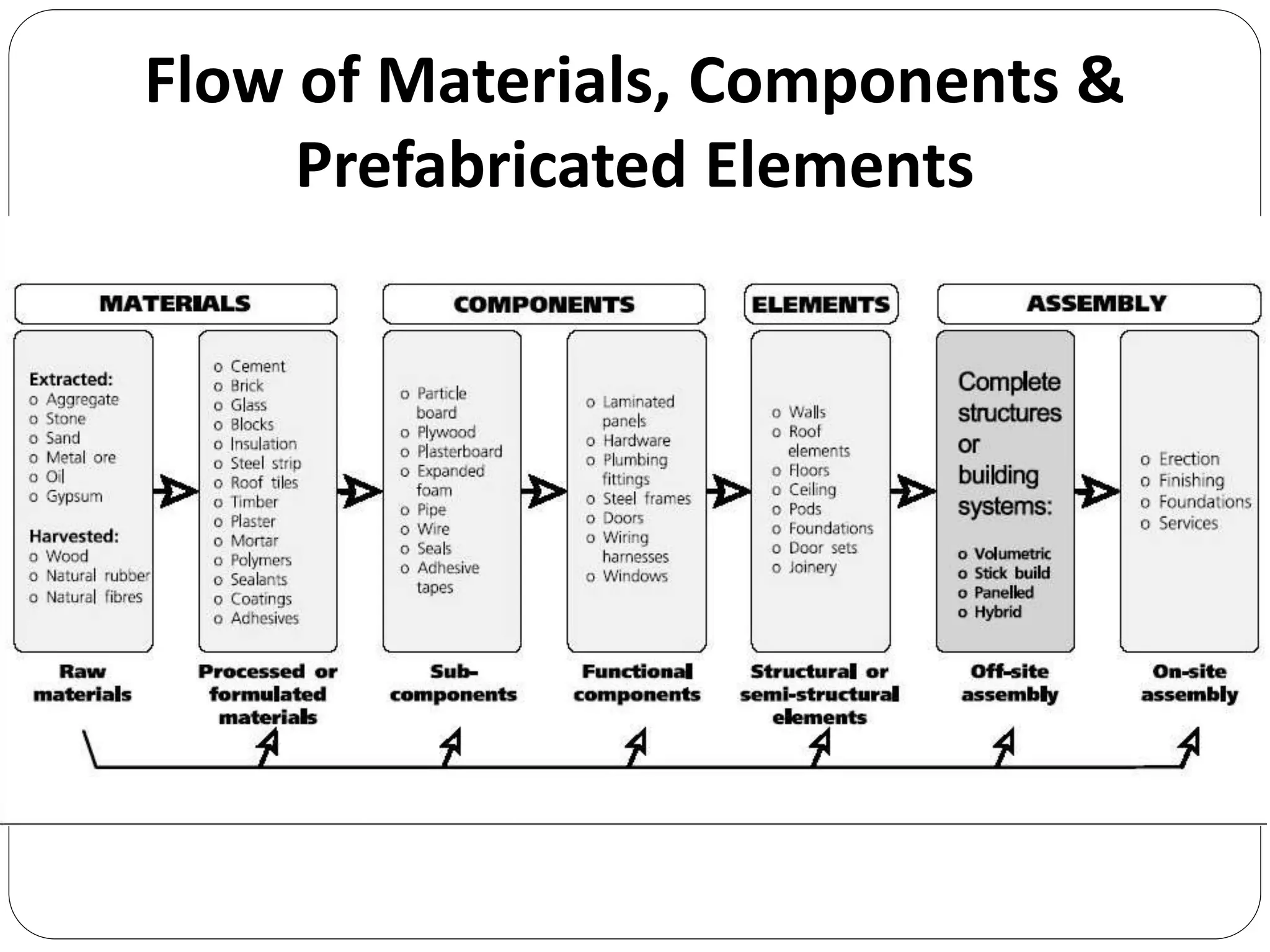
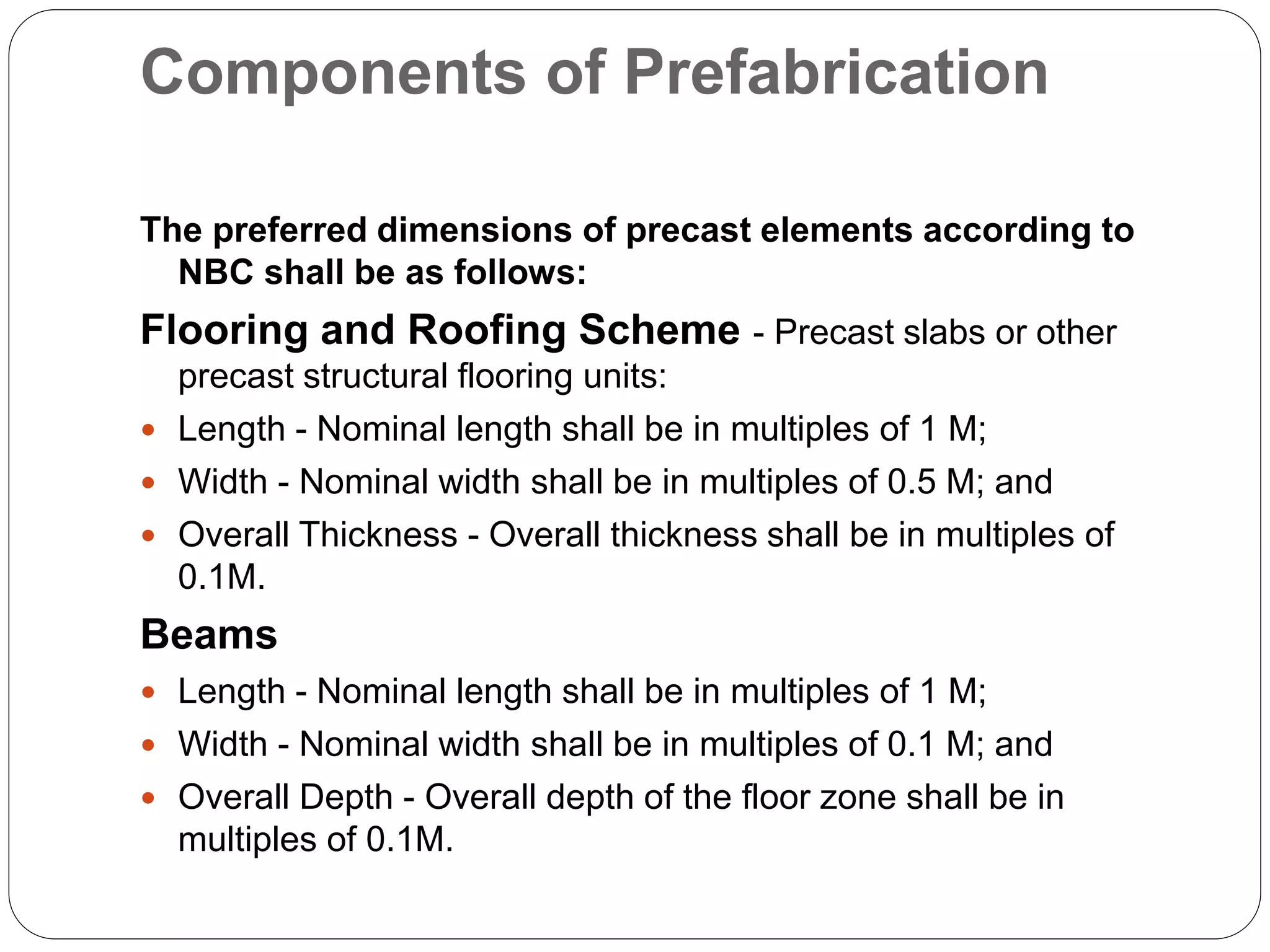
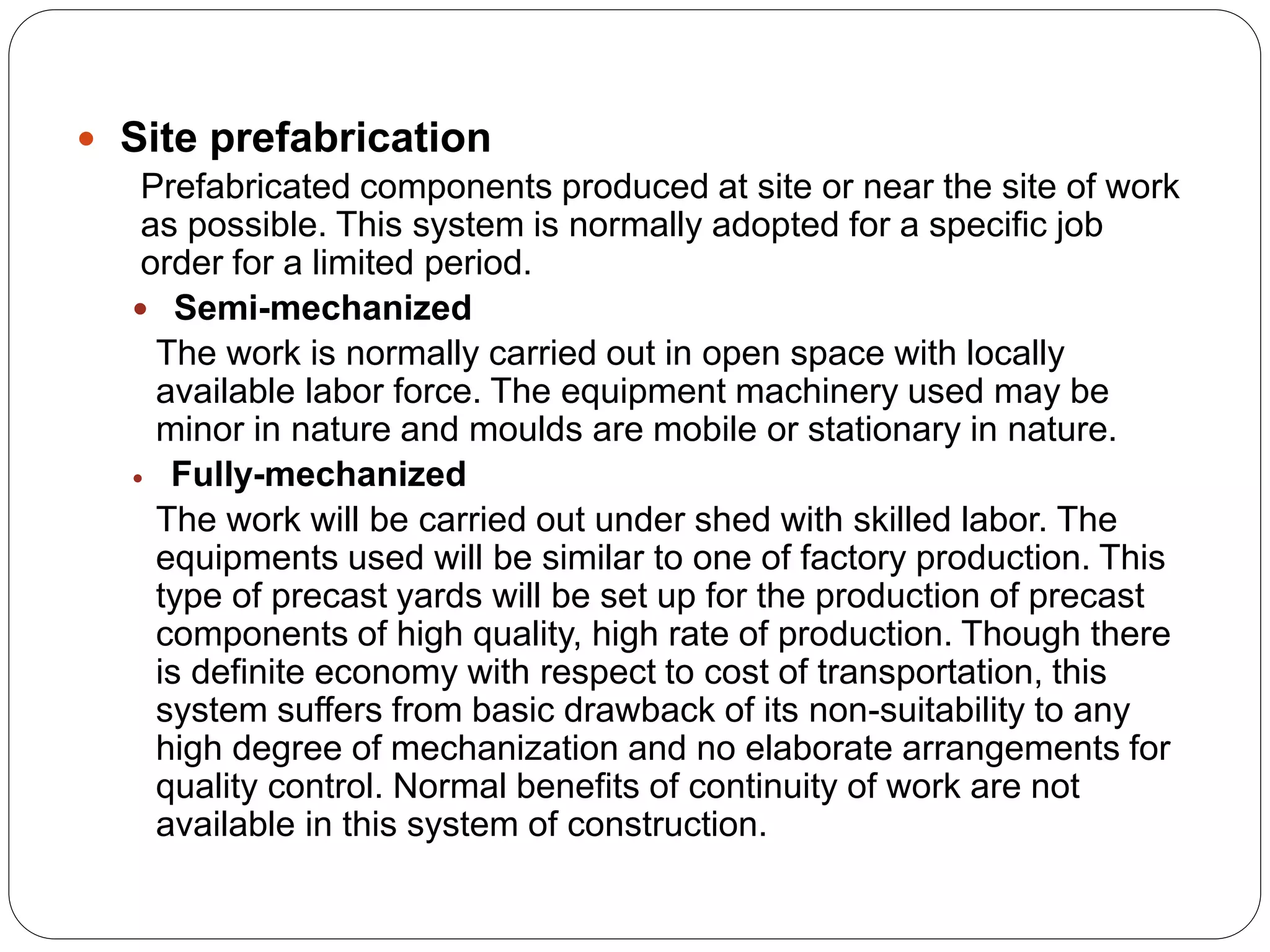
Prefabrication is the process of manufacturing building components in a controlled environment and transporting them to the construction site to reduce costs and construction time. It aims to enhance construction efficiency while minimizing waste, ensuring quality, and improving worker safety, utilizing materials that allow flexibility and structural integrity. Factors like transportation logistics, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of various prefabrication systems and materials, are critical for effective implementation in construction projects.