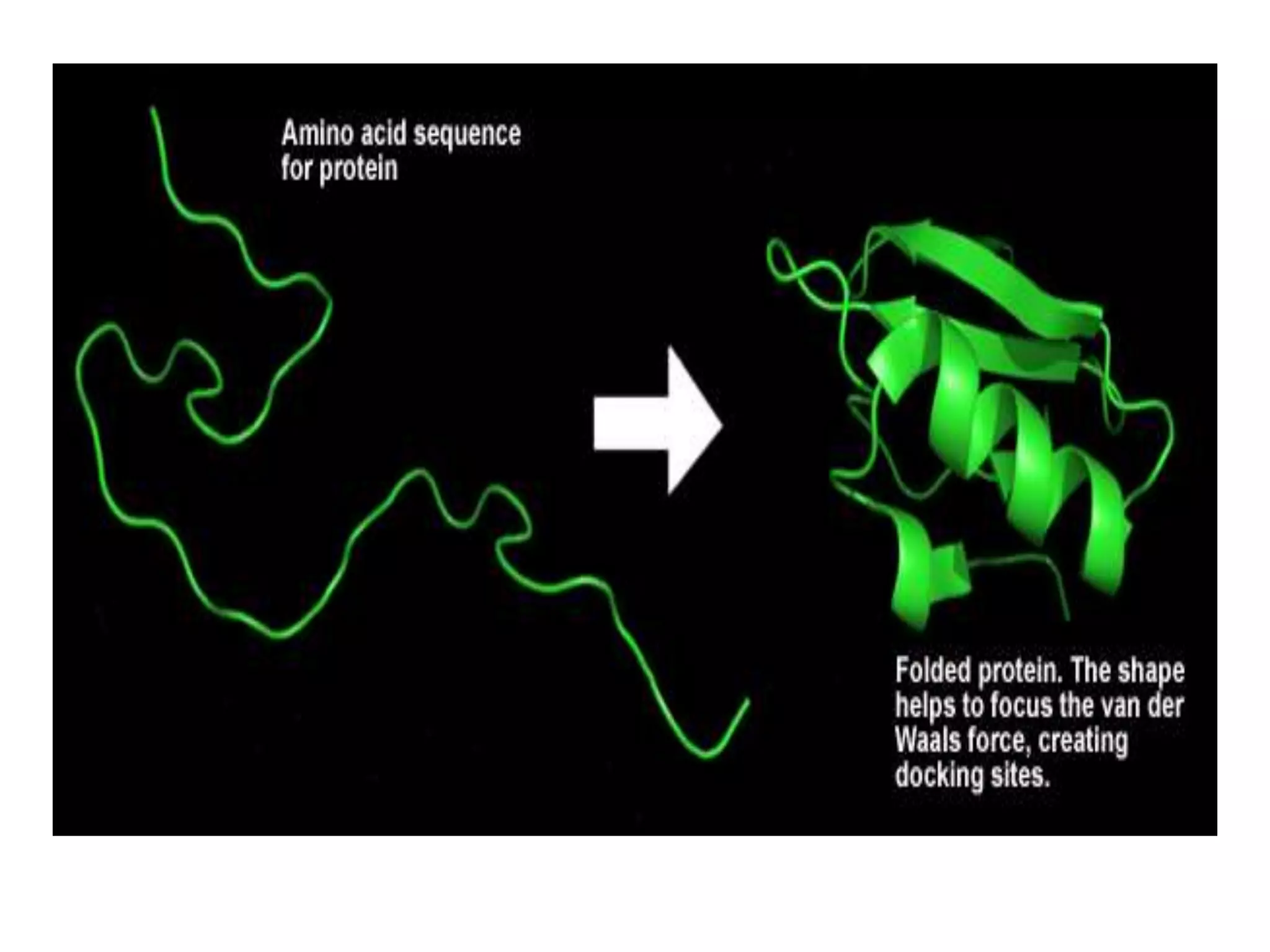
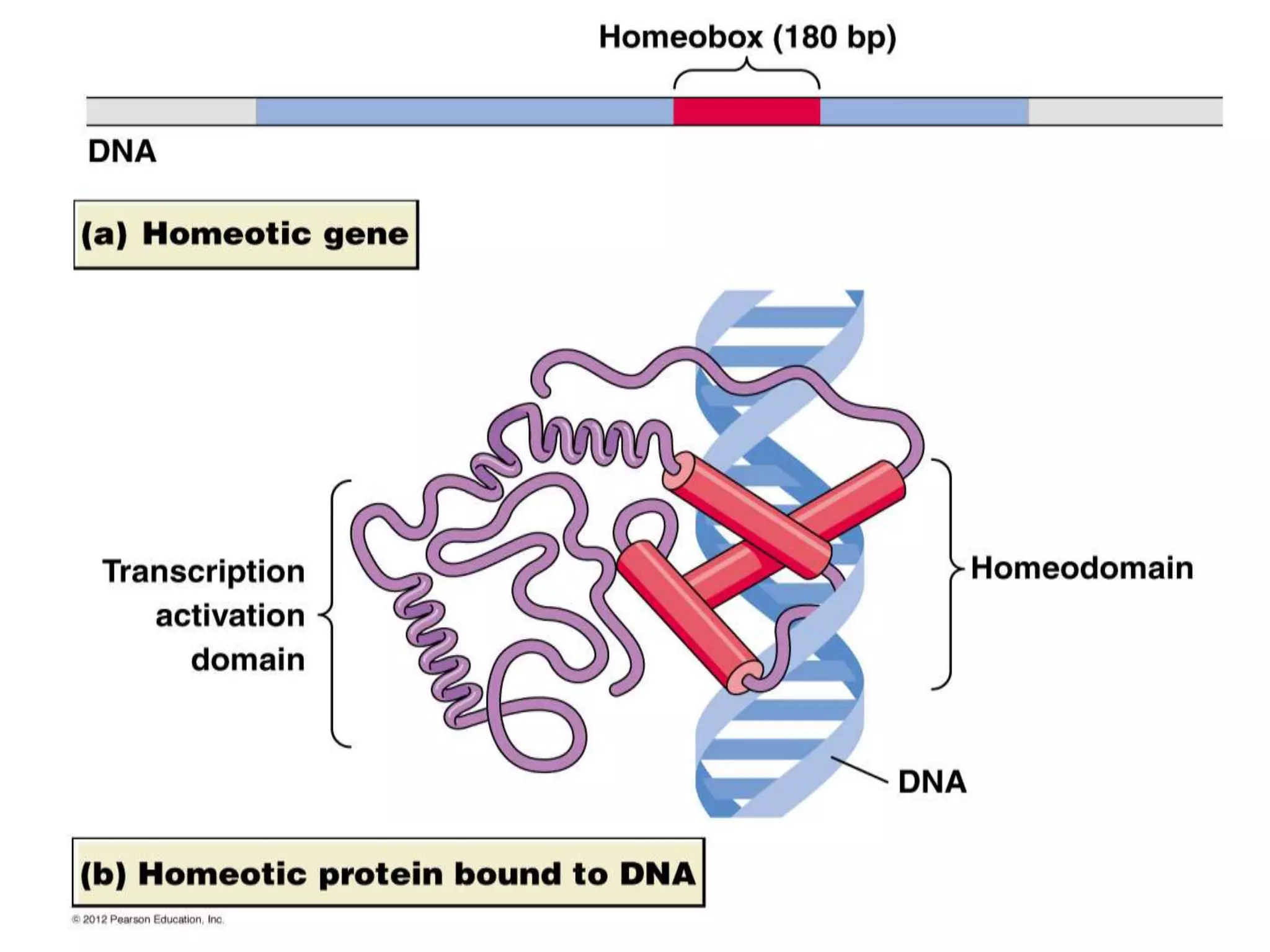
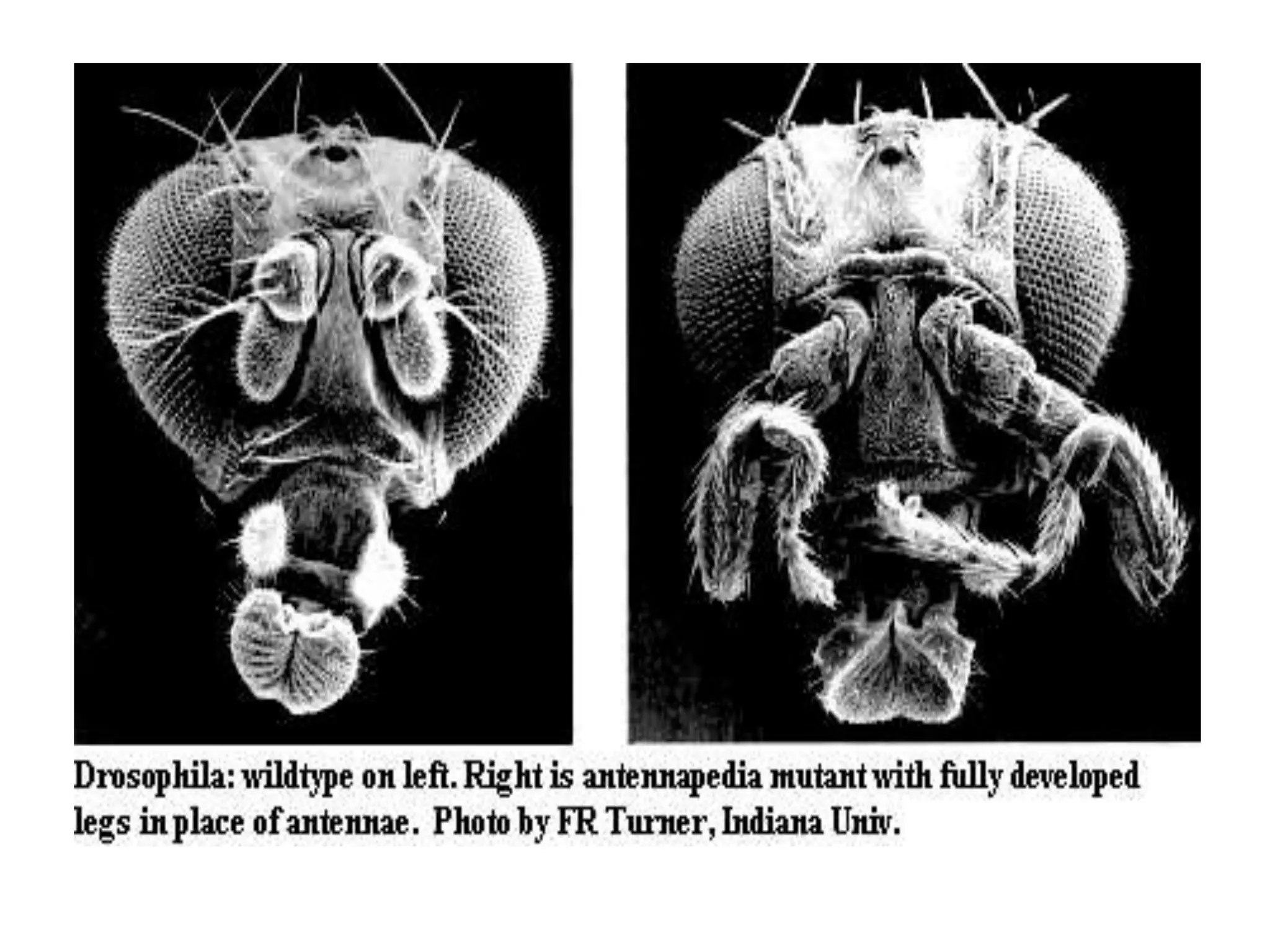
