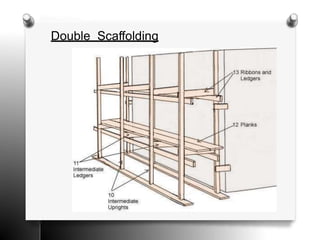
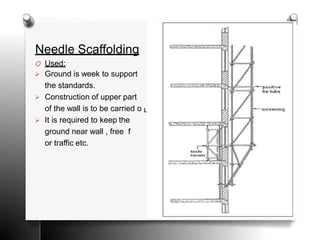
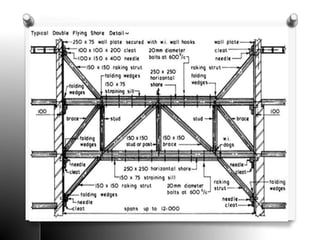
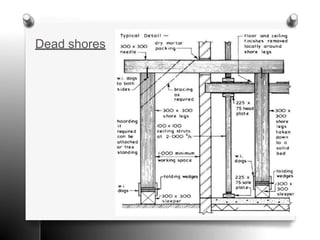
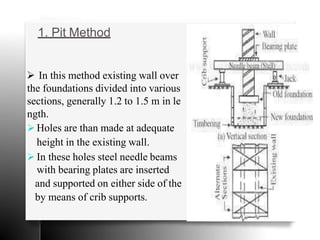
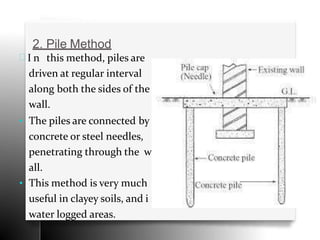
The document provides an overview of temporary works in construction, specifically focusing on scaffolding, shoring, and underpinning. It details various types of scaffolding, including single and double scaffolding, as well as different shoring methods such as raking, flying, and dead shores. Underpinning methods are also described, highlighting the pit and pile methods along with miscellaneous options for reinforcing existing foundations.