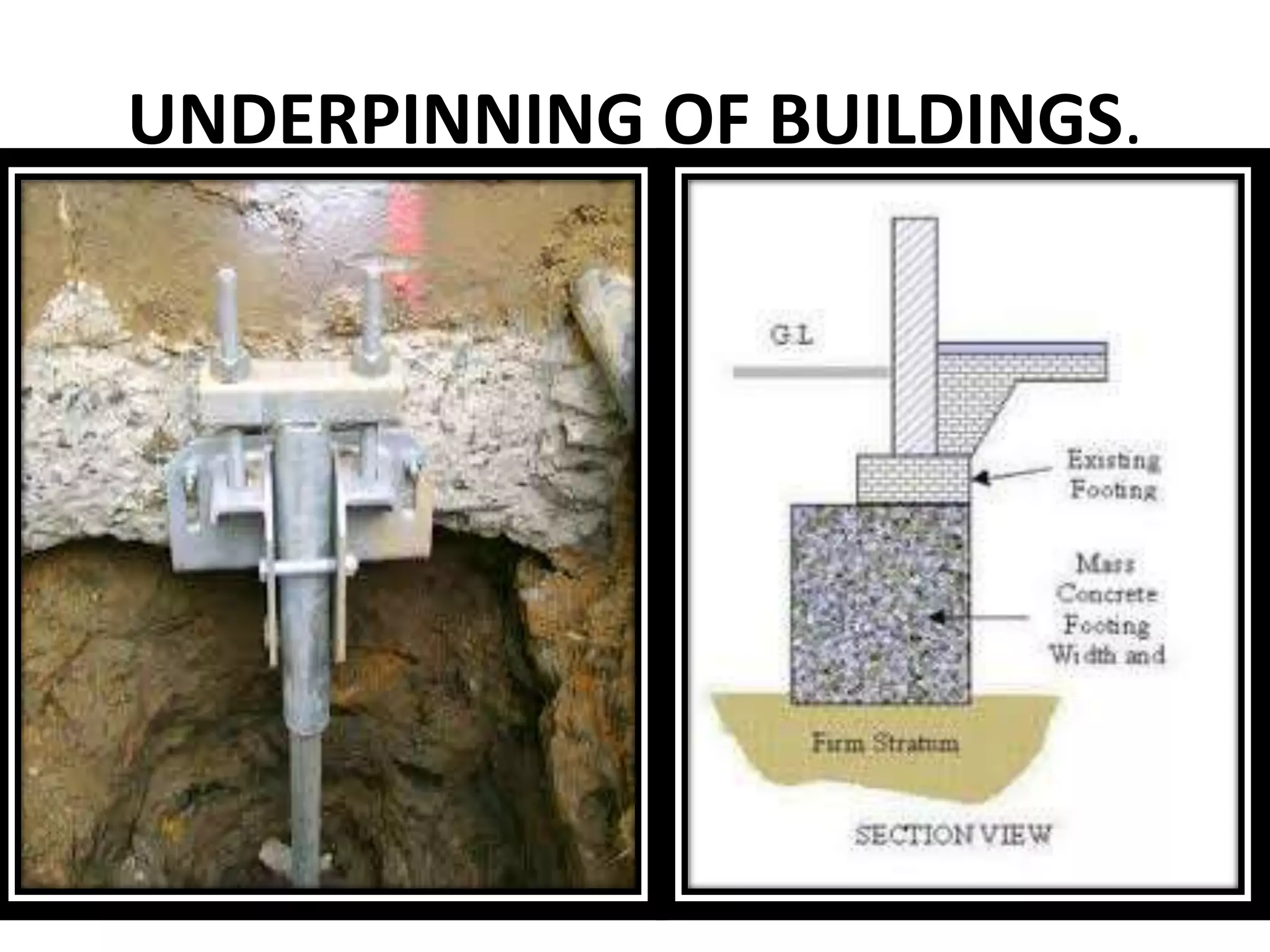
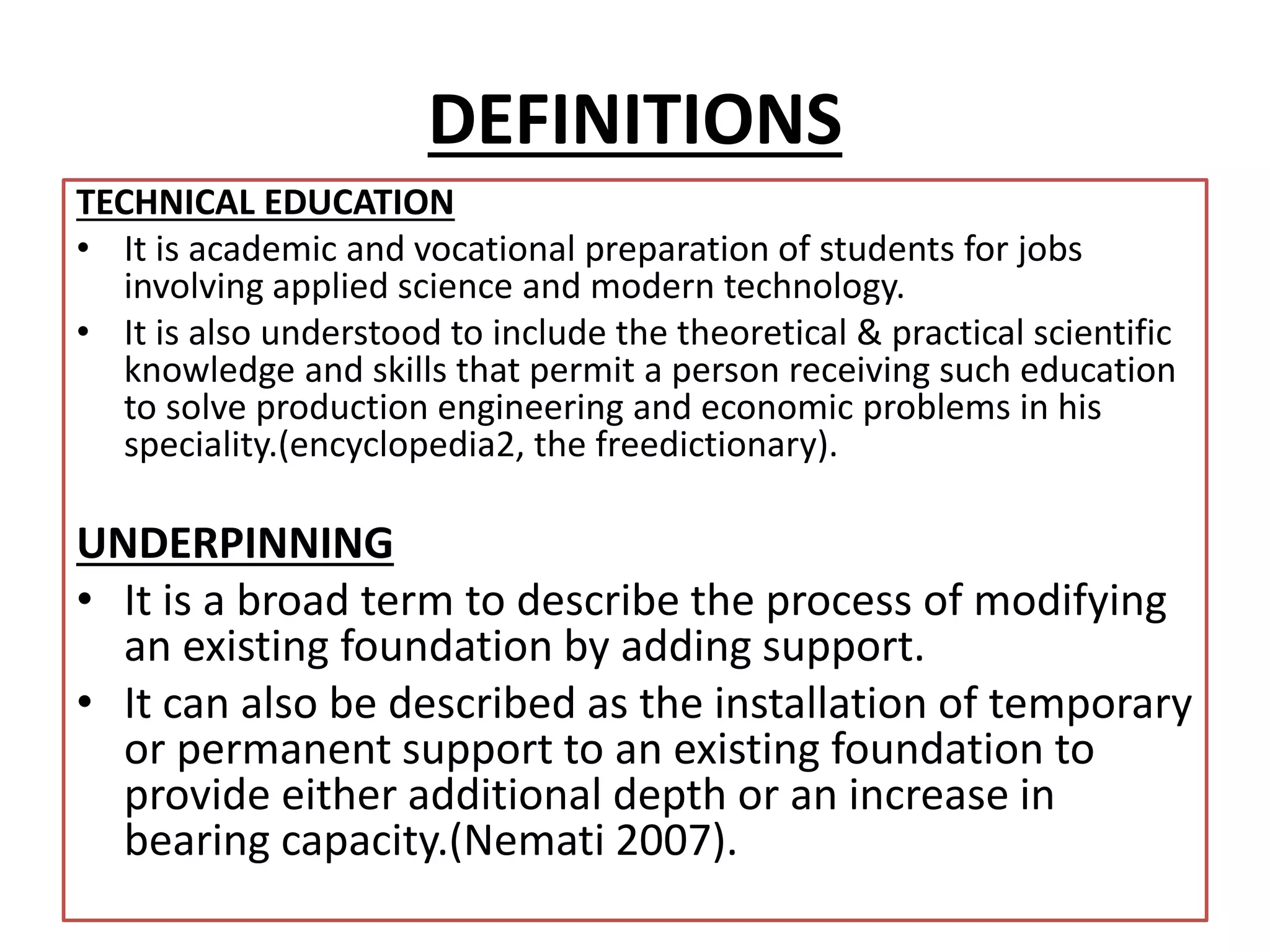
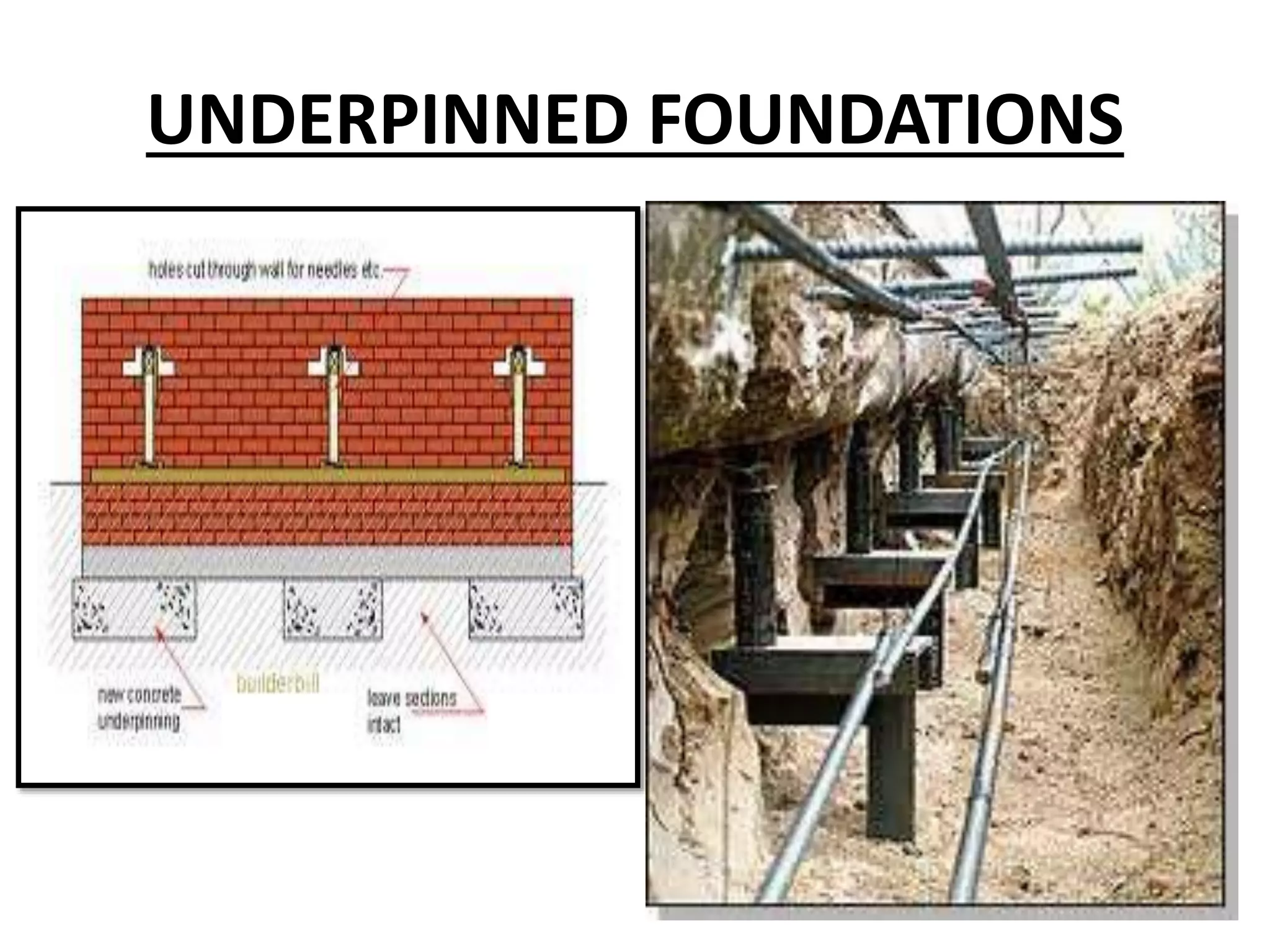
