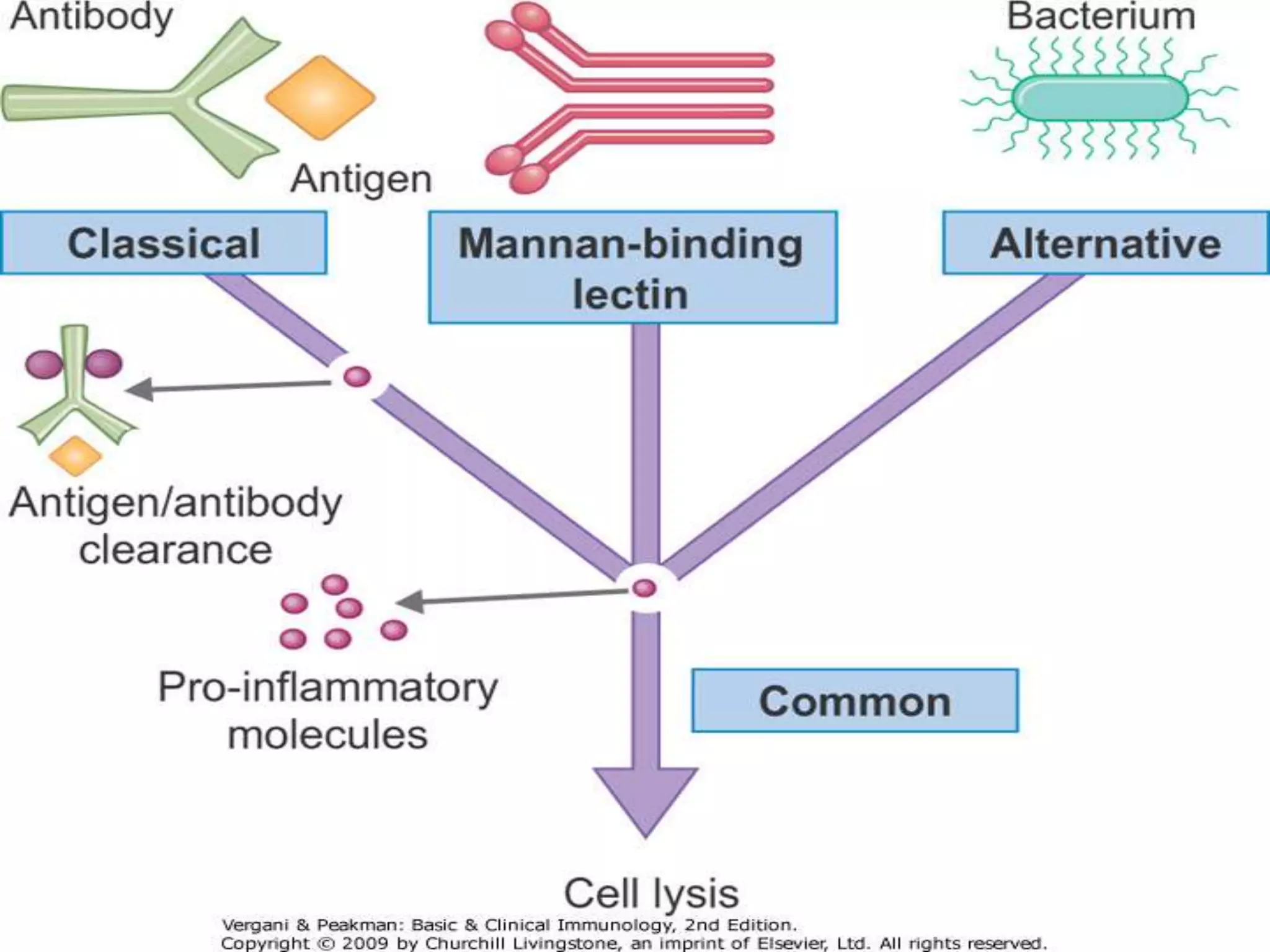
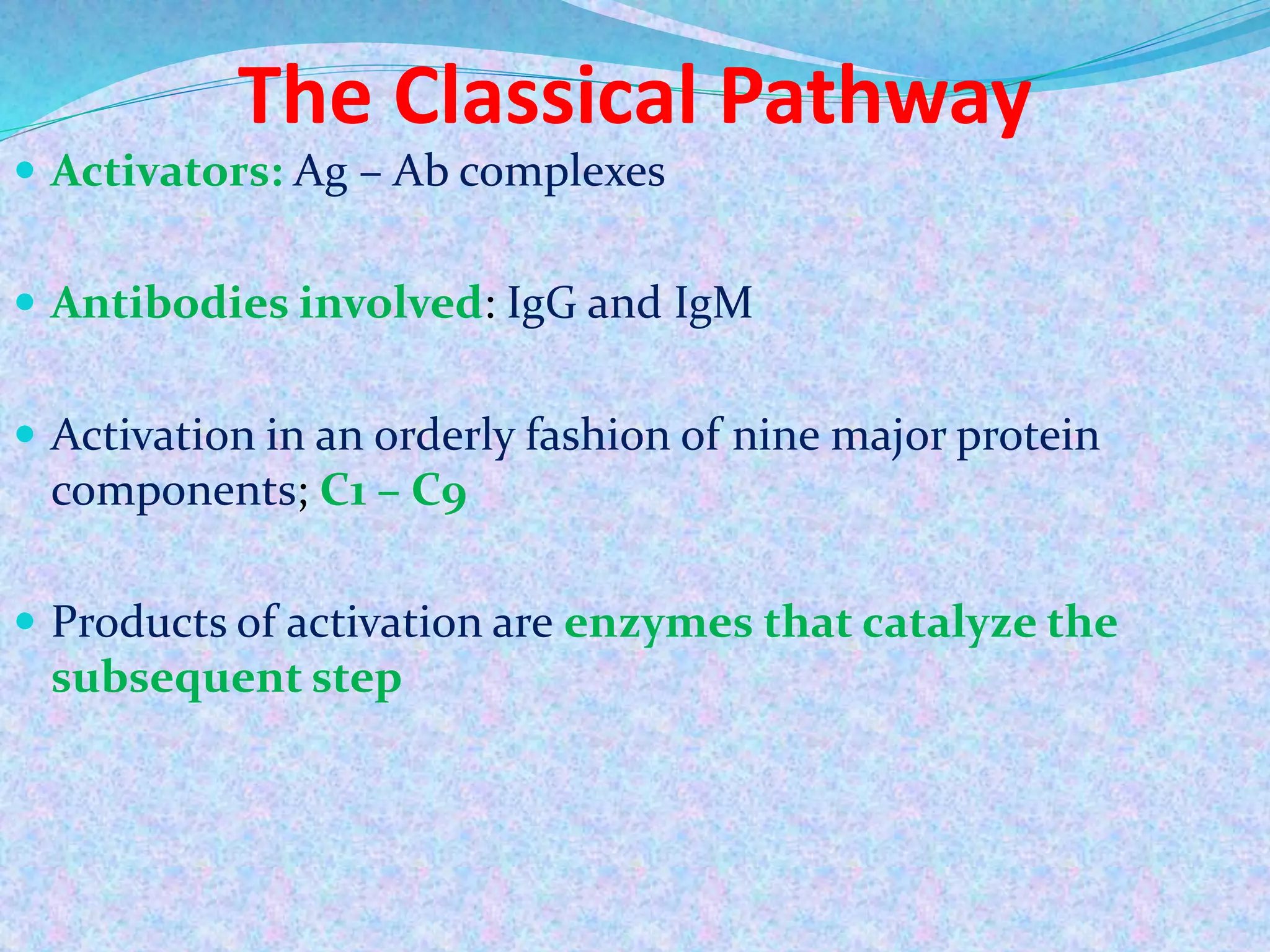
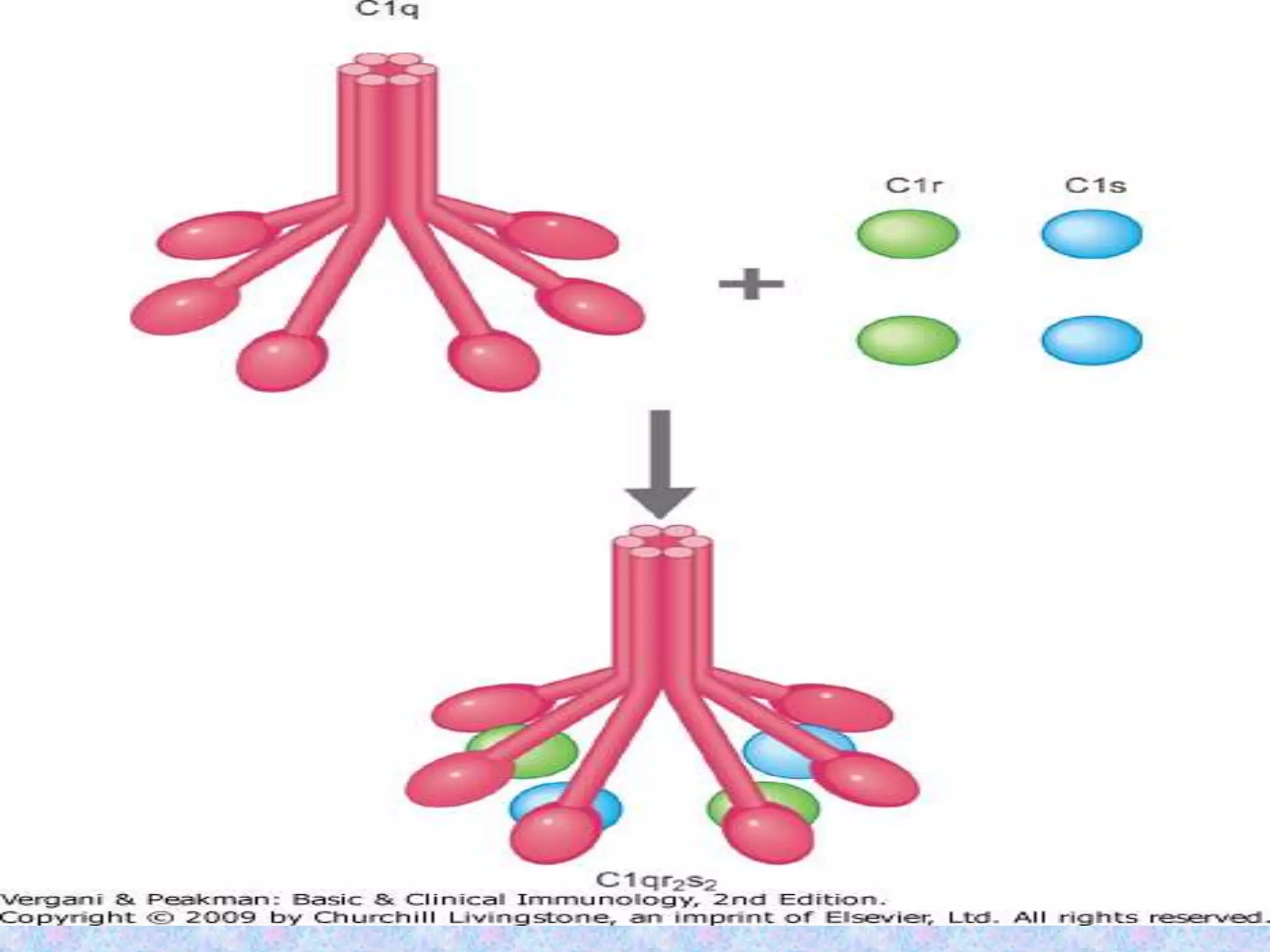
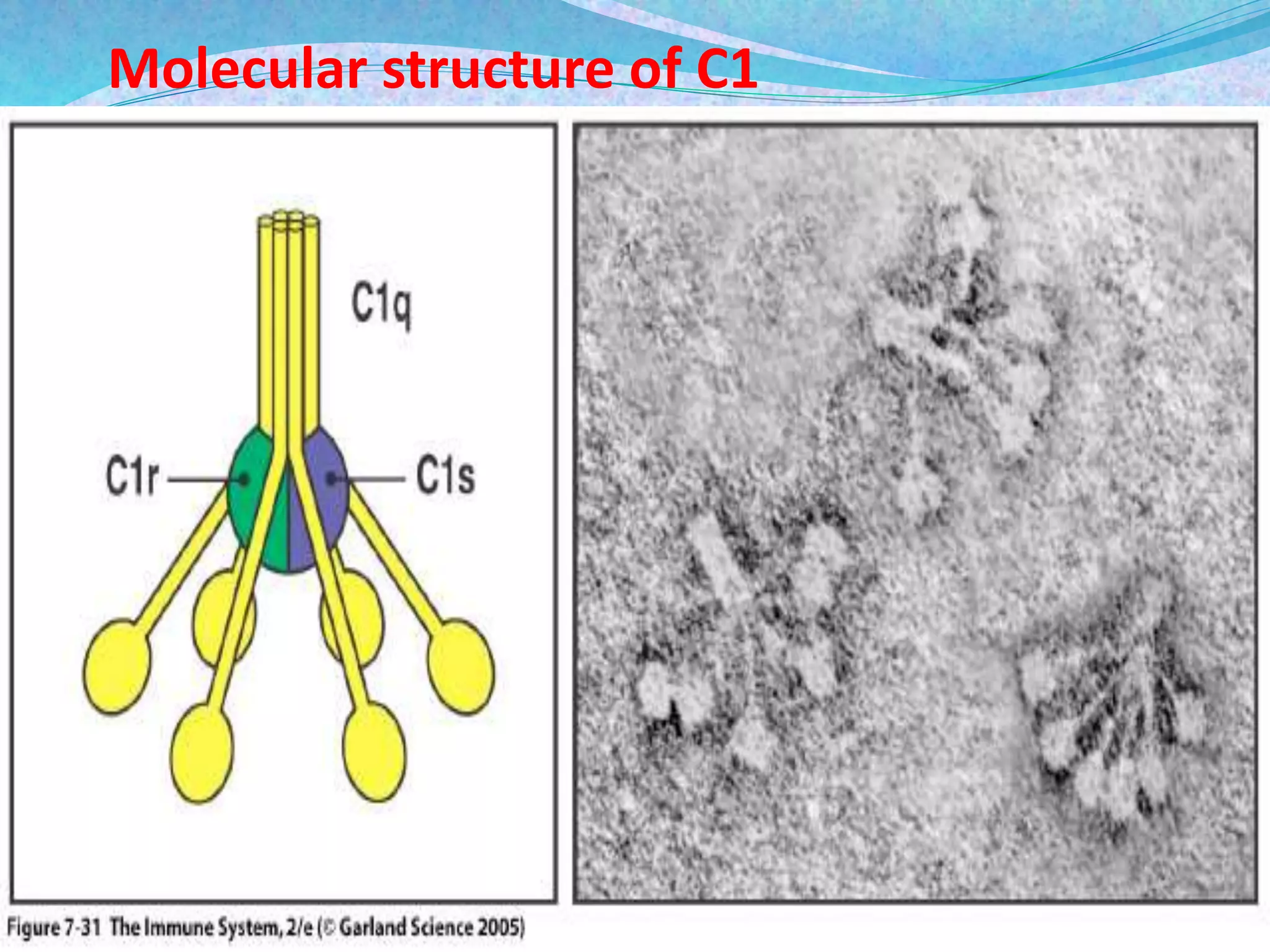
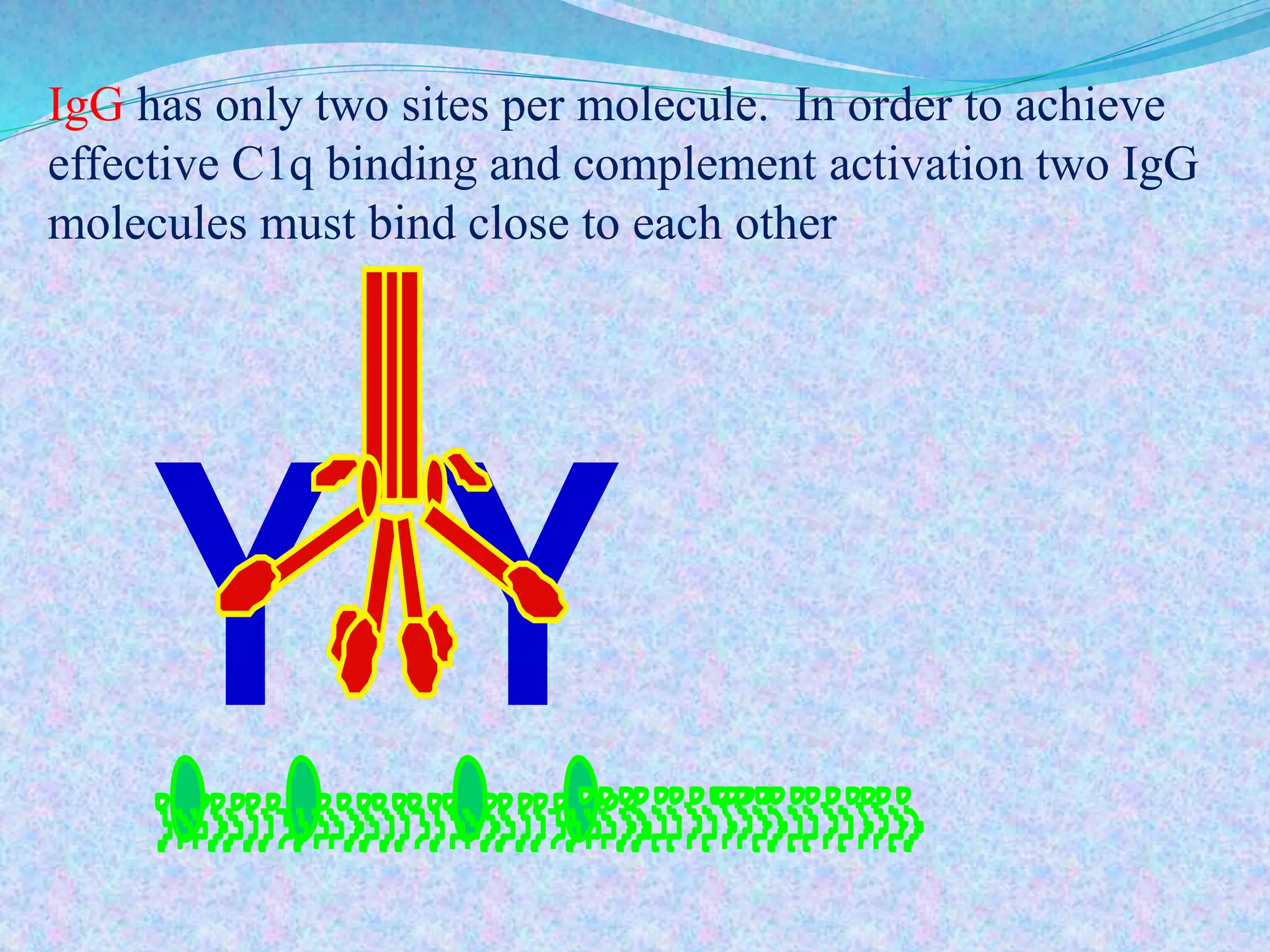
