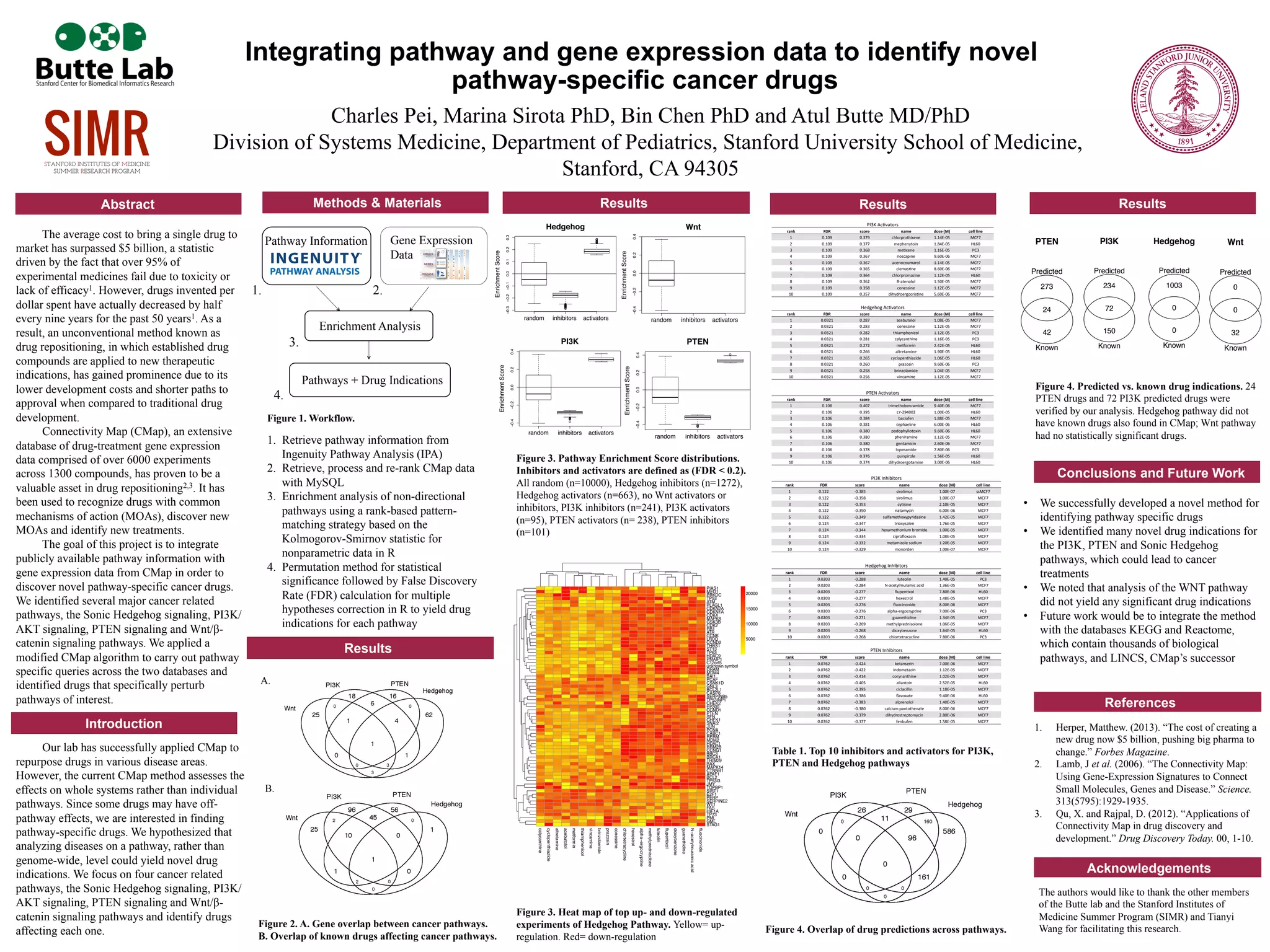
The document describes a study that integrated pathway and gene expression data to identify novel pathway-specific cancer drugs. The researchers identified major cancer pathways including Sonic Hedgehog, PI3K/AKT, PTEN and Wnt/beta-catenin. They applied a modified Connectivity Map algorithm to identify drugs that specifically perturb these pathways. They successfully identified many novel drug indications for the PI3K, PTEN and Sonic Hedgehog pathways that could lead to new cancer treatments. Future work includes integrating additional pathway databases and the LINCS database to identify more pathway-specific drugs.