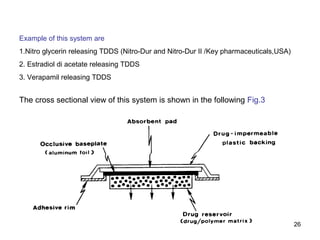
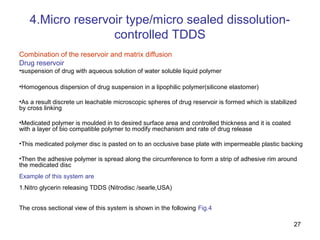
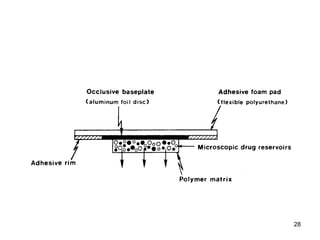
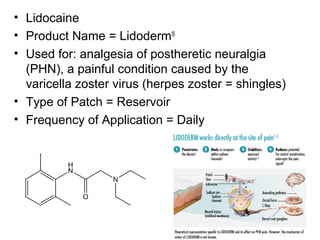
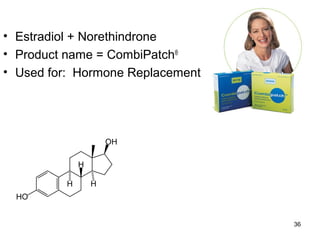
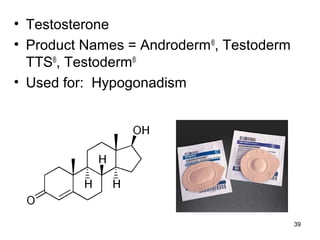
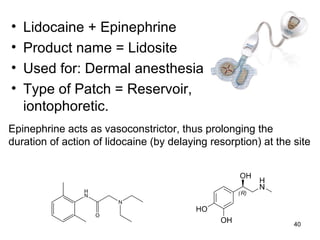
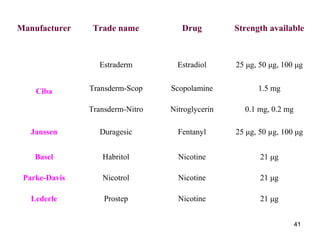
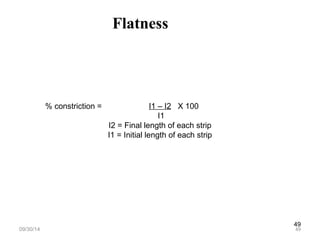
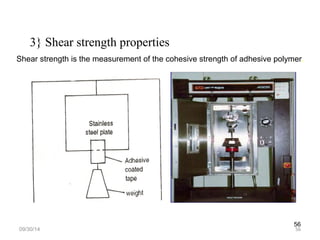
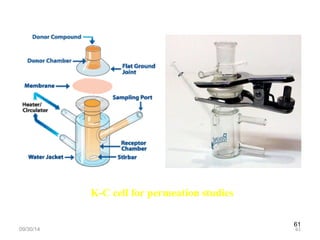
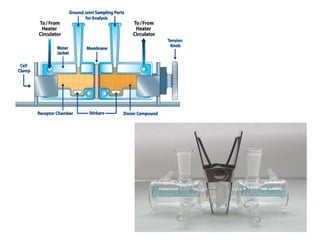
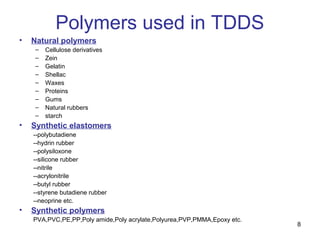
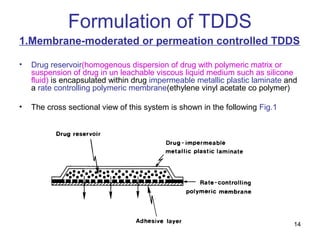
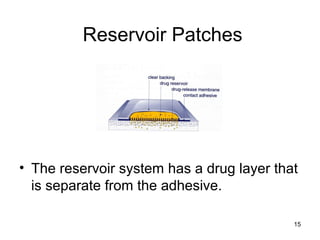
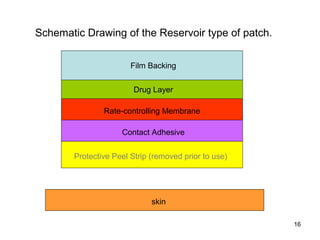
The document discusses transdermal drug delivery systems (TDDS), outlining their advantages such as elimination of oral absorption variables and the ability to self-administer. It also details limitations, design factors, and the essential components involved in TDDS including polymers, drug candidates, permeation enhancers, and adhesives. Furthermore, various types of transdermal systems, market products, and evaluation parameters are presented, emphasizing the mechanisms of drug release and application methods.














![25
• the rate of drug release from this sytem is defined as
A Cp Dp
Dq/dt = [ ---------------------] 1/2
2t
where
A initial drug loading dose
Cp and Dp are solubility and diffusivity of drug in poymer matrix
the rate of drug release from this system at steady state is defined as
Q/t1/2= [(2A-Cp) Cp Dp] 1/2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mpharmtdds-140930003508-phpapp02/85/M-pharm-tdds-25-320.jpg)