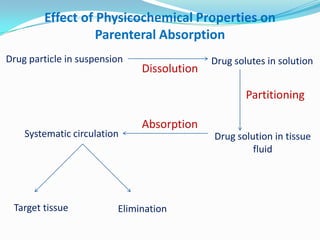
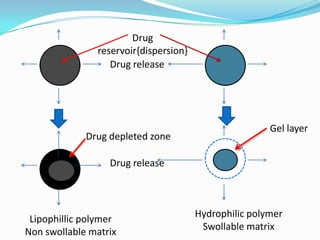
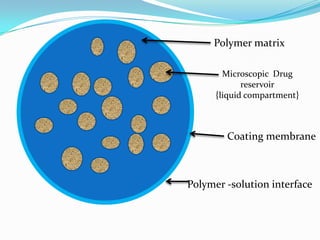
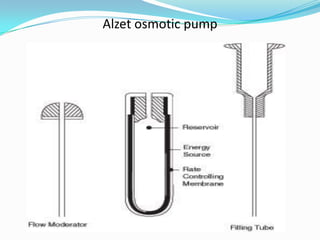
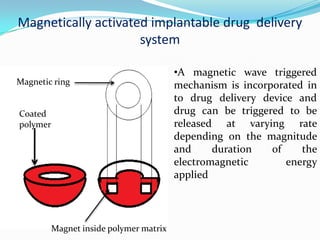
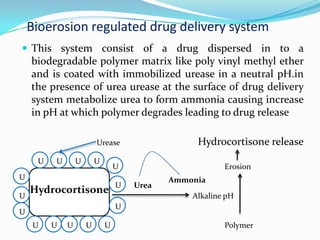
This document discusses various approaches to developing implantable drug delivery systems, including controlled drug delivery via diffusion, activation processes, and feedback regulation. It describes systems that use polymer membranes, matrices, microreservoirs, and hybrid designs to control drug release rates. Activation methods include osmotic pressure, vapor pressure, magnetism, hydration, and hydrolysis. Feedback systems can be regulated by bioerosion and bioresponses to biochemical factors. The document provides examples of implantable systems and discusses how drug and system properties influence release kinetics.