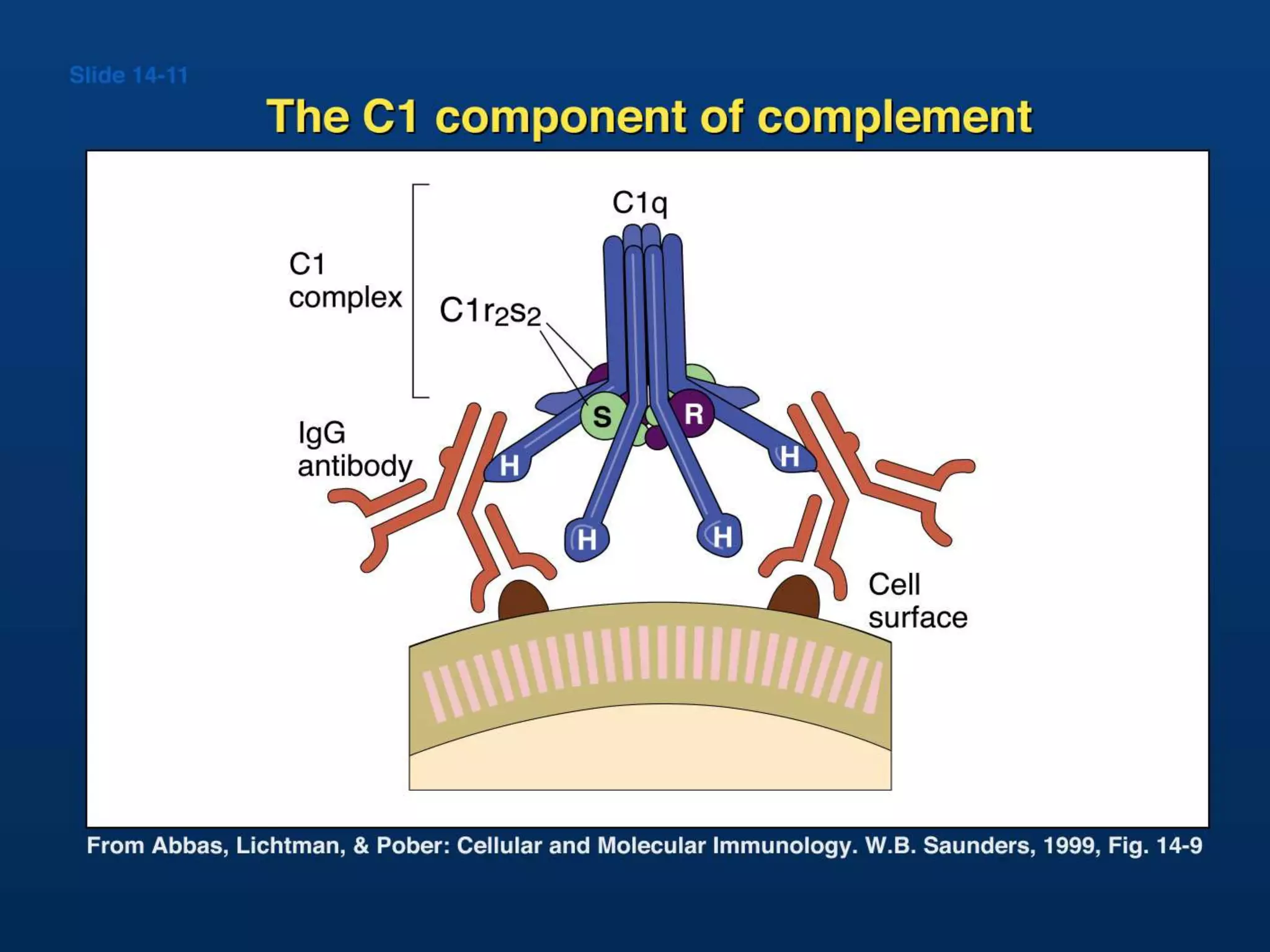
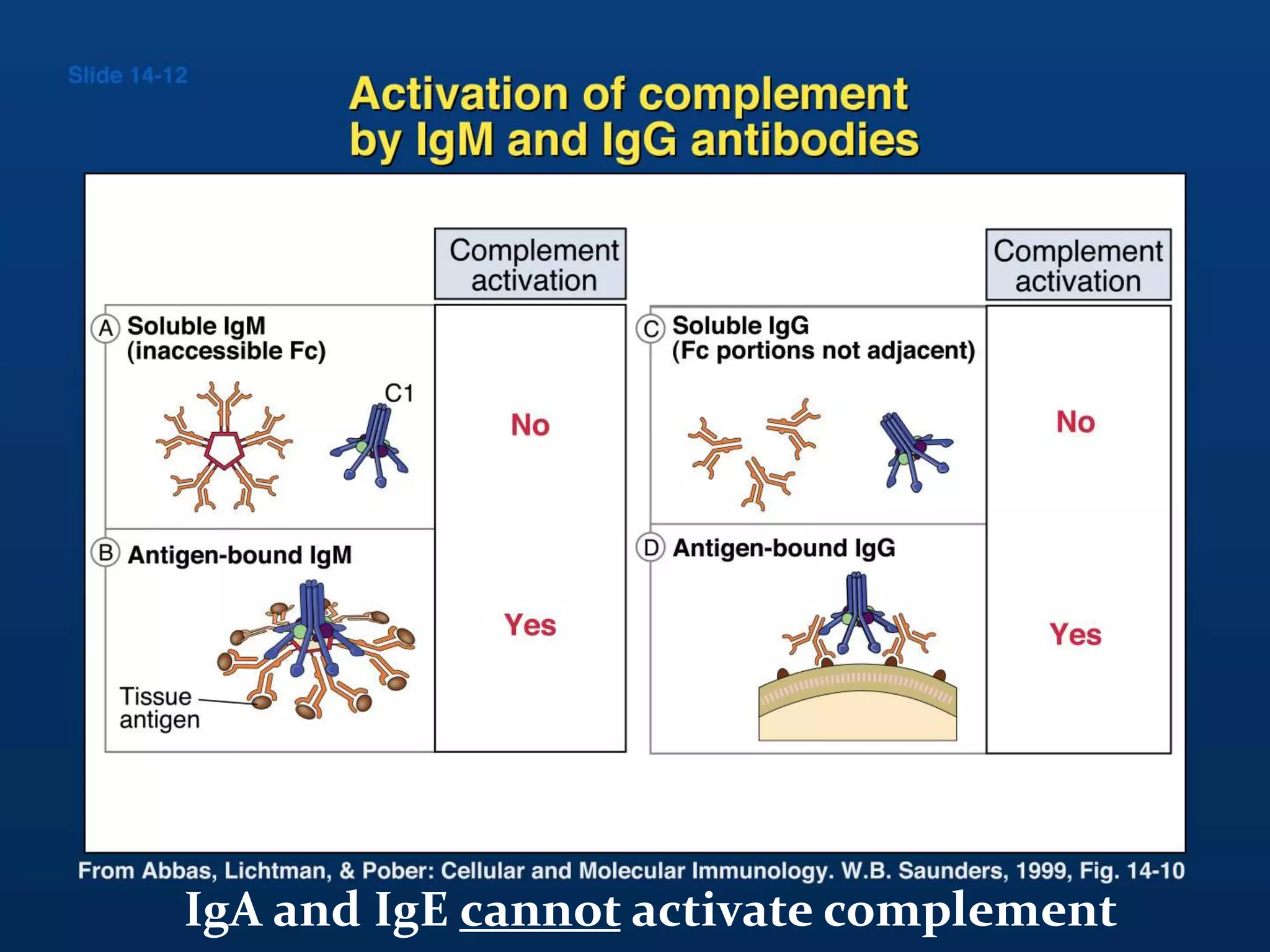
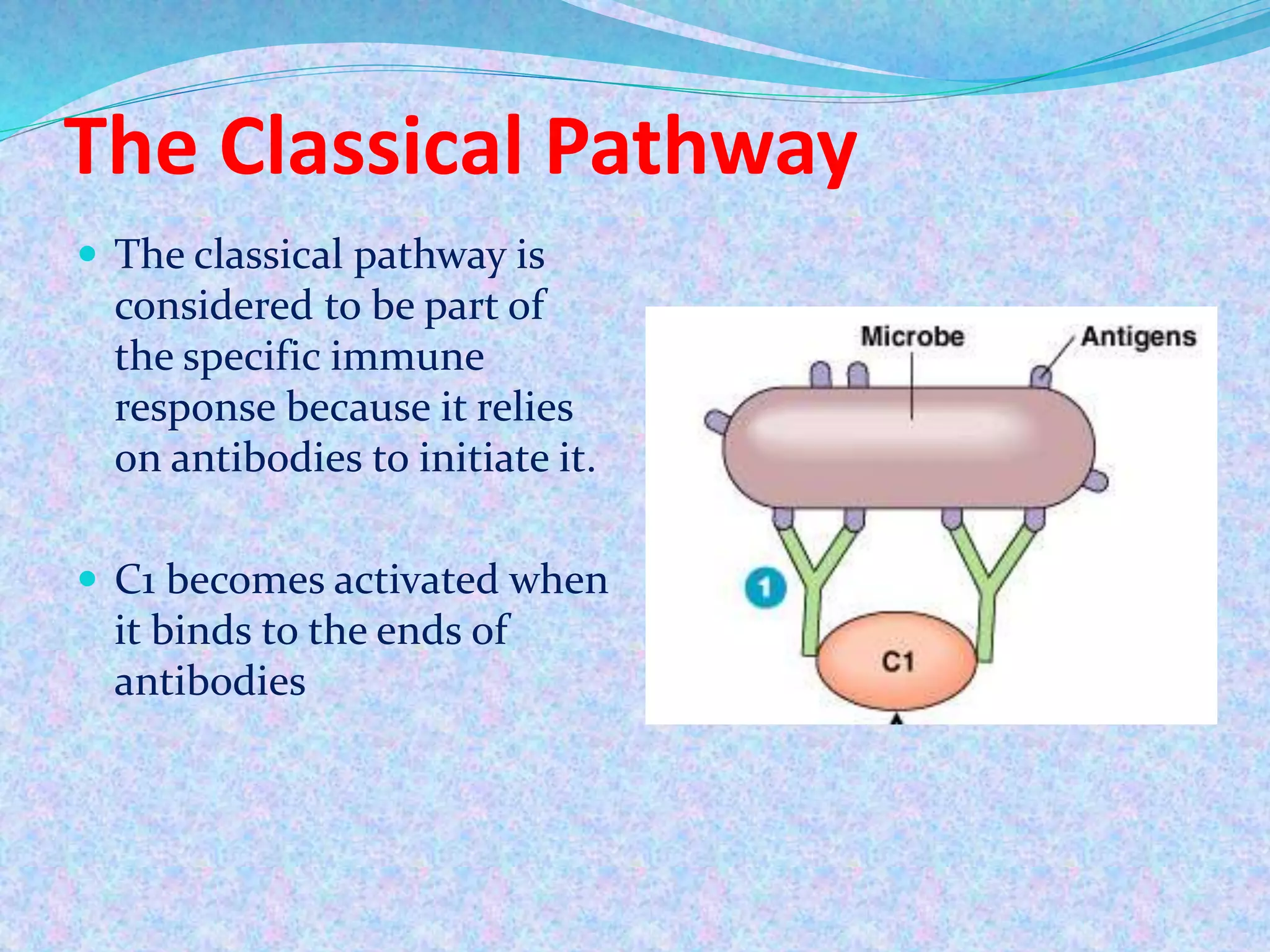
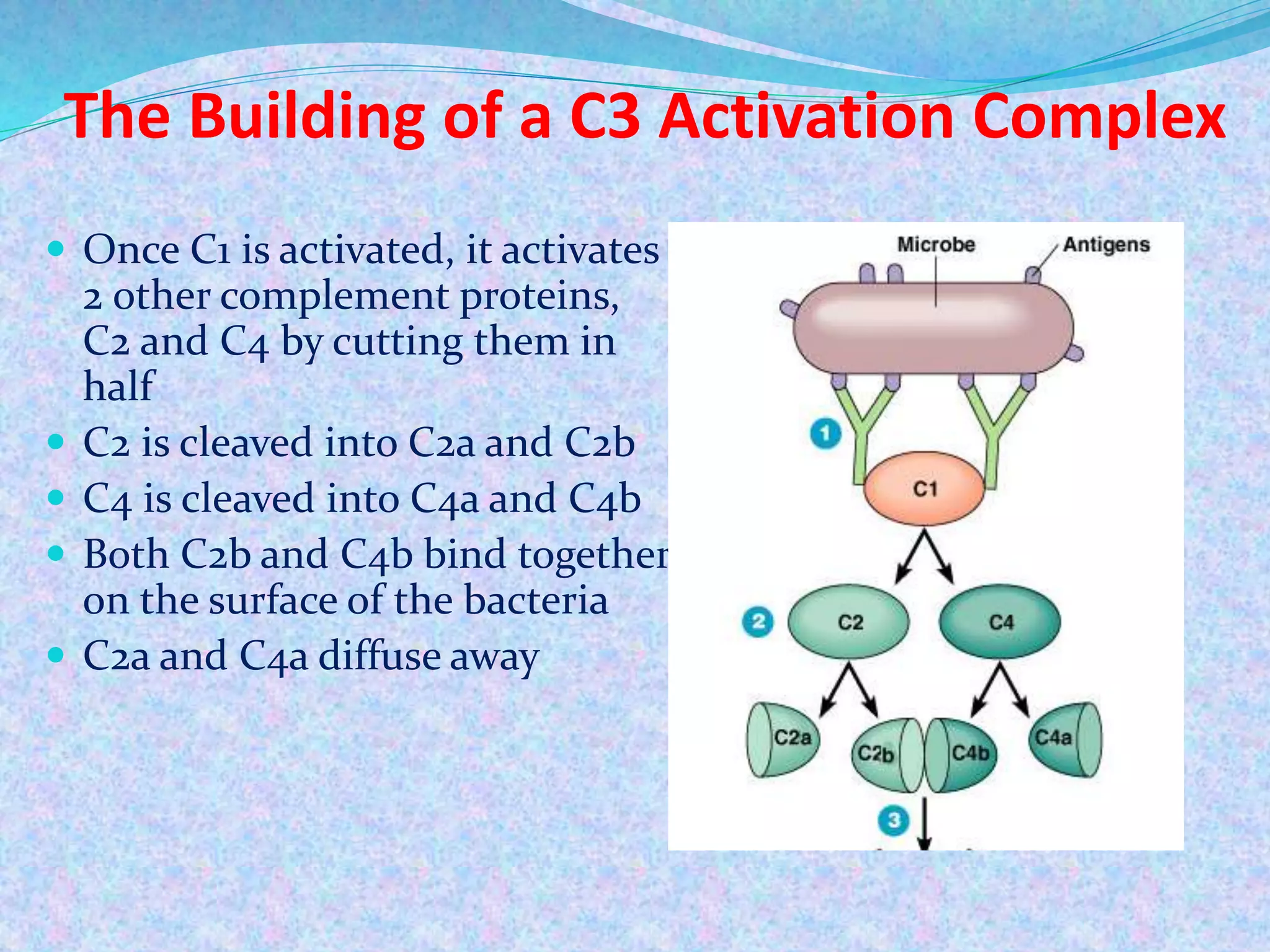
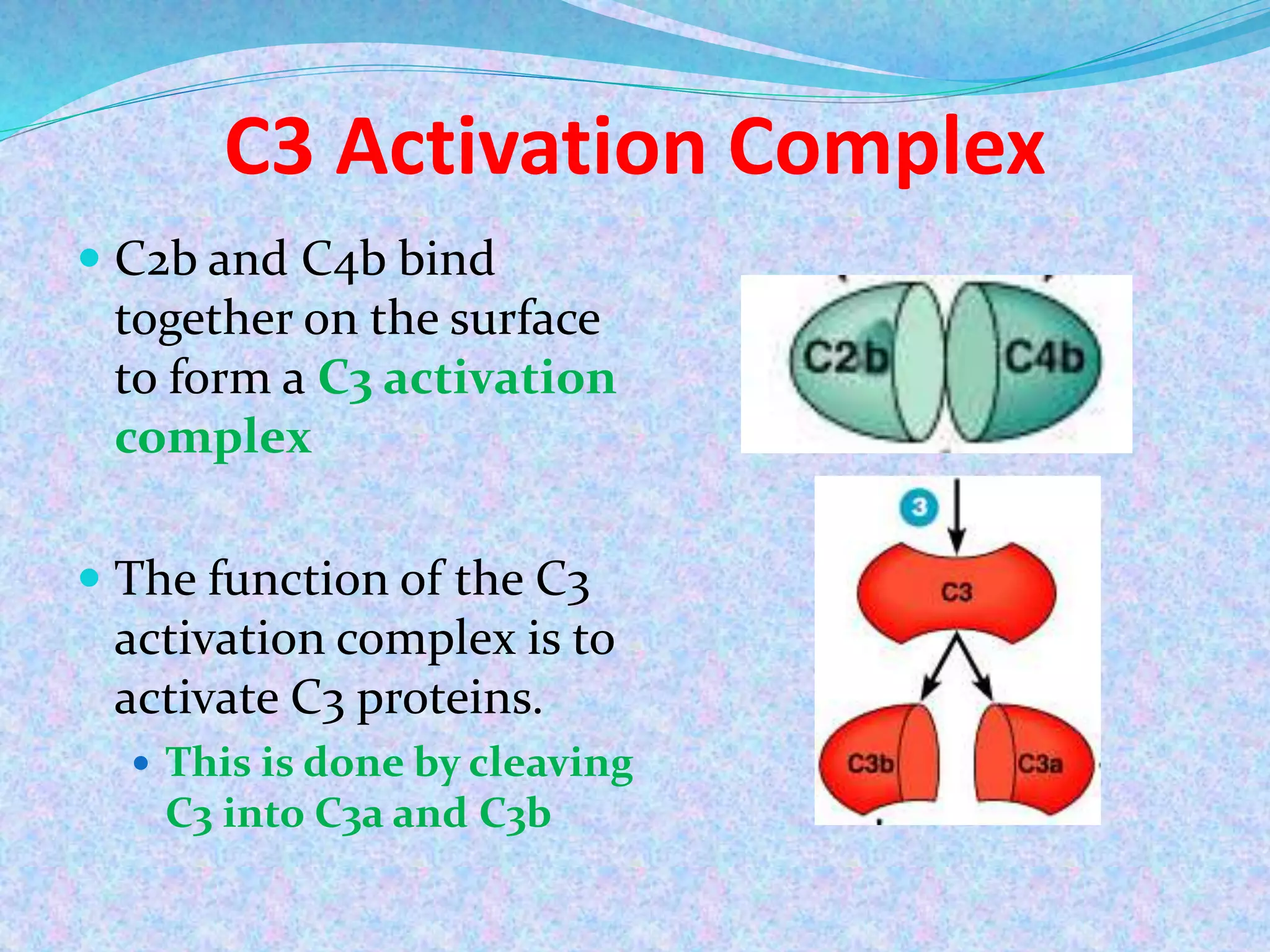
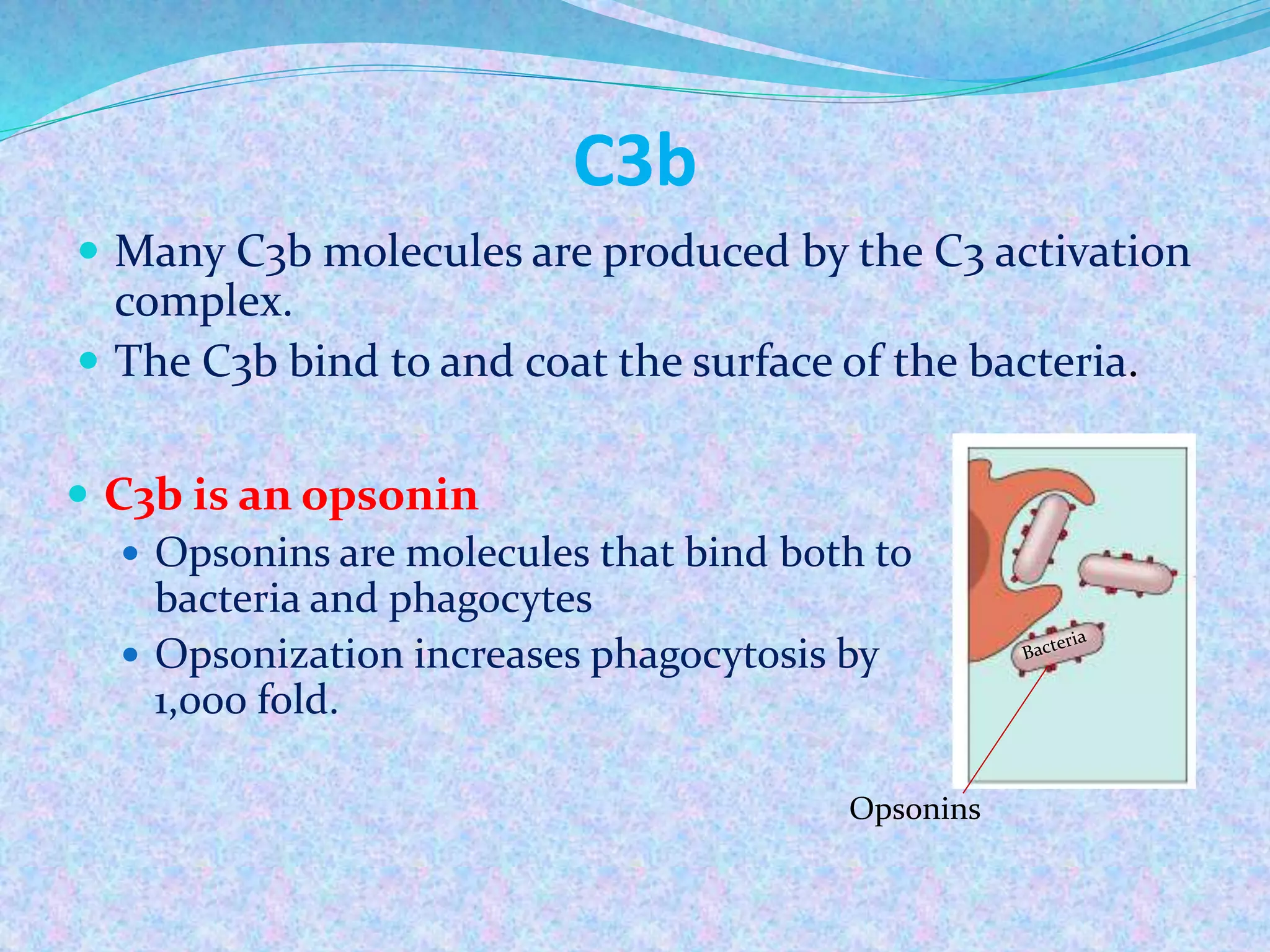
