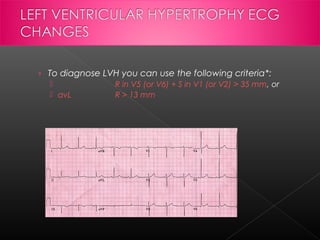
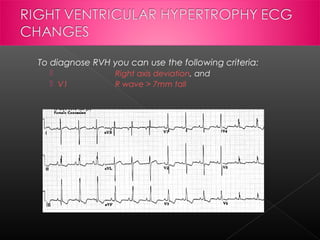
Left ventricular hypertrophy is an increase in the mass of the left ventricle that can be caused by hypertension, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, aortic stenosis, or athletic training. It is defined on an ECG as increased voltages in certain leads. Risk factors include age, gender, high blood pressure, obesity, and genetic factors. If left untreated, LVH can lead to heart failure, arrhythmias, heart attack, or sudden cardiac death. Right ventricular hypertrophy is the enlargement of the right ventricle and can be caused by pulmonary hypertension, congenital heart defects, or lung diseases. Both LVH and RVH are diagnosed using ECG criteria and can cause chest pain, palpitations