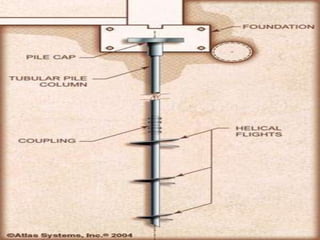
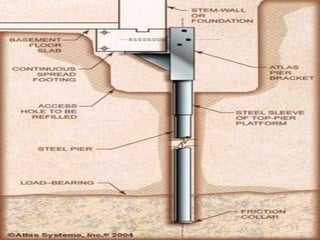
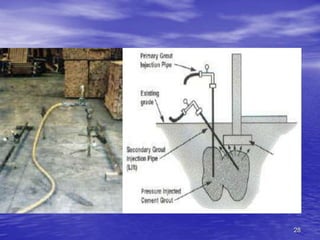
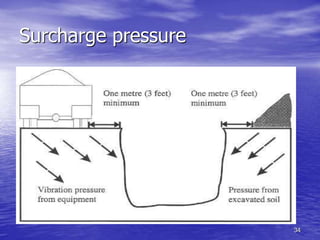
Foundation underpinning involves transferring structural loads to deeper, more stable soils or bedrock when the existing foundation is inadequate. It is done by excavating pits under the foundation and installing concrete piers that the foundation is wedged up onto. Helical piers are also used, which are screwed into the ground to support the foundation. Shoring involves installing a structural system like metal or timber to support the sides of an excavation and prevent collapse, and is needed when excavating under an existing foundation, repairing a foundation, or where loose soil or water are present. The main underpinning and shoring methods were discussed.