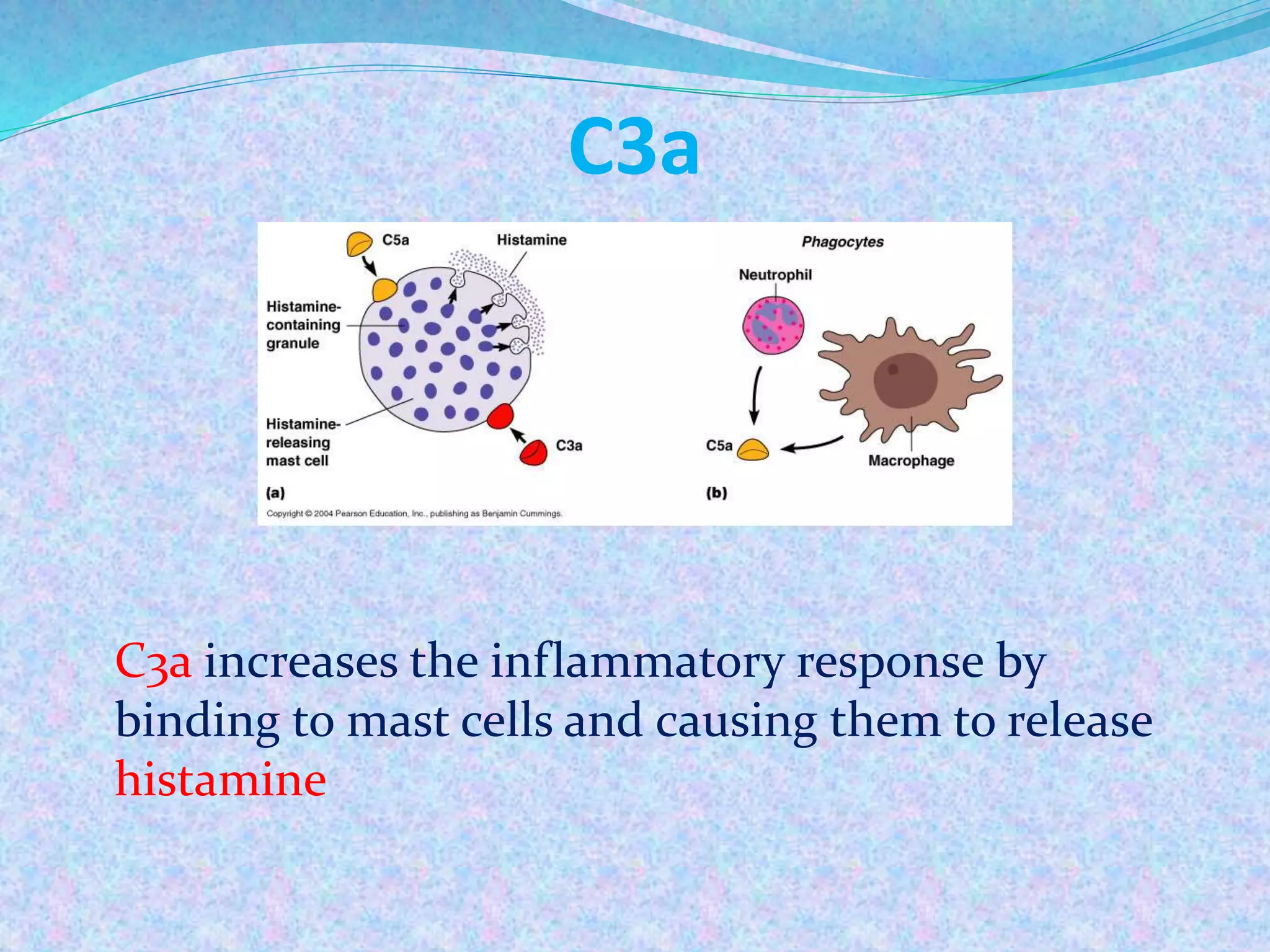
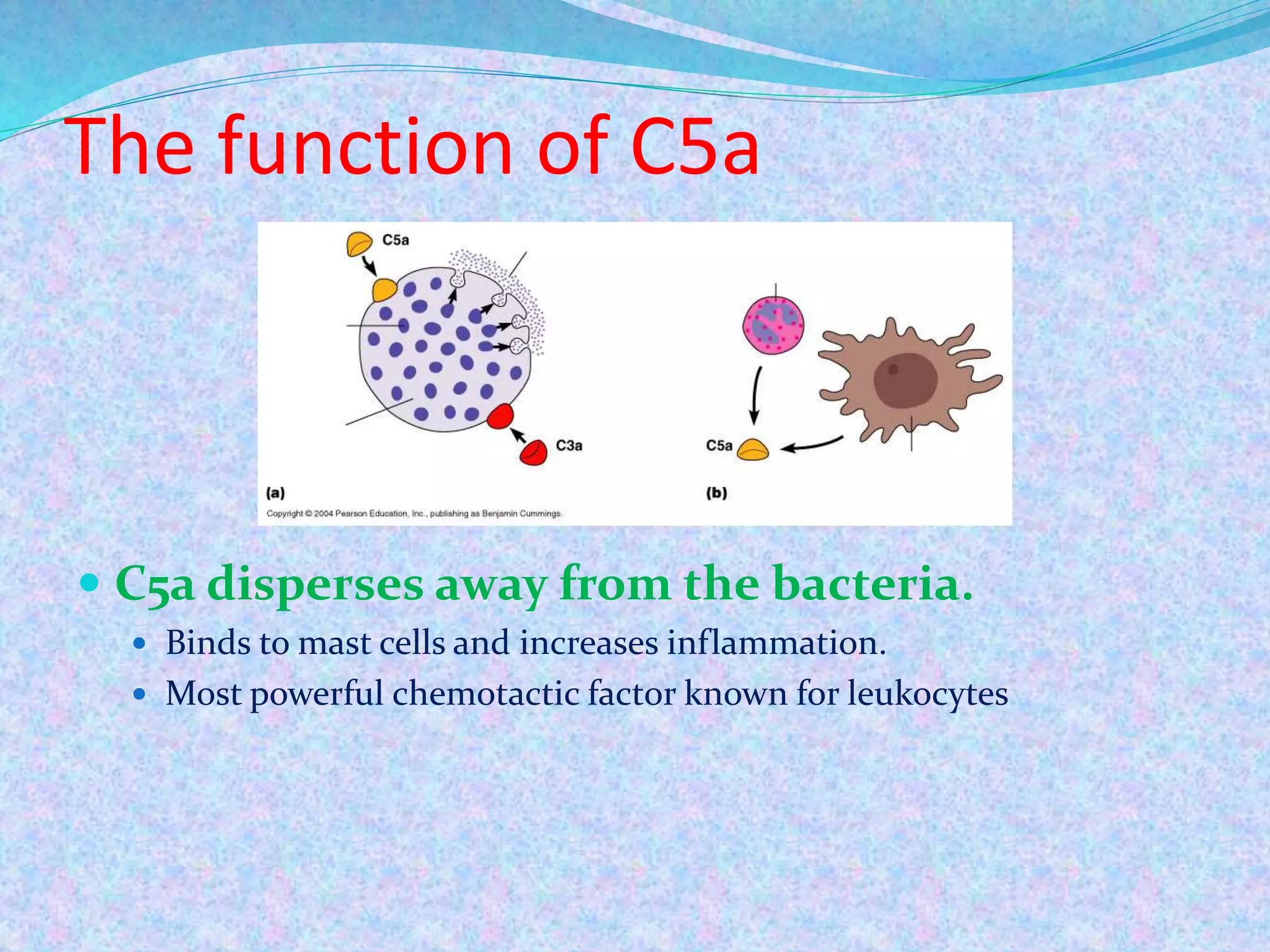
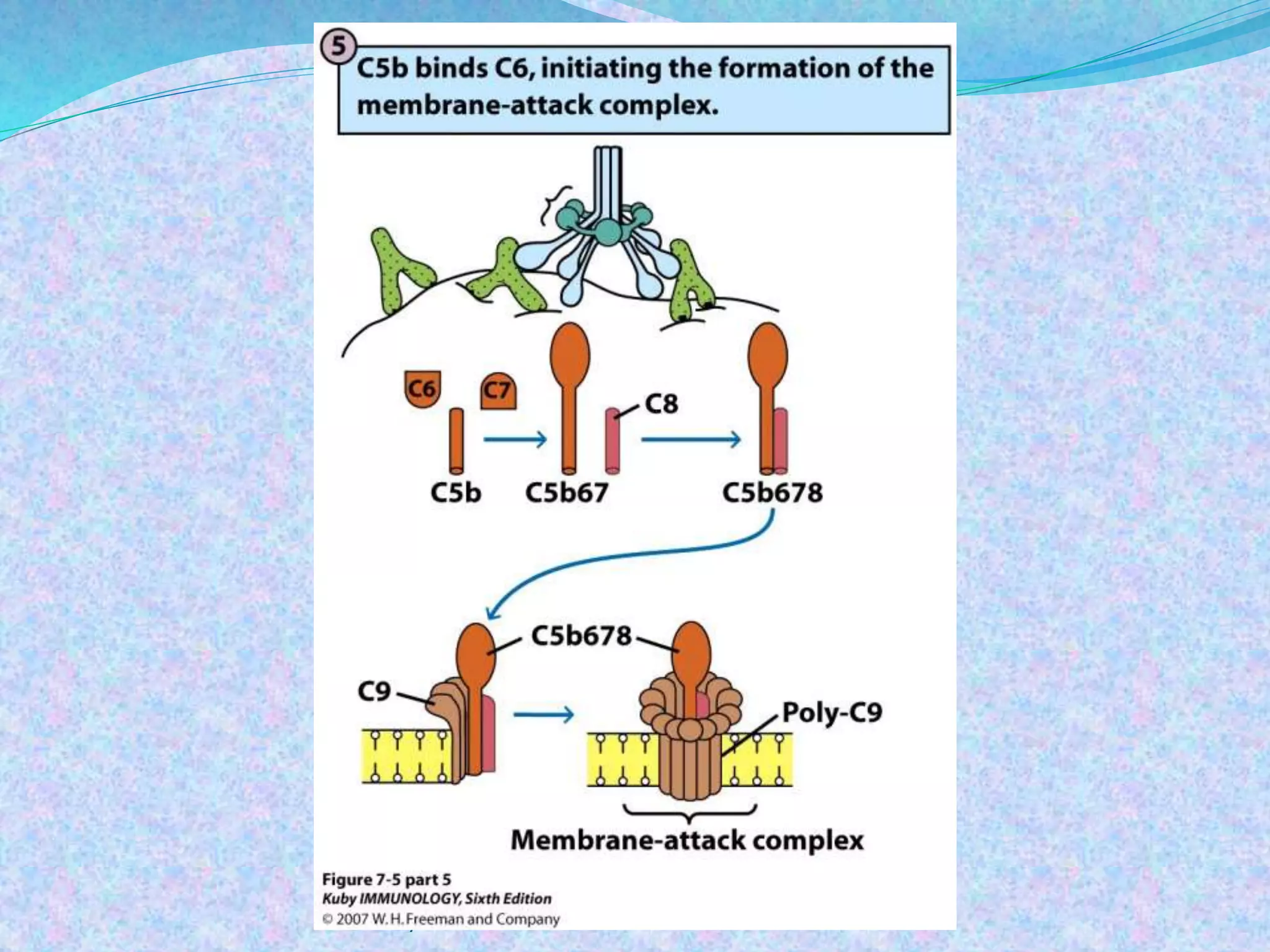
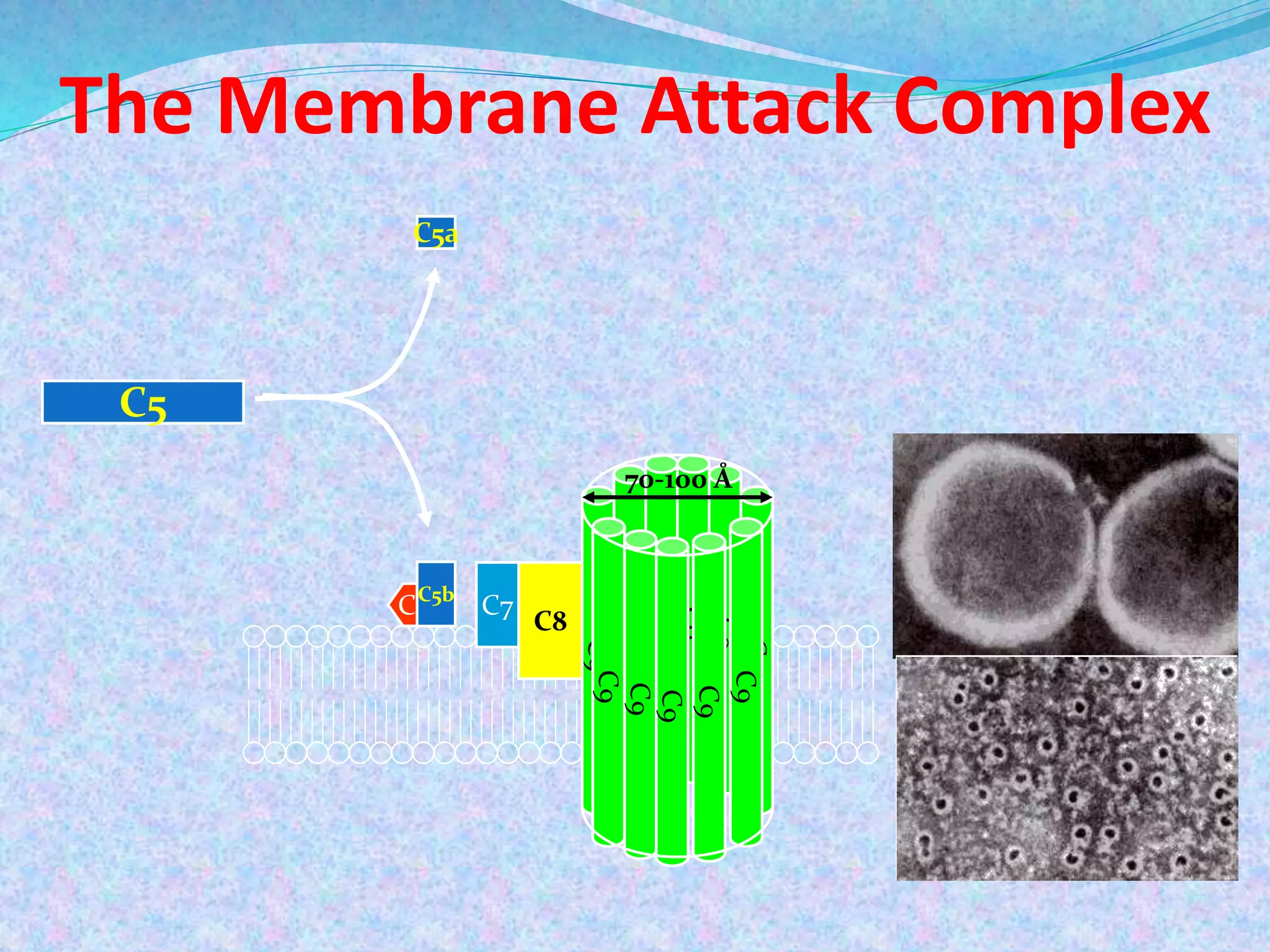
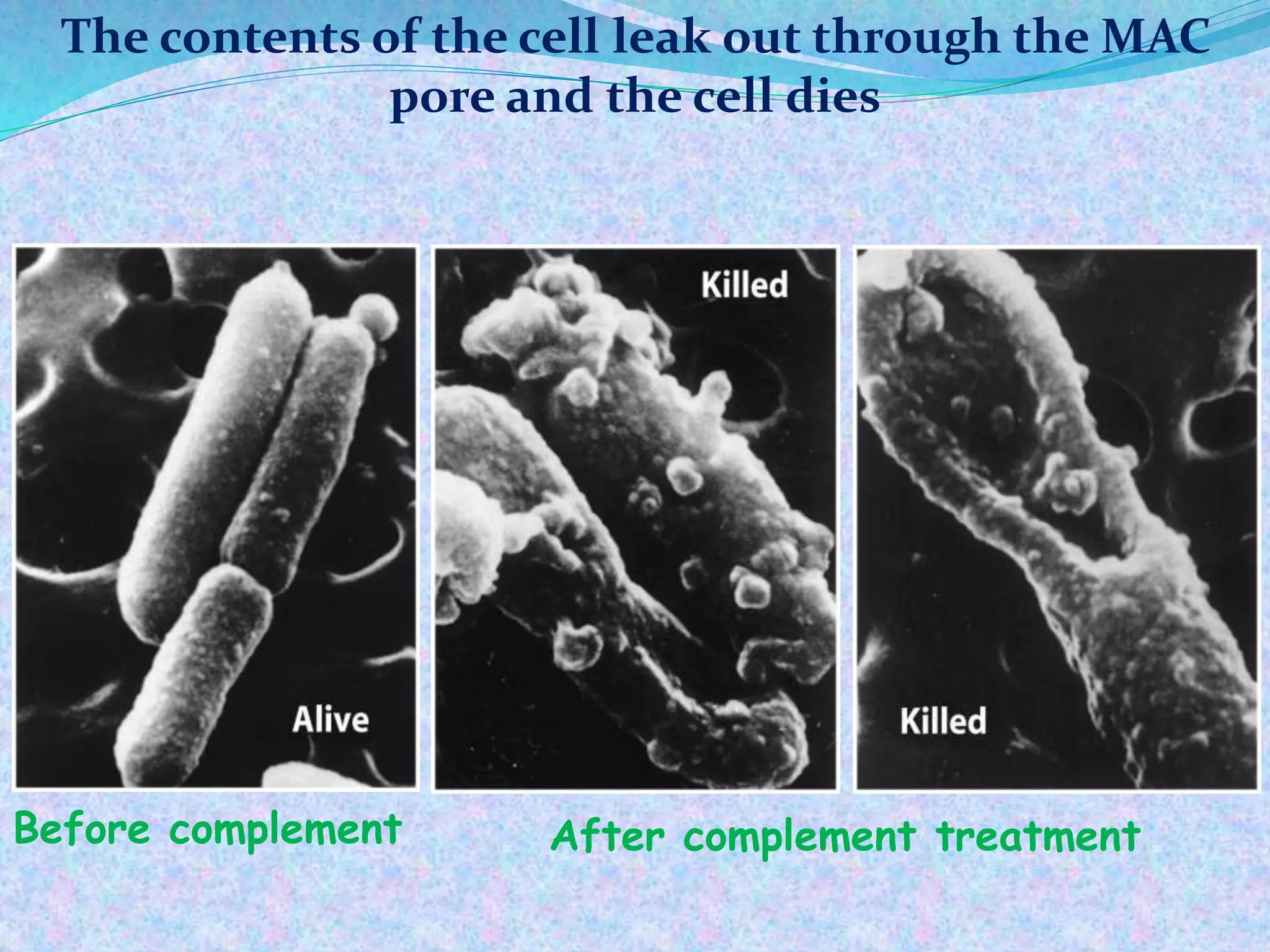