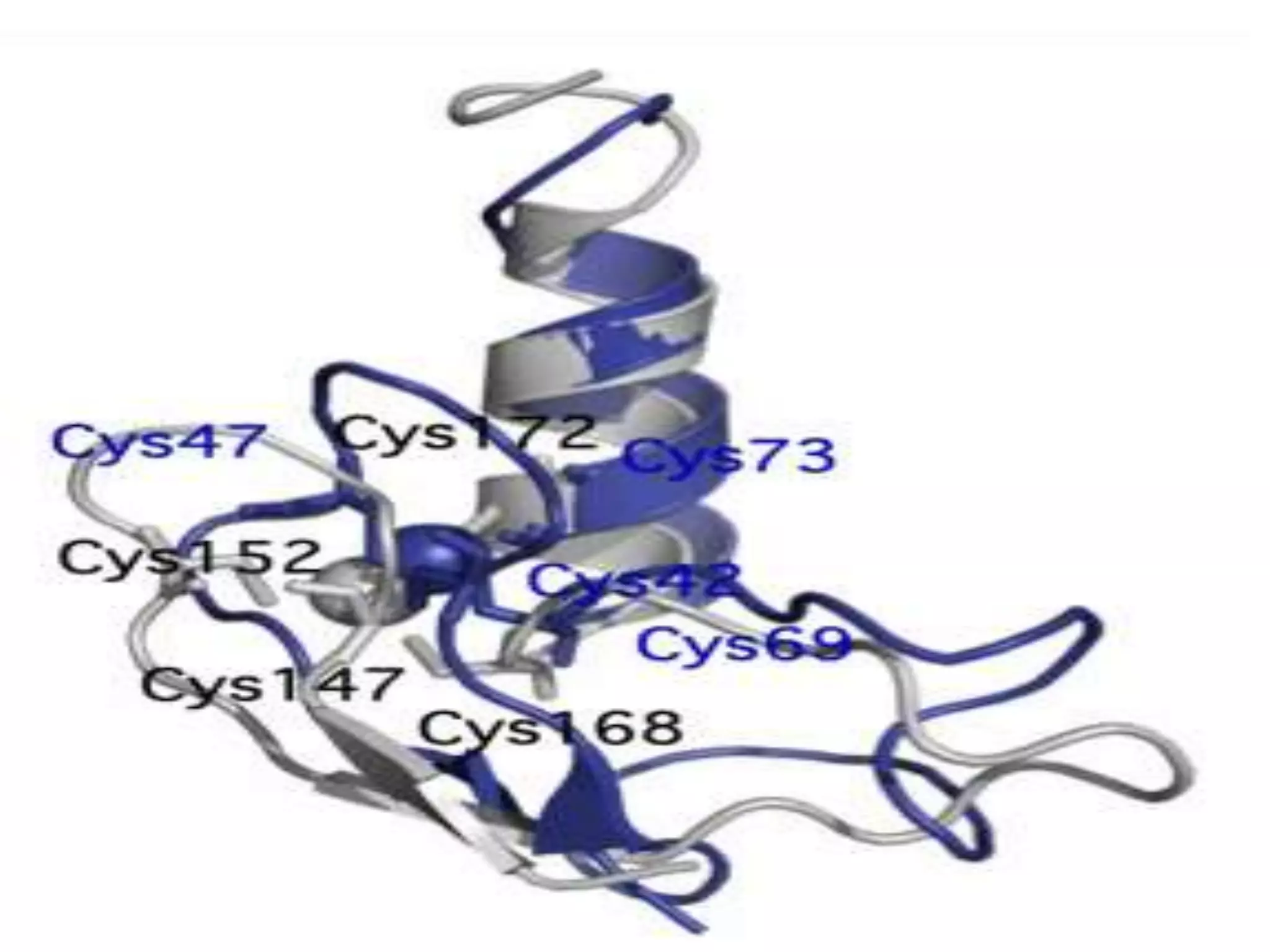
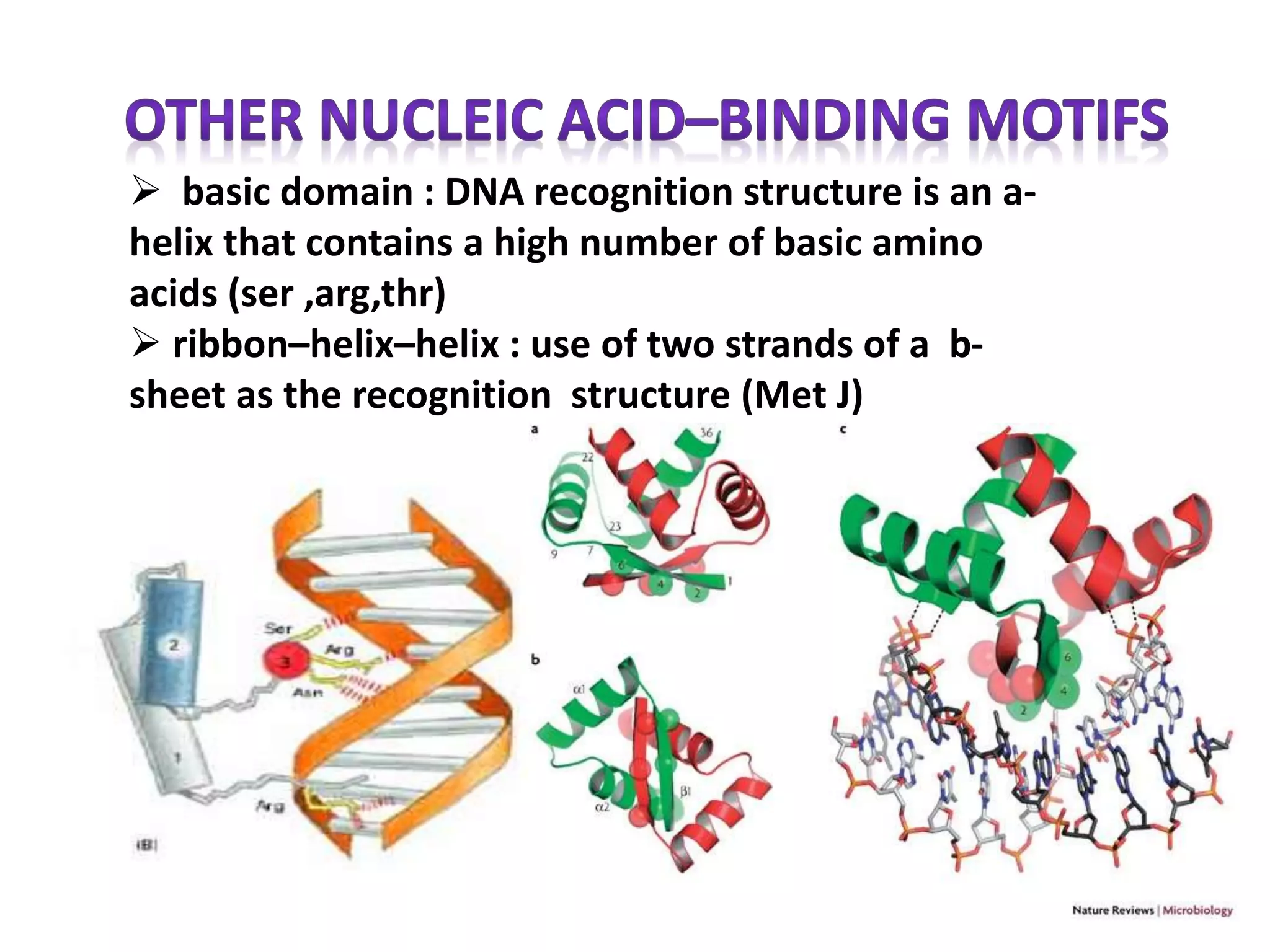
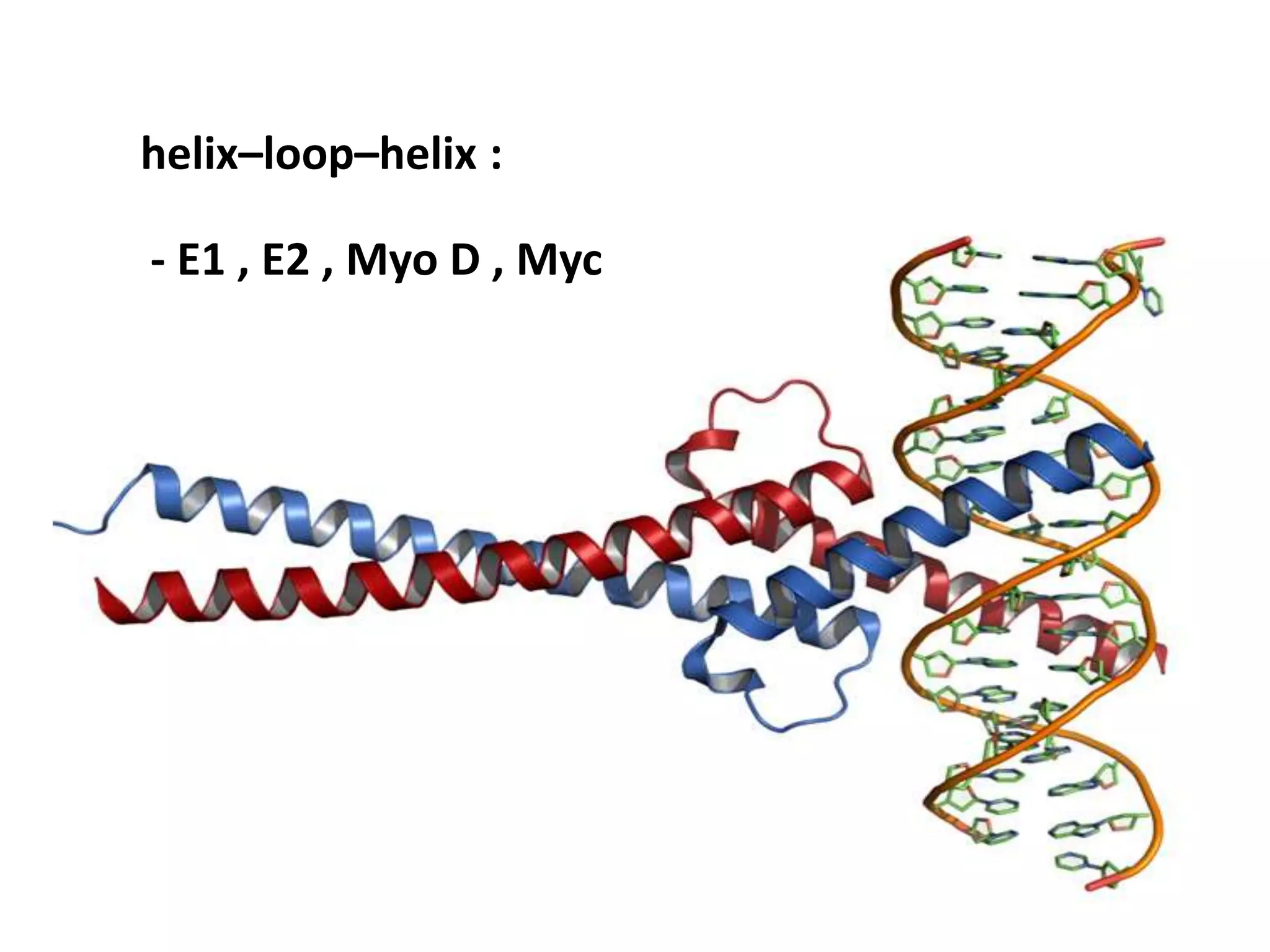
