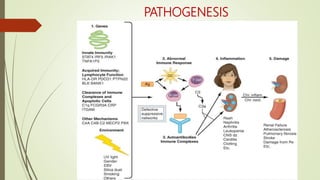
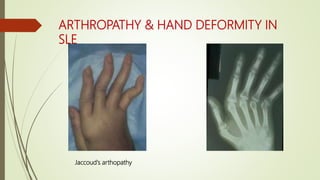
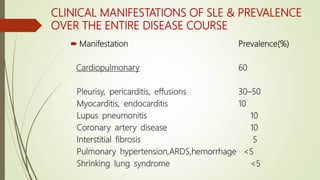
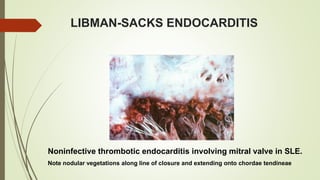
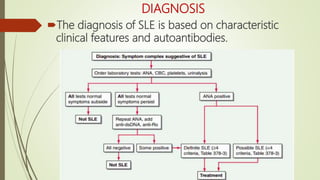
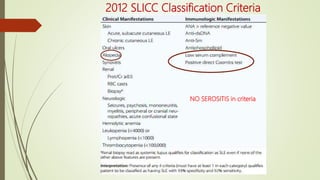
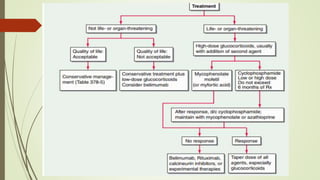
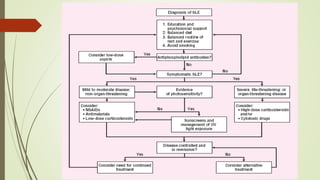
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease most common in women of childbearing age. It can affect multiple organ systems. Common manifestations include fatigue, arthritis, rashes, hematologic abnormalities, and kidney involvement. The diagnosis is based on clinical features and autoantibodies. Treatment involves medications to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system such as antimalarials, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants. Lupus nephritis requires aggressive therapy with corticosteroids and immunosuppressants like cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate mofetil. Research is ongoing into more targeted biologic therapies.




![RISK FACTORS FOR SLE
Female sex
Oestrogen containing OCP or HRT (1.2- to 2-fold)
XXY karyotype (Klinefelter’s syndrome)
Exposure to UV light causes SLE flares in approx. 70% patients.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) can trigger SLE in susceptible individuals
Current tobacco smoking (odds ratio [OR] 1.5)
Prolonged occupational exposure to silica (OR 4.3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systemiclupuserythematosus-myppt-160827102639/85/Systemic-lupus-erythematosus-6-320.jpg)








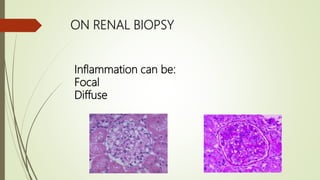

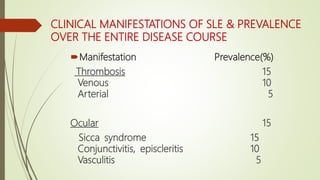
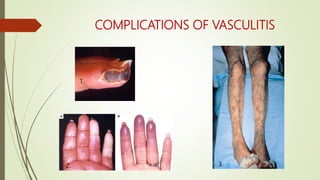
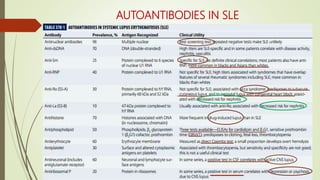




























![Poor Prognostic Factors
High serum creatinine levels (>124 μmol/L [>1.4 mg/dl])
Hypertension
Nephrotic syndrome (24-h urine protein excretion >2.6 g)*
Anemia (haemoglobin <124 g/L [<12.4 g/dl])
Hypoalbuminemia
Hypocomplementemia
Antiphospholipid antibodies
Male sex
Ethnicity (african american, hispanic with mestizo heritage)
Low socioeconomic status](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systemiclupuserythematosus-myppt-160827102639/85/Systemic-lupus-erythematosus-57-320.jpg)


