Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is an inflammatory autoimmune disease characterized by excessive autoantibody production leading to tissue damage. It has a wide variety of clinical manifestations that can affect many different organ systems. Some key points:
- SLE predominantly affects women of childbearing age and has a strong genetic component. Certain genetic and environmental factors can increase risk.
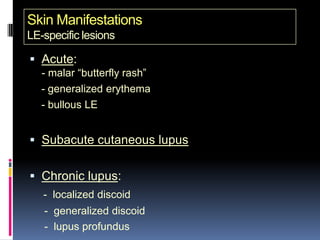
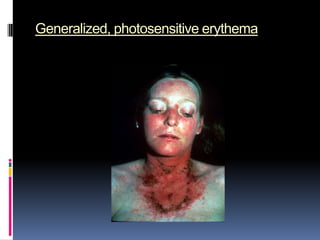
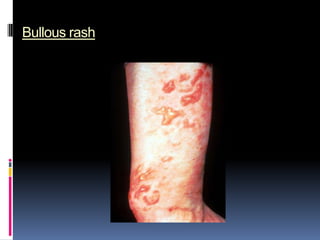
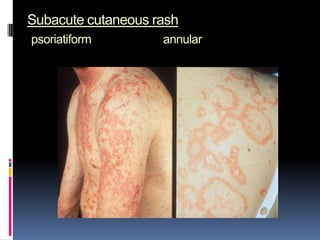
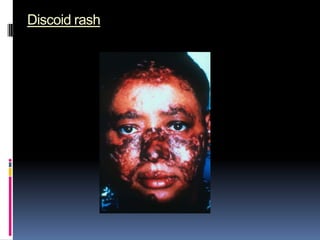
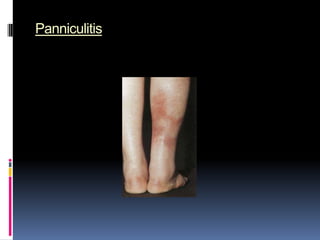
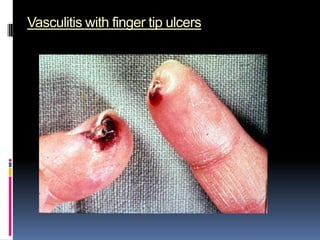
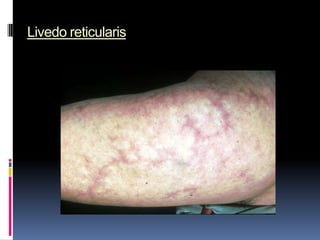
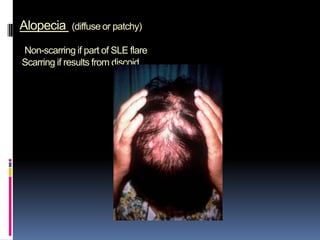
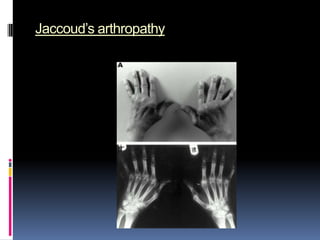
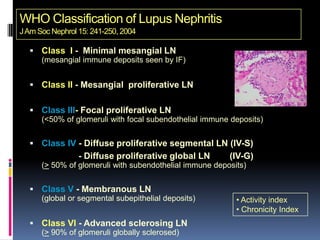
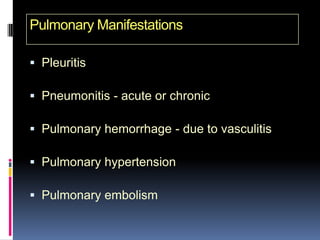
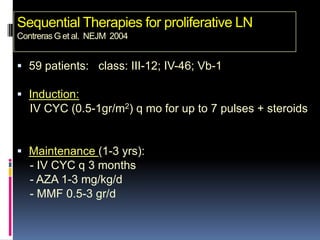
- Clinical features include skin rashes, arthritis, kidney involvement ranging from mild proteinuria to severe nephritis, neurological/psychiatric symptoms, hematological abnormalities and involvement of other organs.
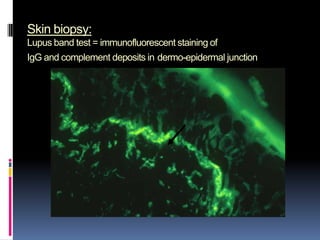
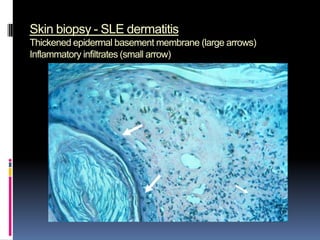
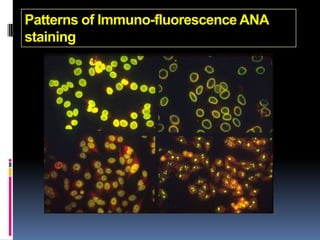
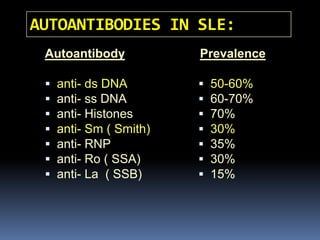
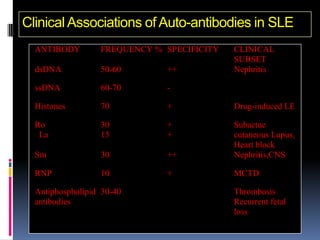
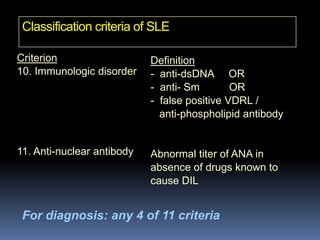
- Diagnosis is based on identifying a combination of clinical and laboratory criteria including high titers of antinu