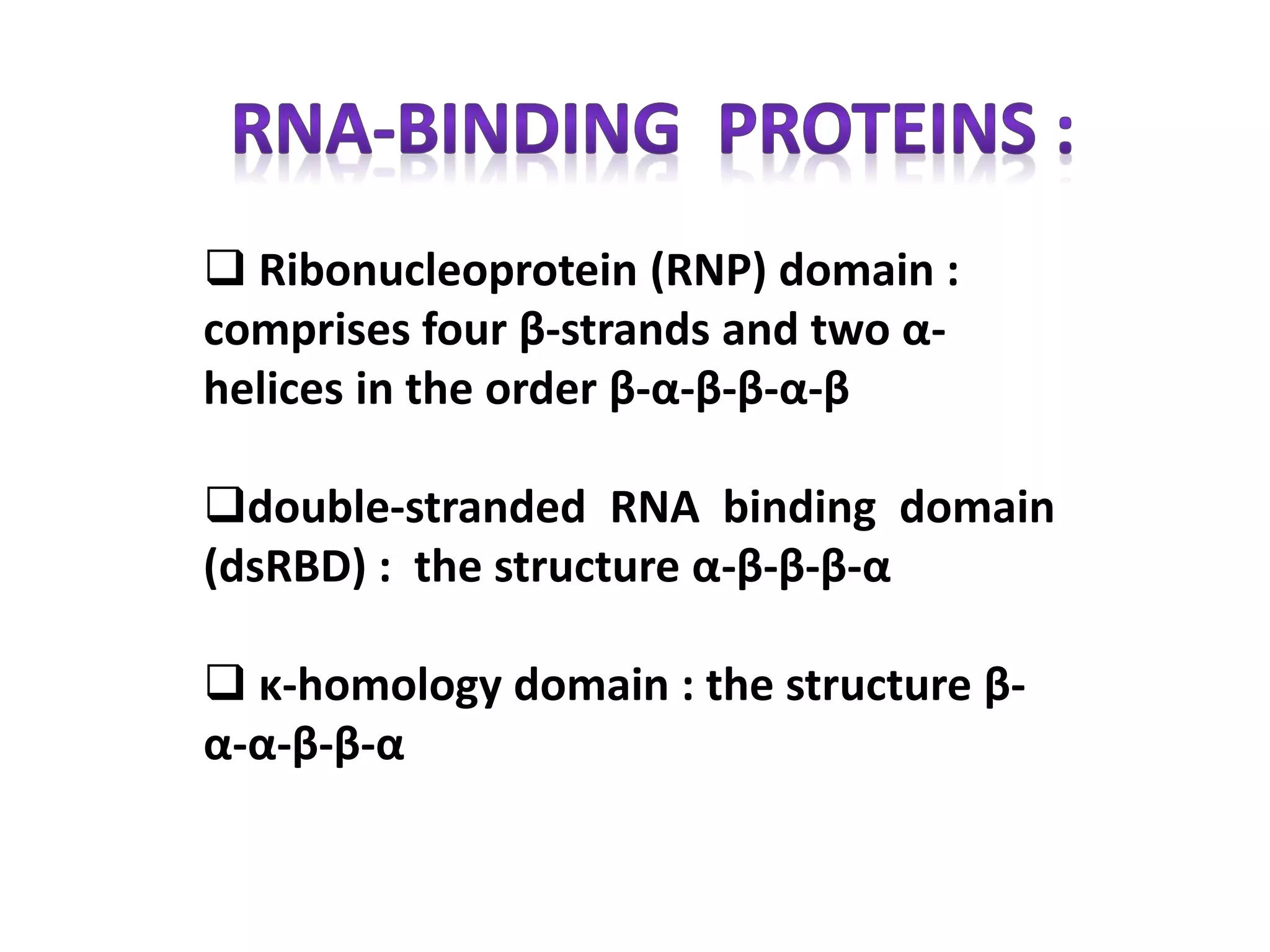
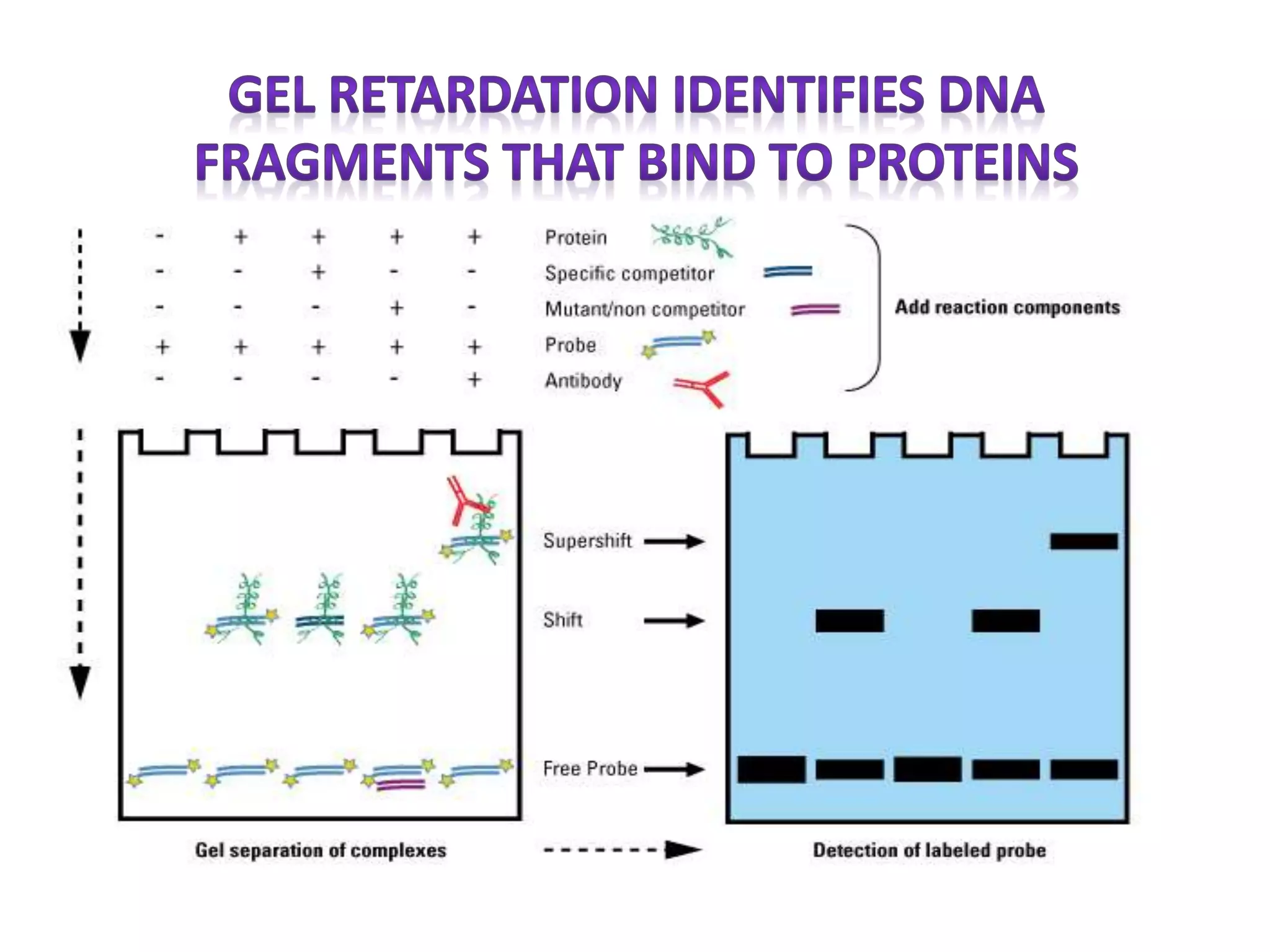
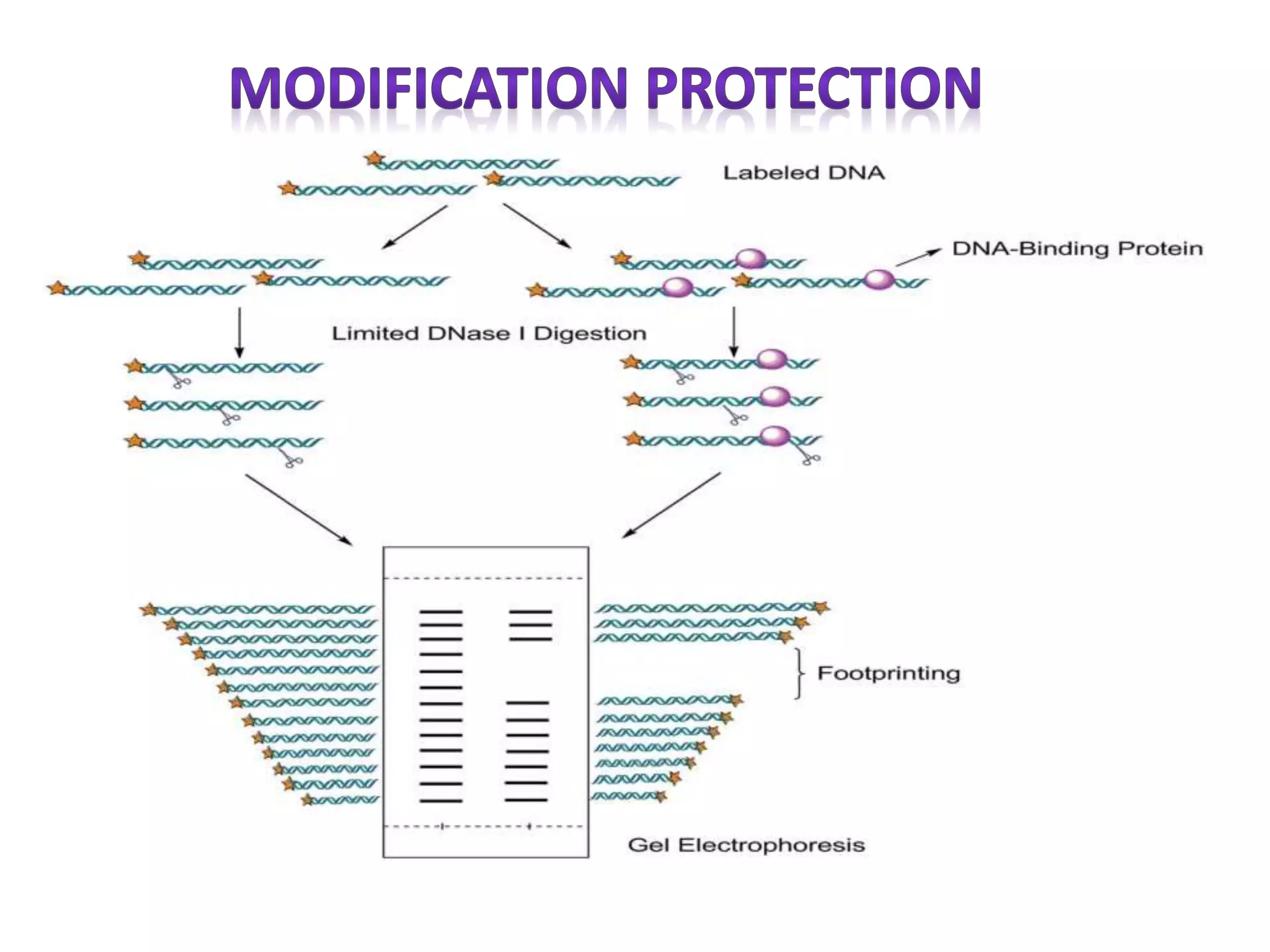