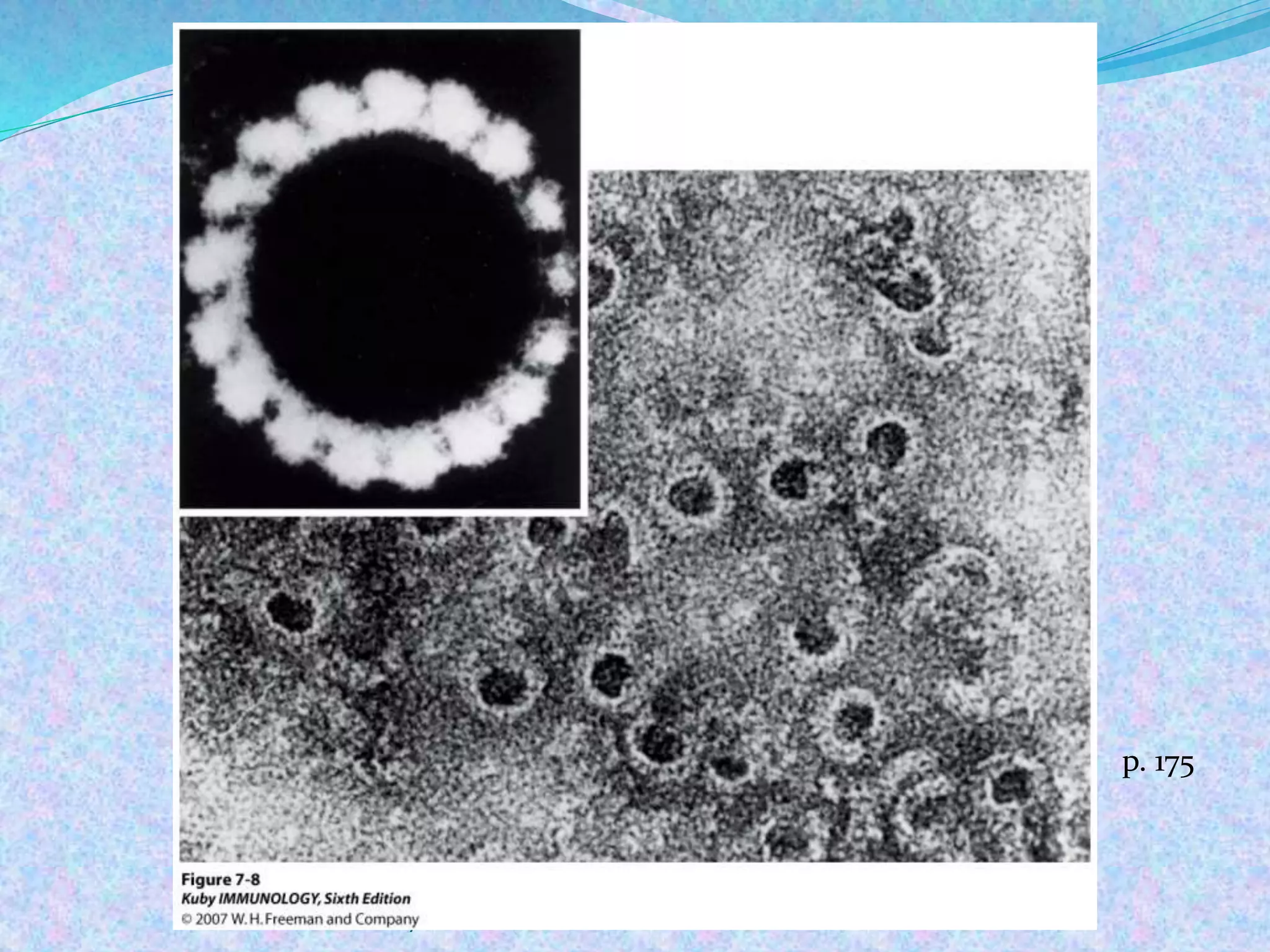
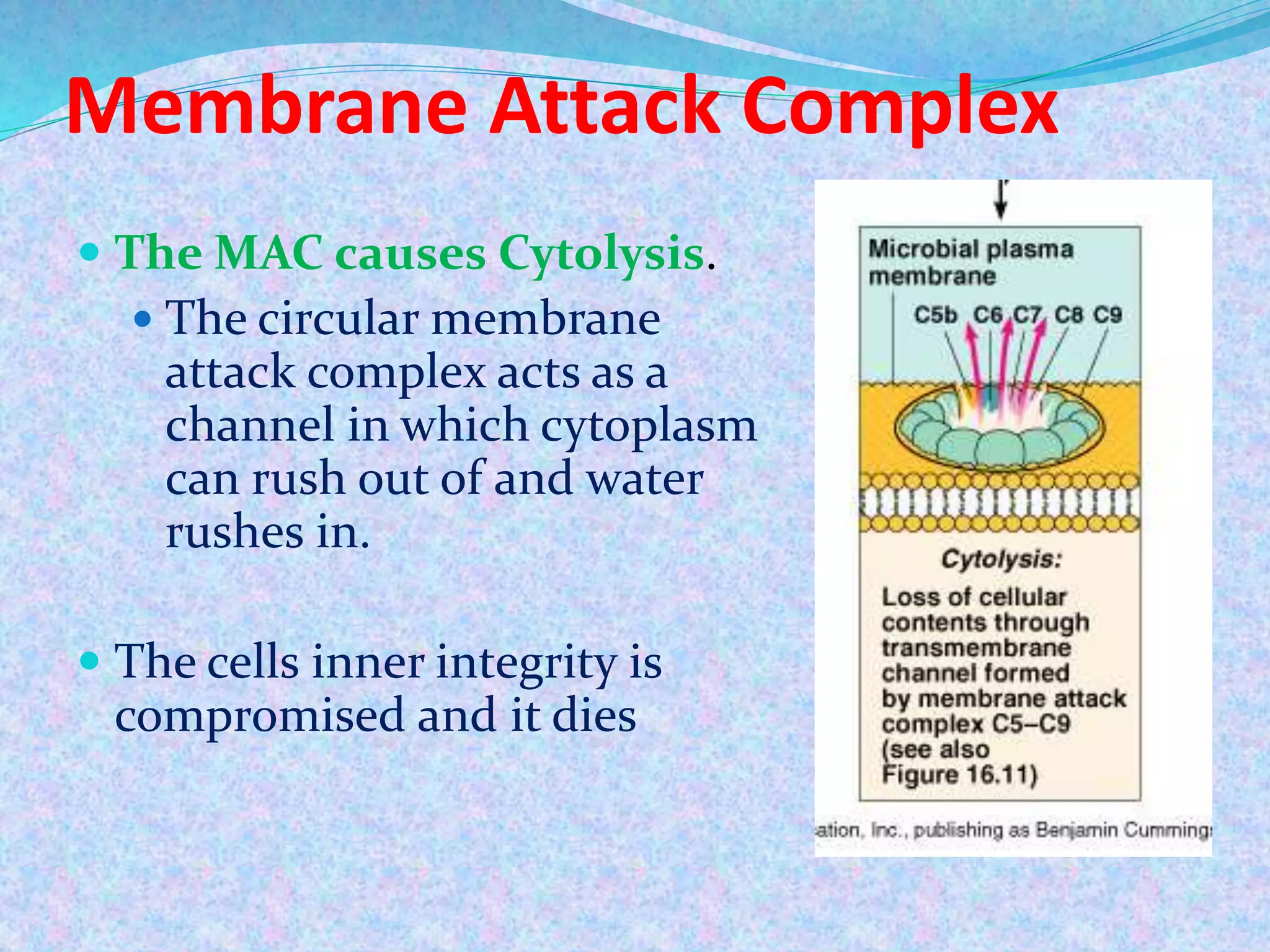
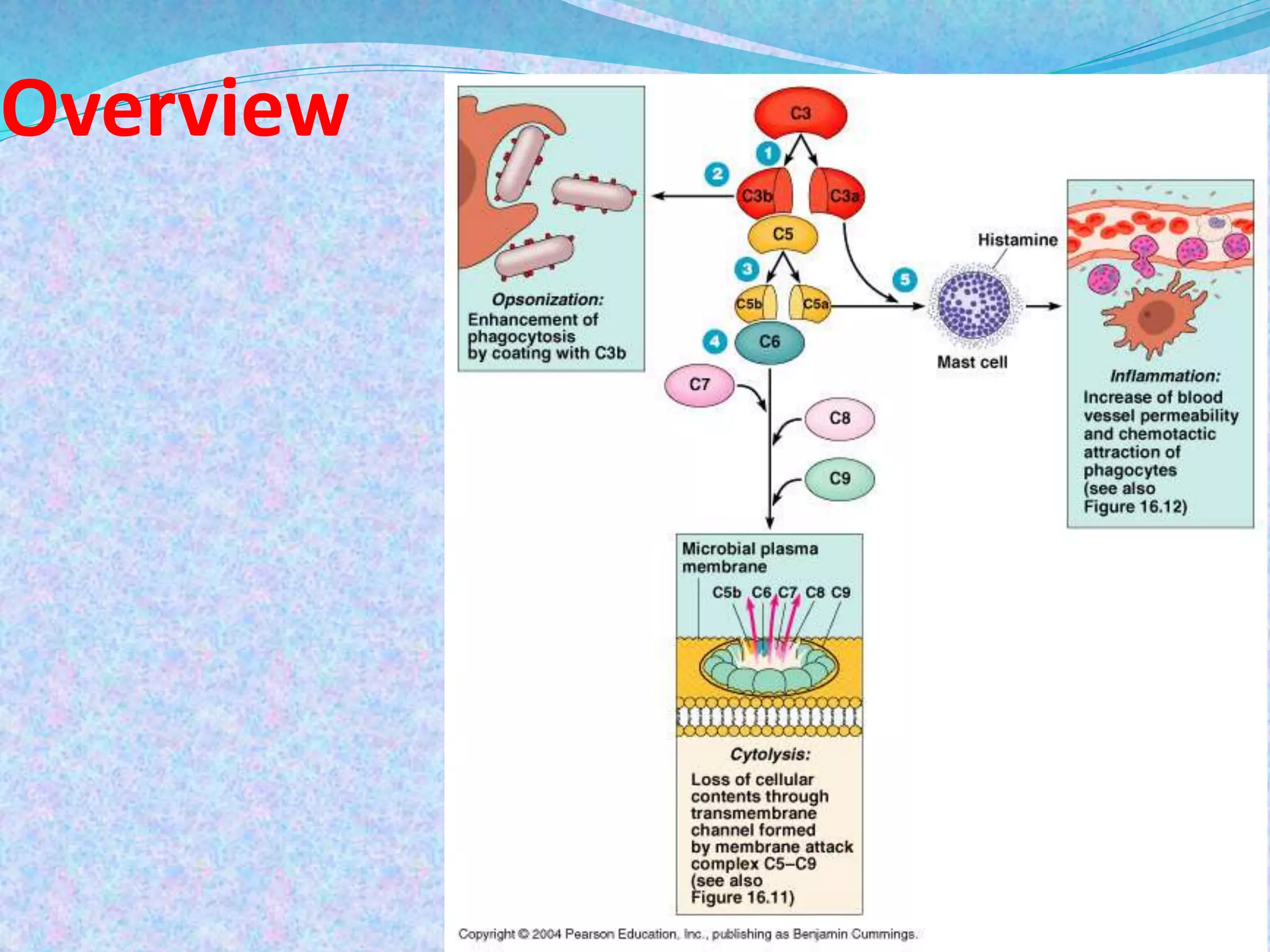
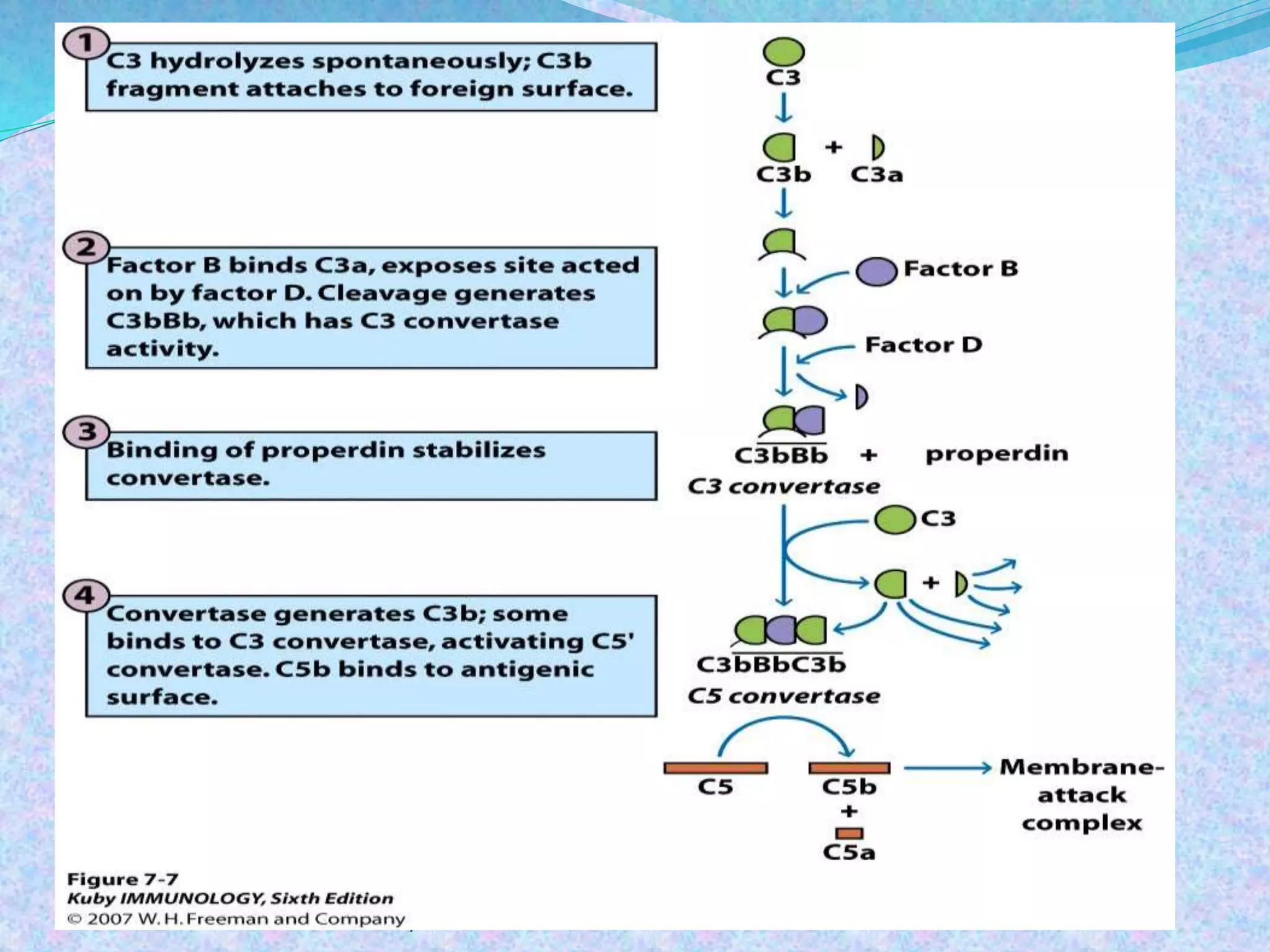
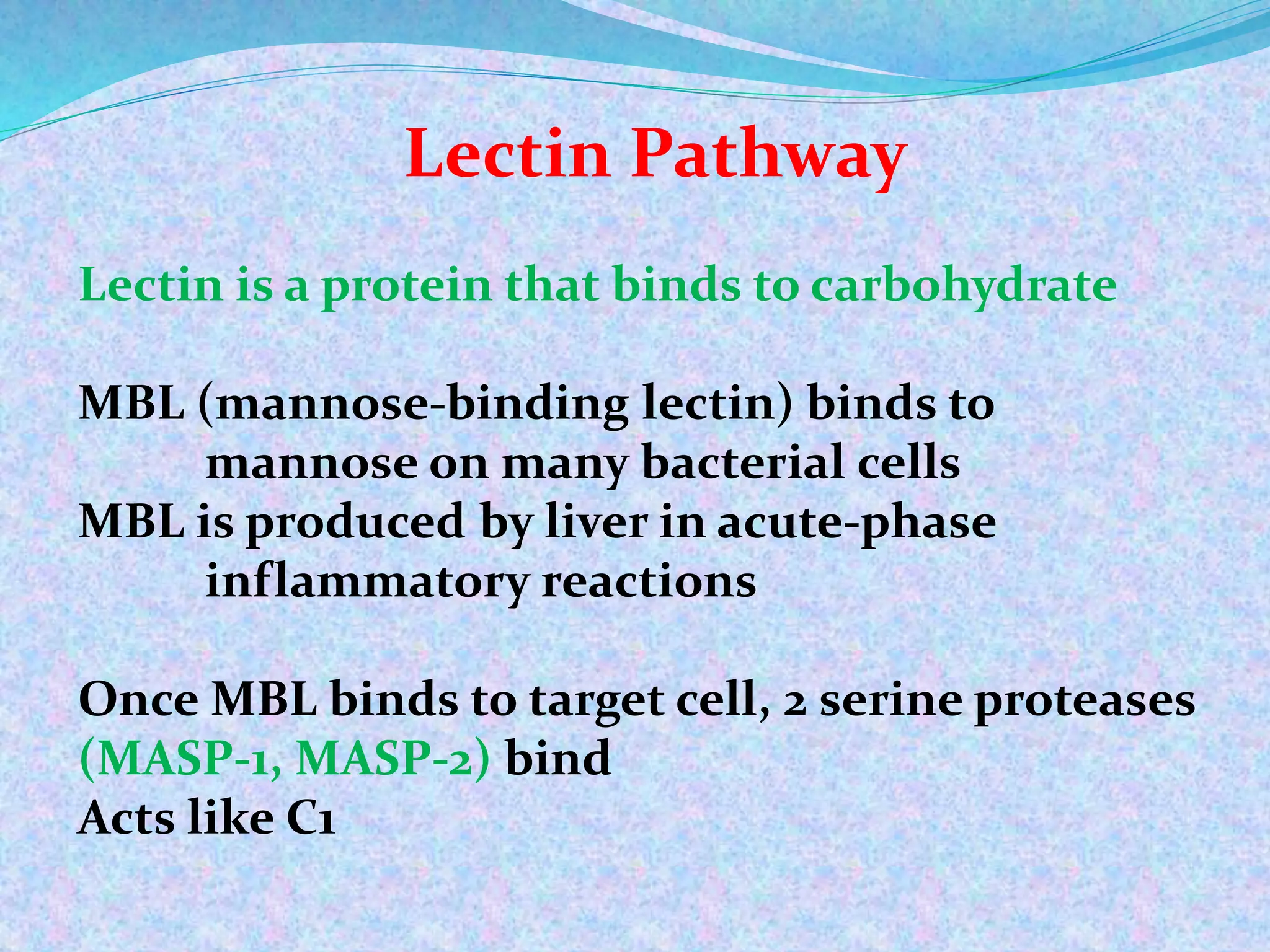
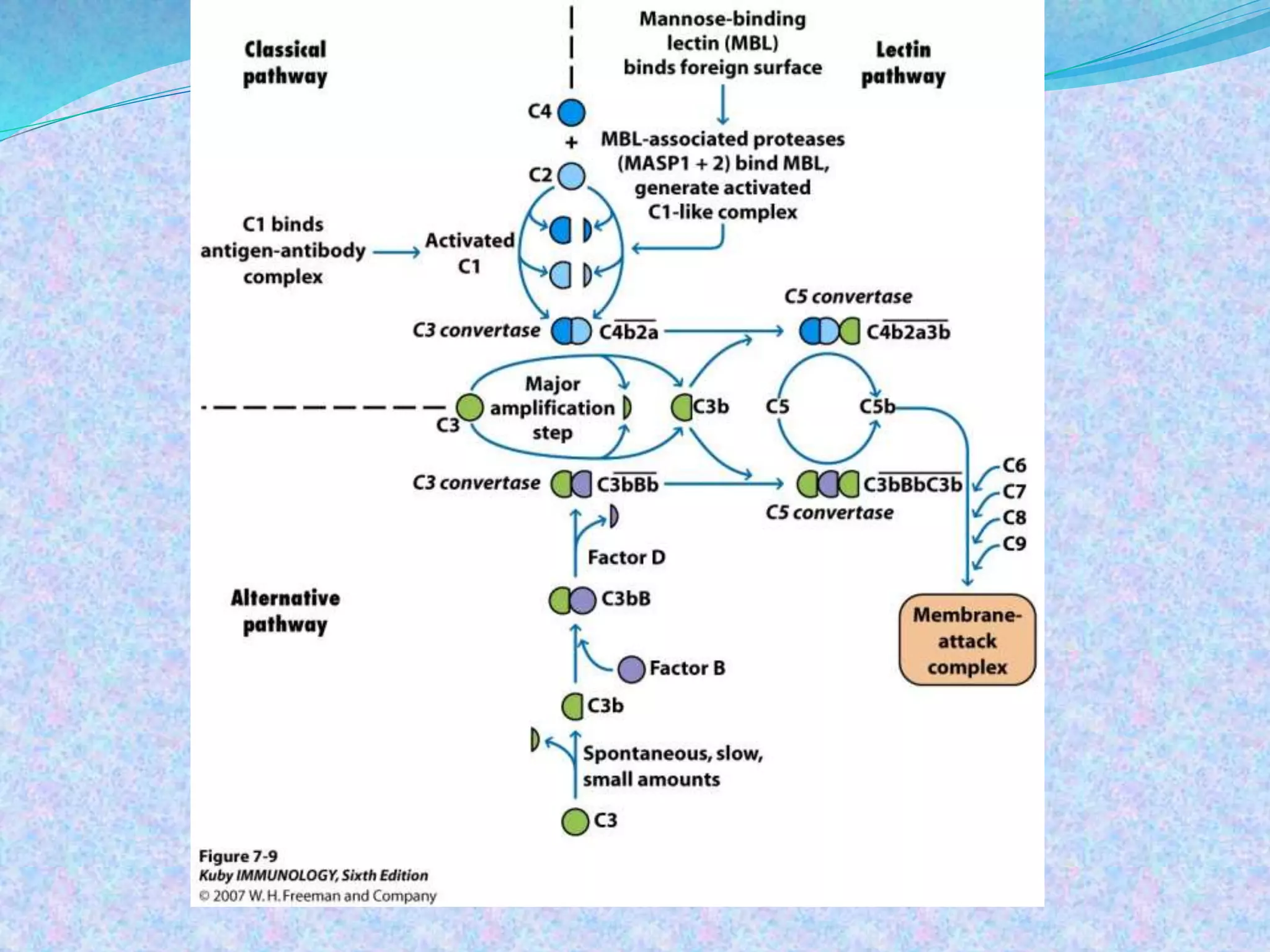
