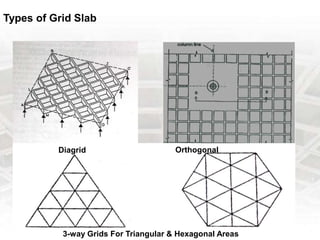
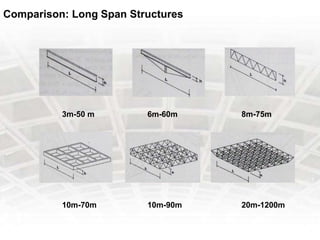
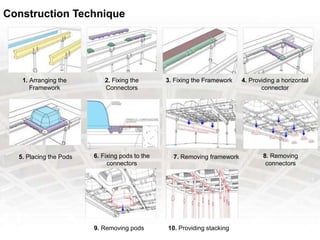
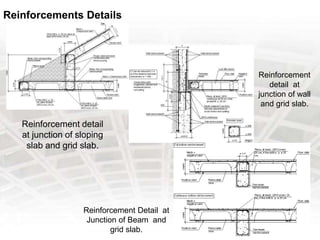
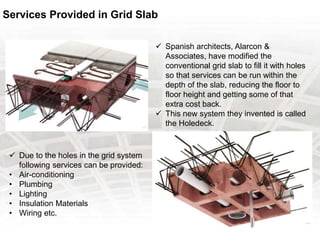
A grid slab is a type of building material that has two-directional reinforcement in the shape of a waffle. It can be used as both ceilings and floors, especially in areas requiring large spans with fewer columns. Features include panels on a 1 meter grid with trench mesh or individual bars. Grid slabs use less concrete and steel than conventional slabs while providing strength and resistance to cracking and sagging. Construction involves arranging a framework, fixing connectors and pods, then removing forms. Services like HVAC, plumbing and wiring can be run through holes in modified grid slabs. Benefits include flexibility, lighter weight, speed of construction, vibration control and fire resistance. Famous structures using grid slabs include terminals,