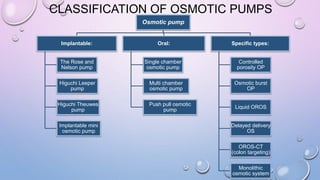
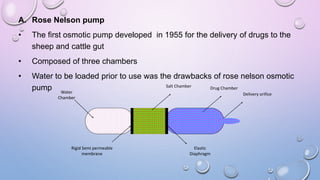
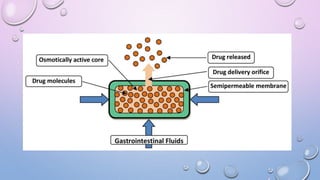
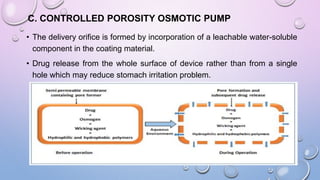
Osmotic drug delivery systems use osmotic pressure to provide controlled release of drugs over extended periods of time. They consist of a drug core surrounded by a semipermeable membrane with a delivery orifice. When exposed to fluids, osmotic pressure causes water to enter the system, dissolving the drug and pushing it out through the orifice at a controlled rate. The three main types are Rose-Nelson pumps, elementary osmotic pumps, and controlled porosity osmotic pumps. These systems offer advantages over traditional methods for conditions requiring prolonged, consistent drug levels.