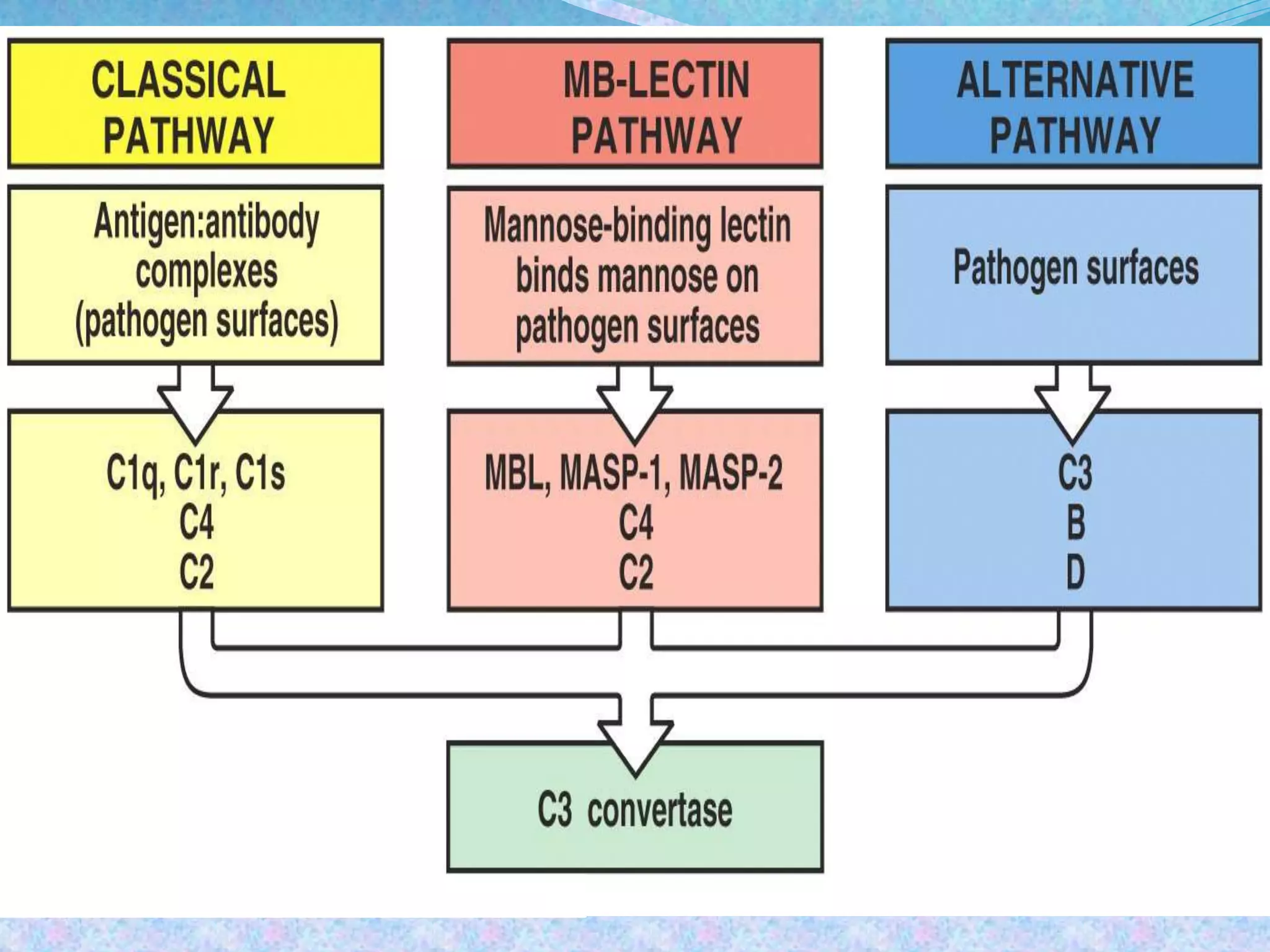
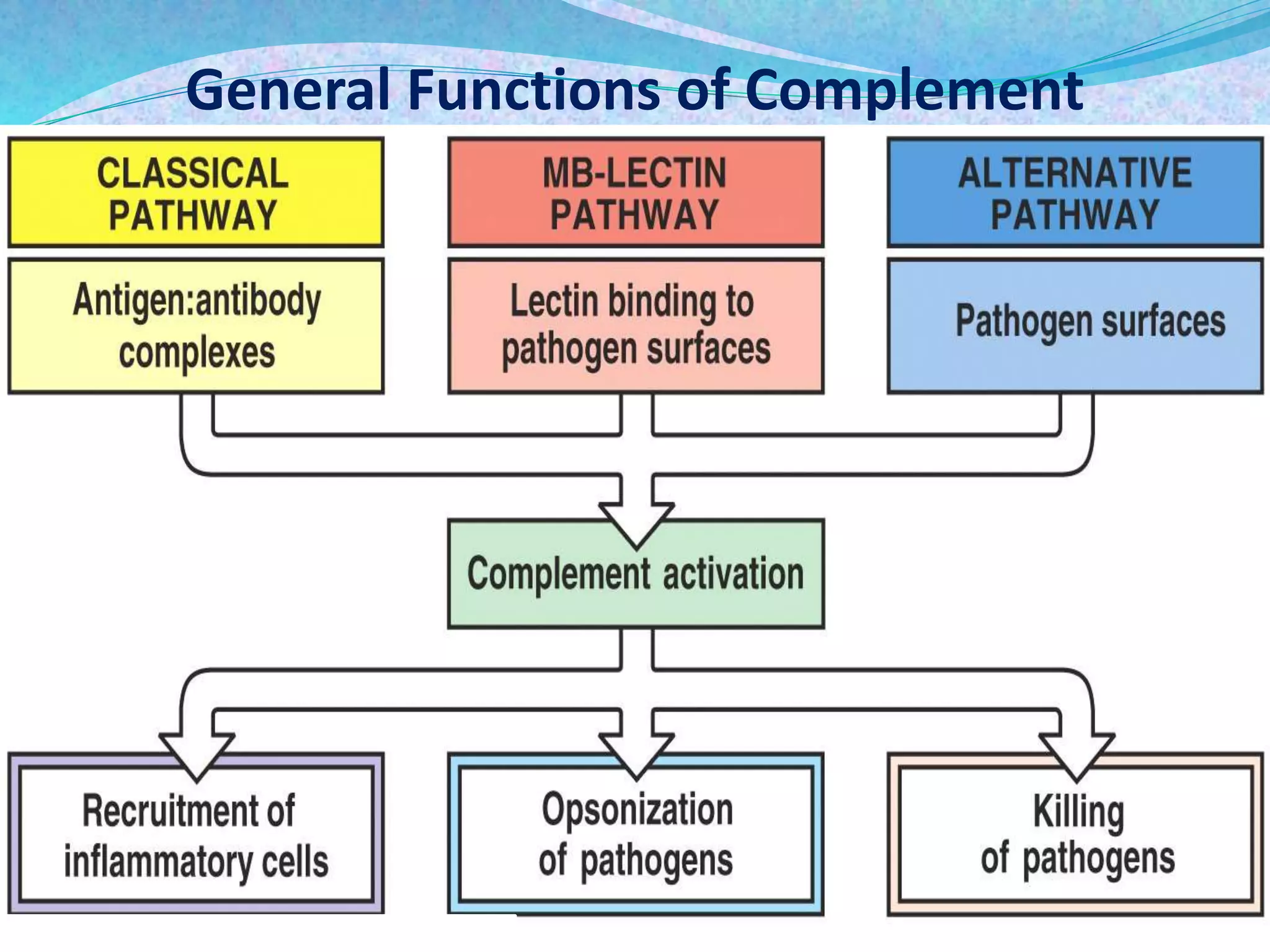
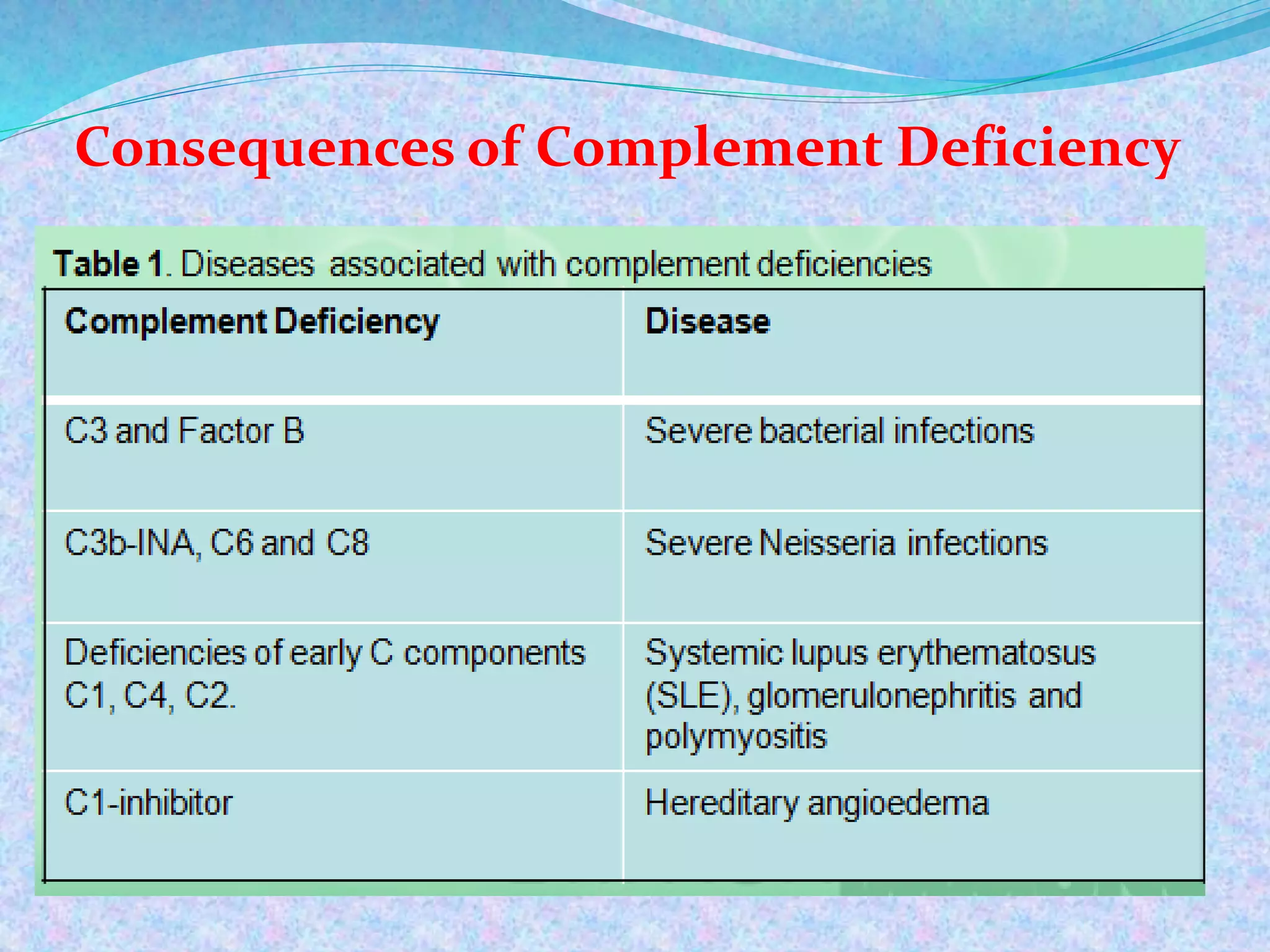
The document discusses the complement system, which consists of over 30 proteins produced by the liver that function in the immune system but are not antibodies. It works as a cascade system where one activation triggers another in a chain reaction. Complement activation can lead to cell lysis and generation of inflammatory substances. It plays a role in defense against bacteria and in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. There are three complement activation pathways: classical, alternative, and lectin. The classical pathway is antibody-dependent while the alternative and lectin pathways are antibody-independent. Complement activation results in opsonization, inflammation, clearance of immune complexes, and lysis of pathogen cells.