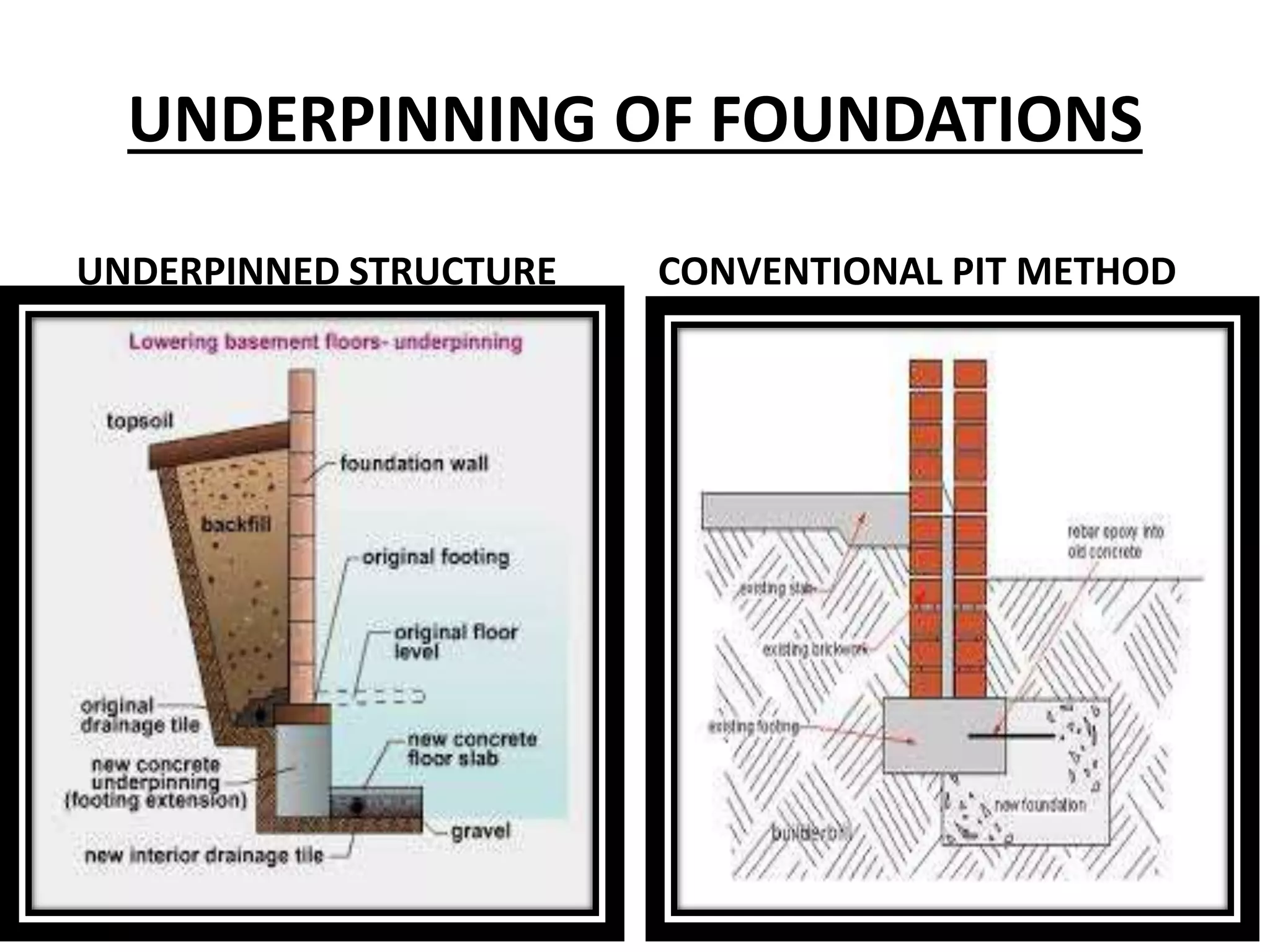
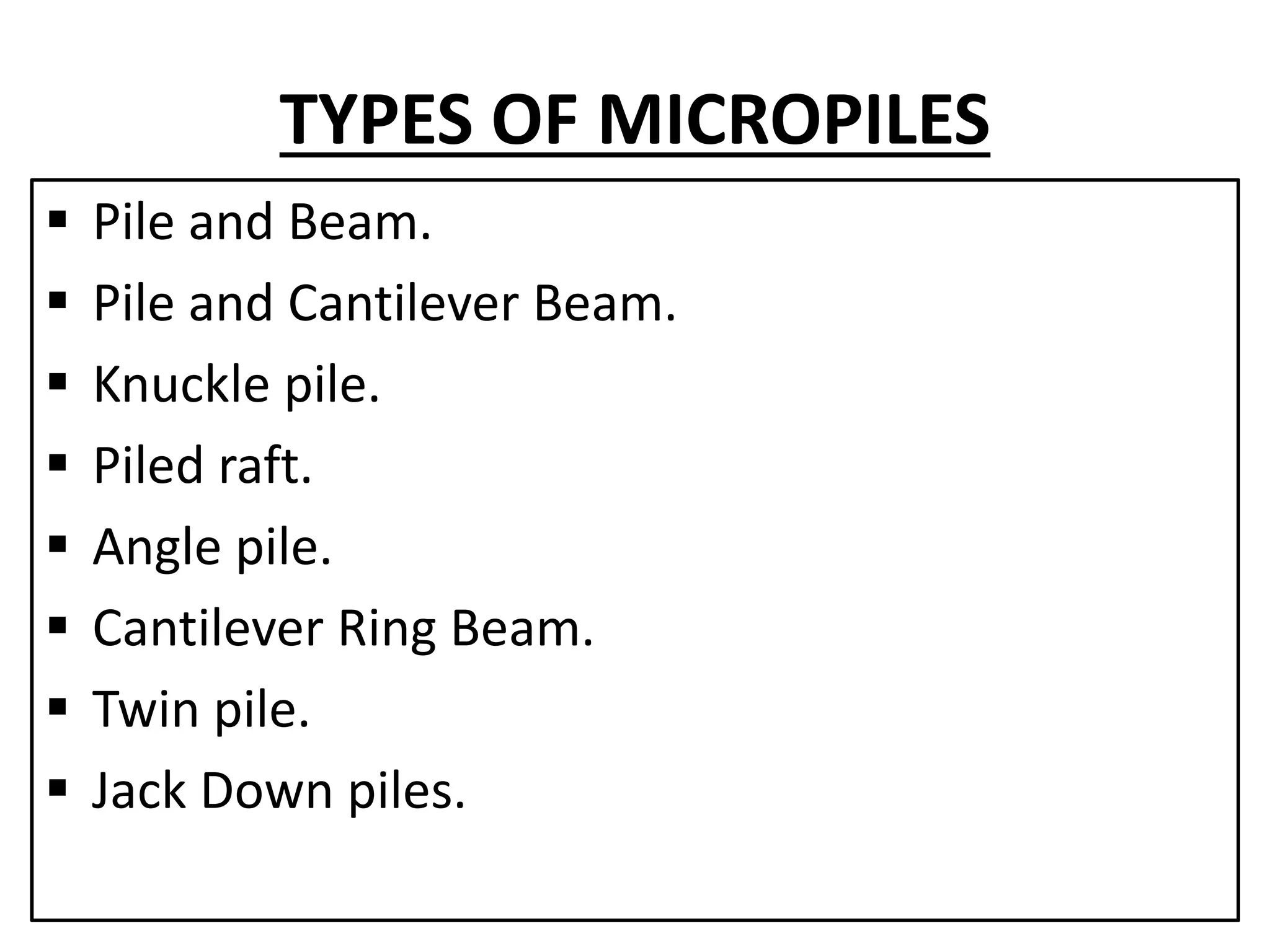
