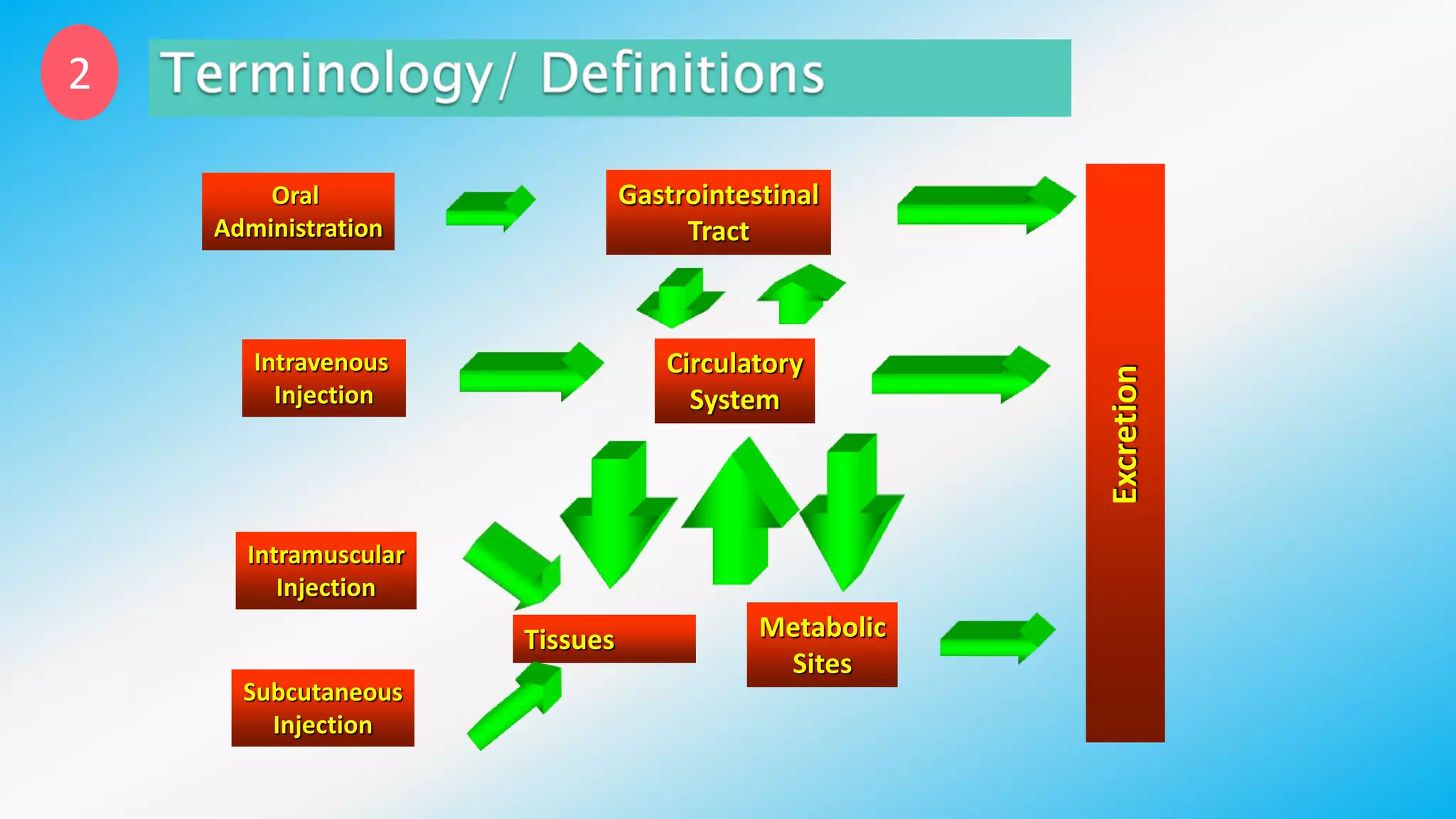
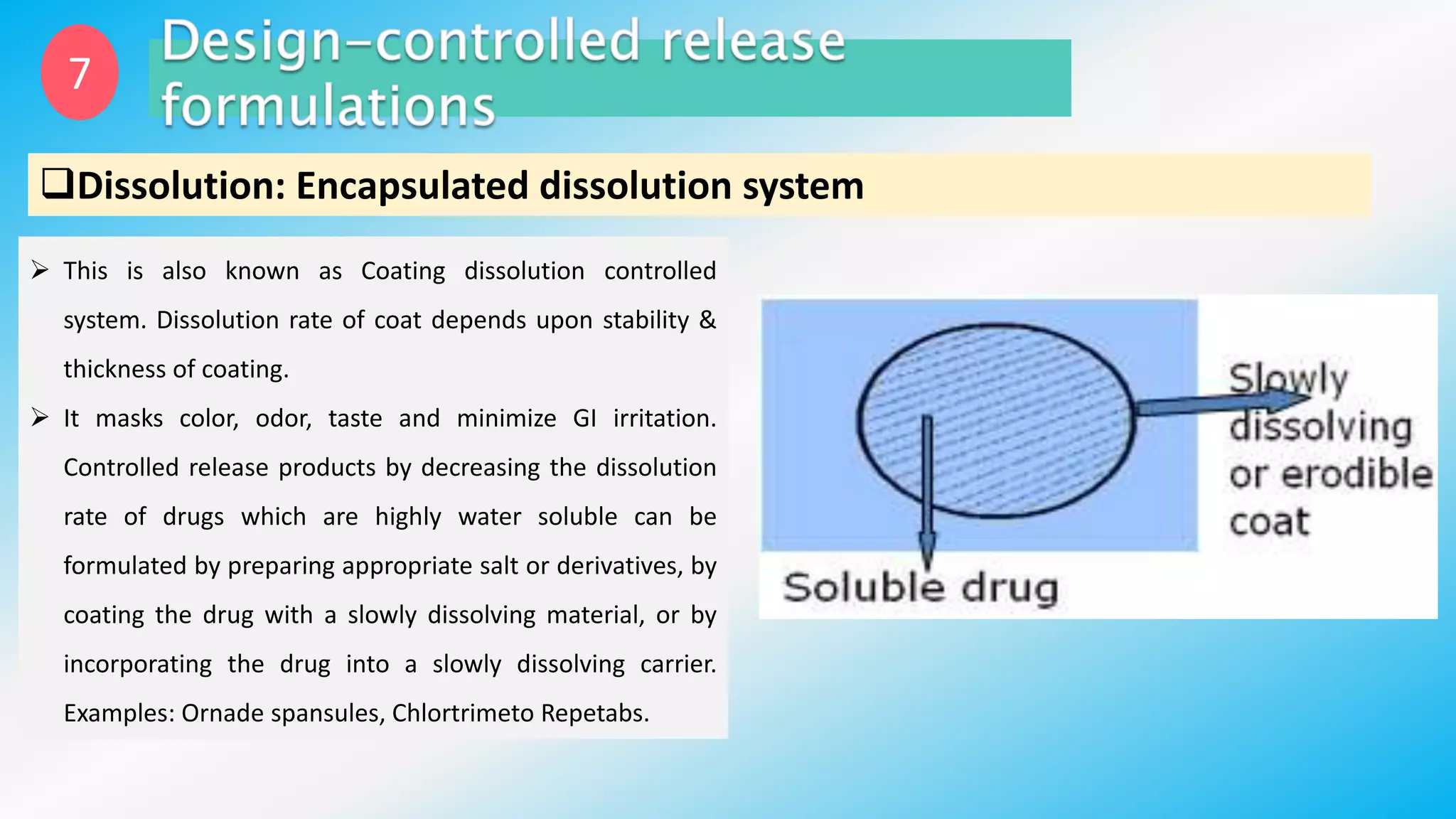
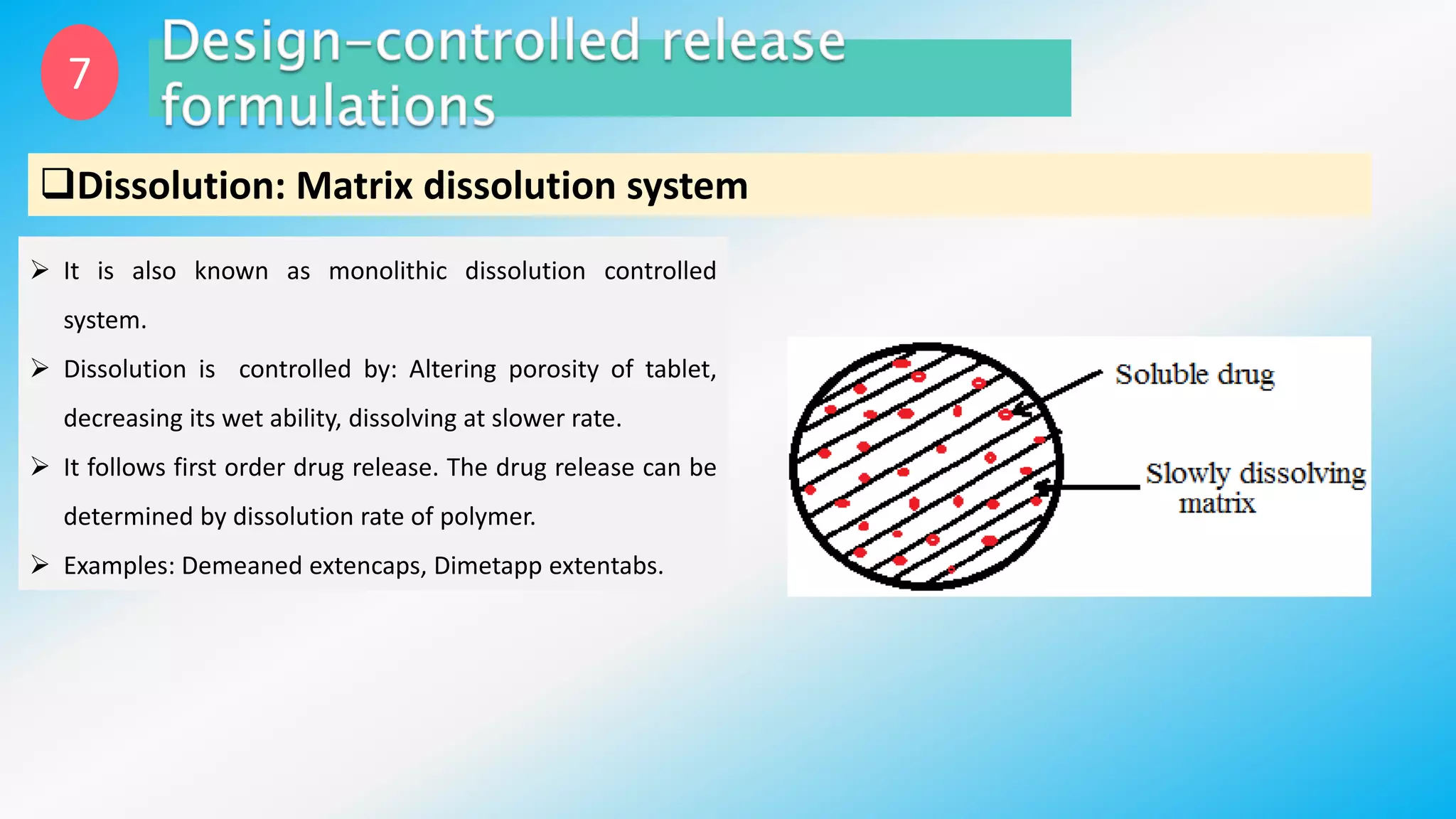
Controlled drug delivery systems (CDDS) are designed to release drugs at predetermined rates for specified durations, enhancing patient compliance and treatment efficacy. The development of these systems has evolved since the 1940s, with significant advantages over conventional delivery methods, though they also present challenges such as higher costs and potential toxicity risks. Ideal CDDS are biocompatible, mechanically strong, and capable of delivering drugs safely while minimizing side effects and administration frequency.