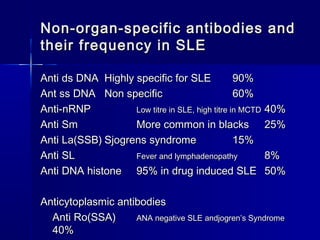
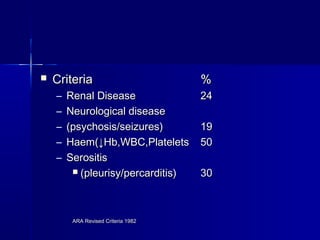
This document discusses systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an inflammatory disease that results in multisystem involvement with a varied clinical presentation. SLE is more common in women and African Americans. Genetic and environmental factors may predispose individuals to SLE. The disease is characterized by autoantibody production, immune complex formation, and tissue damage. Certain drugs can also cause a lupus-like condition. The document outlines diagnostic criteria for SLE, treatments including corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, and issues regarding prognosis and management of the disease.