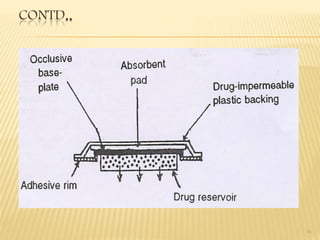
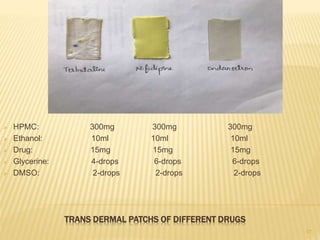
Transdermal drug delivery systems (TDDS) are patches that deliver drugs through the skin for systemic effects. They have advantages like avoidance of first-pass metabolism and increased patient compliance. The key components of TDDS include a drug reservoir, rate-controlling membrane, adhesives, and backing membrane. There are various approaches to formulation, including polymer membrane and matrix systems. Evaluation involves testing the patches' thickness, drug content, adhesion, stability, and skin permeation in diffusion cell studies. TDDS can effectively deliver drugs while overcoming challenges like limited skin permeability.
























![References:
• Dr. dheeraj T. baviskar, Dr. dinesh K. jain; Novel
drug delivery. Nirali prakashan;2016 .
• Jonathan hadgraft, Richard H. guy; transdermal
drug delivery. Marcel dekker, newyork;1989 .
• Joseph R. robinson, Vincent H.L.Lee; controlled
drug delivery. Informa health care, newyork
[Edition 2]; 2009 .
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tdds-180404091916/85/TDDS-by-Ranjeet-singh-27-320.jpg)