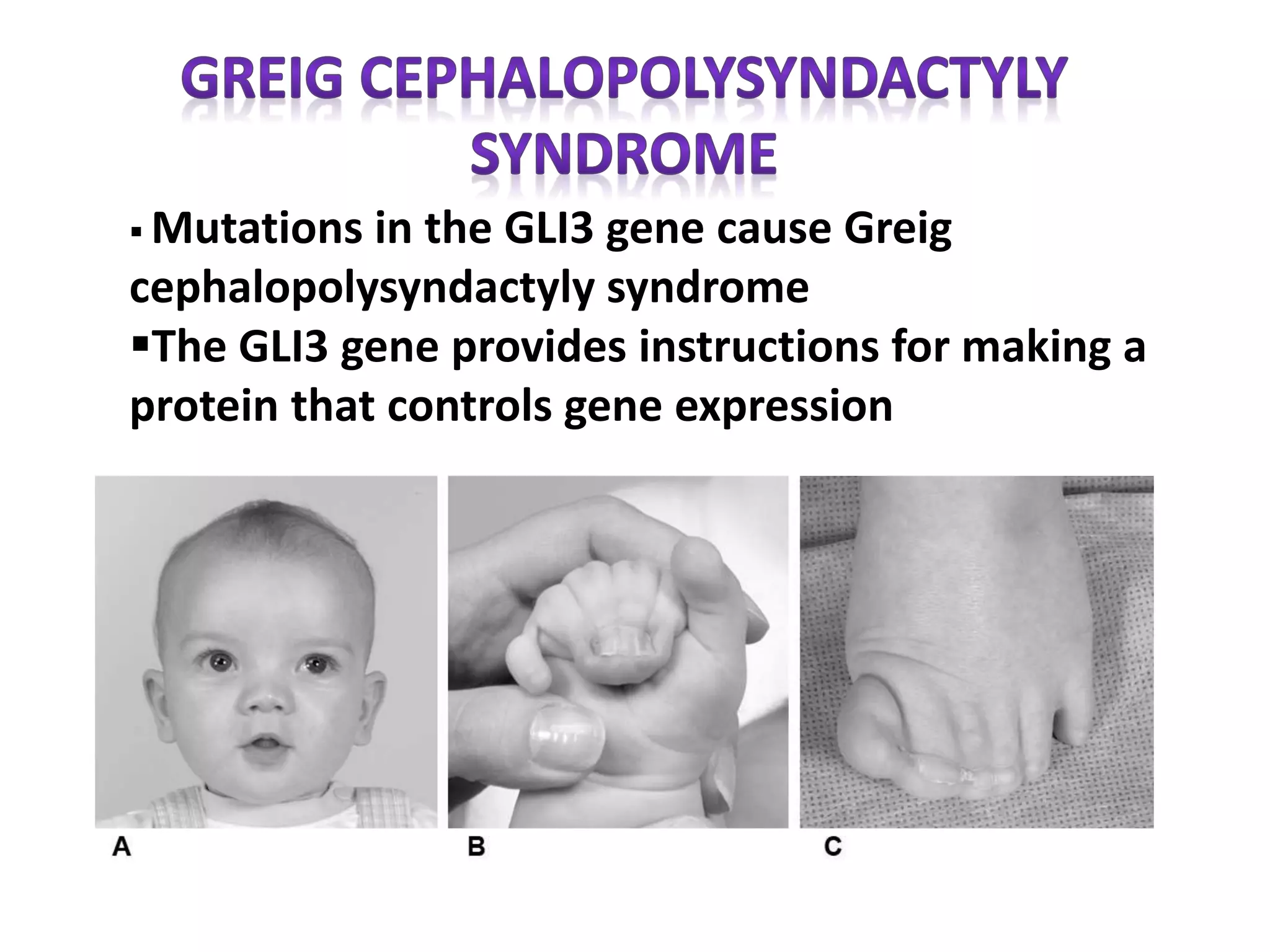
This document discusses various protein domains and motifs that are involved in DNA binding and gene regulation. It describes several common DNA-binding domains including helix-turn-helix, zinc fingers, basic domains, and leucine zippers. It provides examples of proteins that contain these domains like the lactose repressor and GABP. The document also mentions how mutations in genes encoding DNA-binding proteins can cause developmental disorders by altering gene expression, like in Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome and Denys-Drash syndrome.