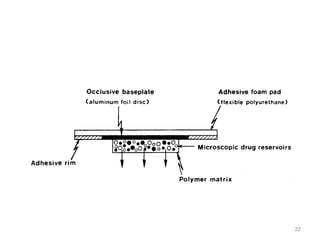
This document provides an overview of transdermal drug delivery systems (TDDS). It discusses the advantages and limitations of TDDS, skin structure, components of transdermal patches, types of patches, factors affecting transdermal permeability, polymers used, therapies that use TDDS, classification of TDDS, basic components, evaluation, and drug release mechanisms. The document contains detailed information on formulation, evaluation parameters, in vitro and in vivo testing of TDDS.


















![• the rate of drug release from this sytem is defined as
A Cp Dp
Dq/dt = [ ---------------------] 1/2
2t
where
A initial drug loading dose
Cp and Dp are solubility and diffusivity of drug in poymer matrix
the rate of drug release from this system at steady state is defined as
Q/t1/2= [(2A-Cp) Cp Dp] 1/2
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tdds-140930004526-phpapp01/85/Tdds-19-320.jpg)