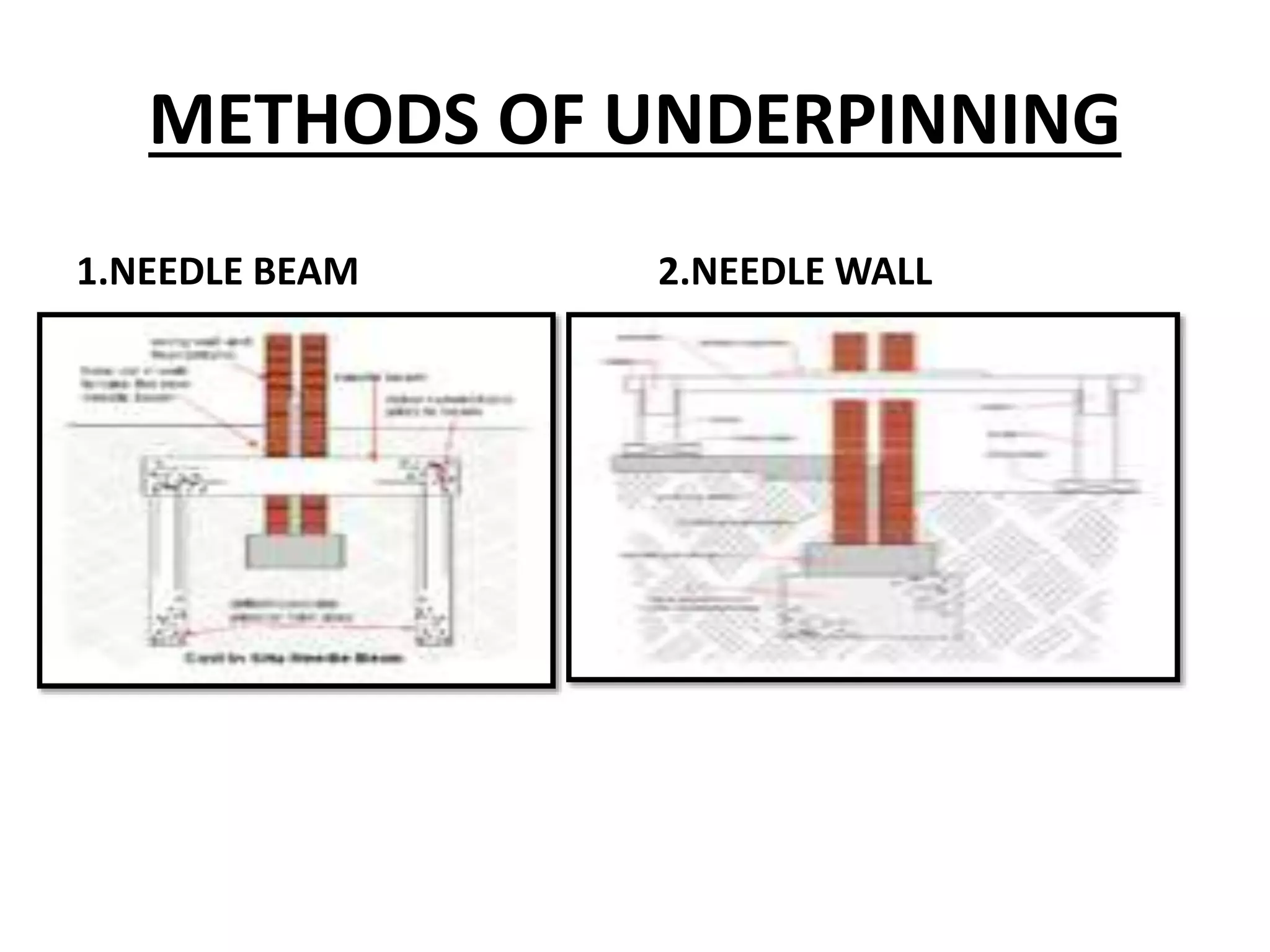
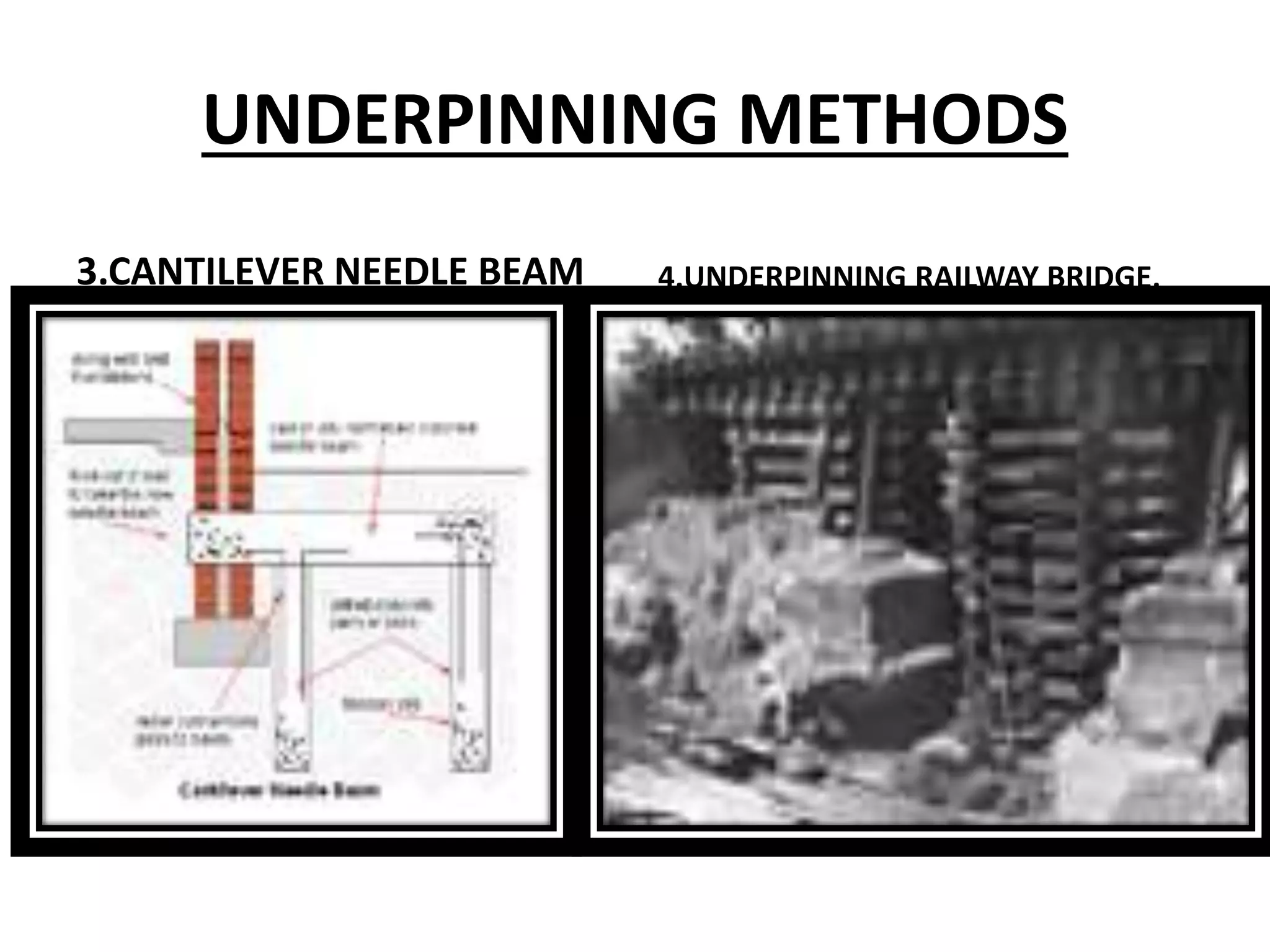
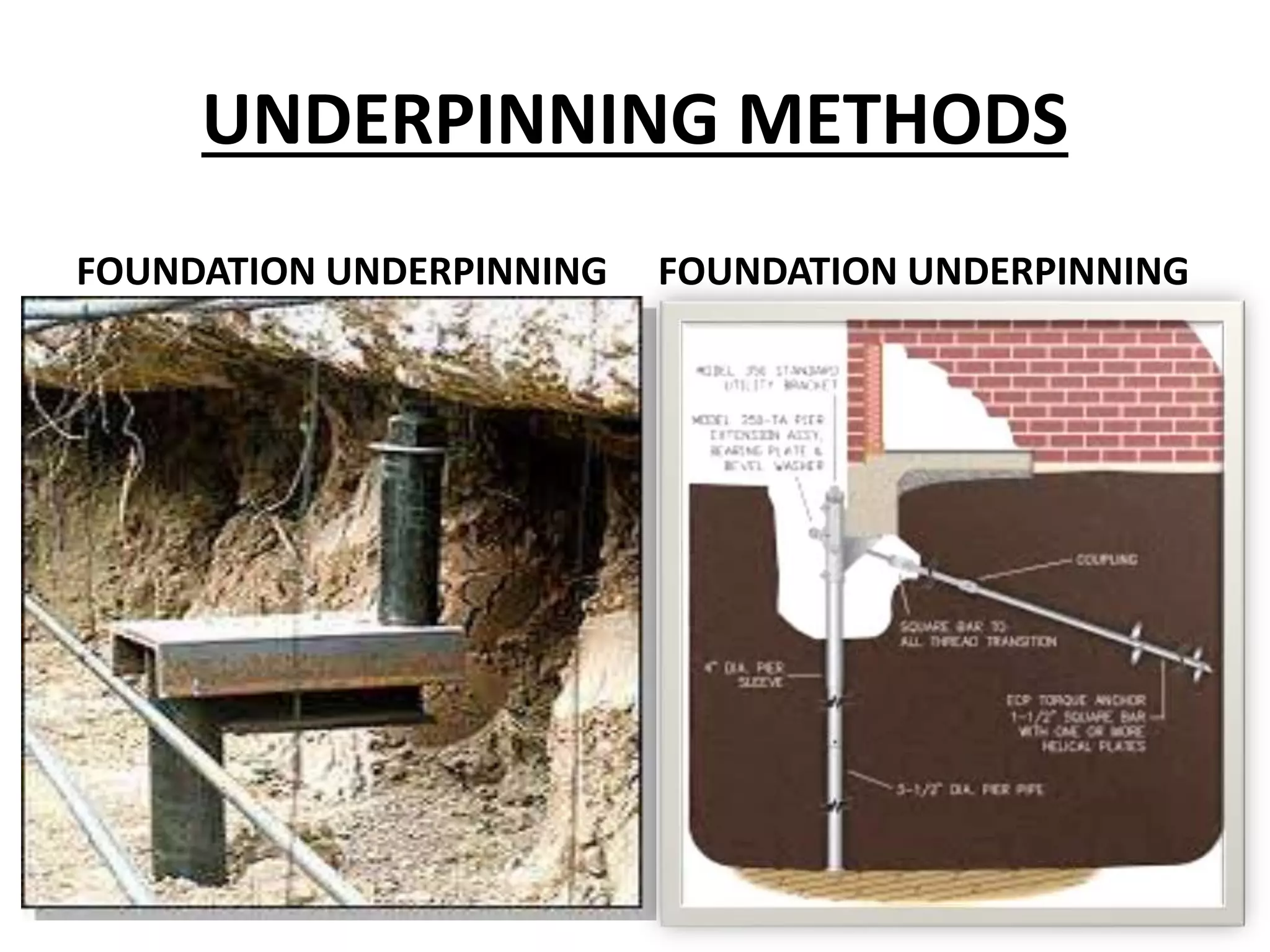
This document discusses technical education and underpinning foundations. It begins with definitions of technical education and underpinning. Reasons for underpinning include new construction, structural issues, soil instability, and excavation. Common underpinning methods discussed include conventional pit method, jet grouting, micropiles, needle beams, cantilever needle beams, and underpinning railway bridges. The document emphasizes that underpinning requires expert design and execution to safely renovate structures and protect surrounding buildings.