Embed presentation
Downloaded 23 times
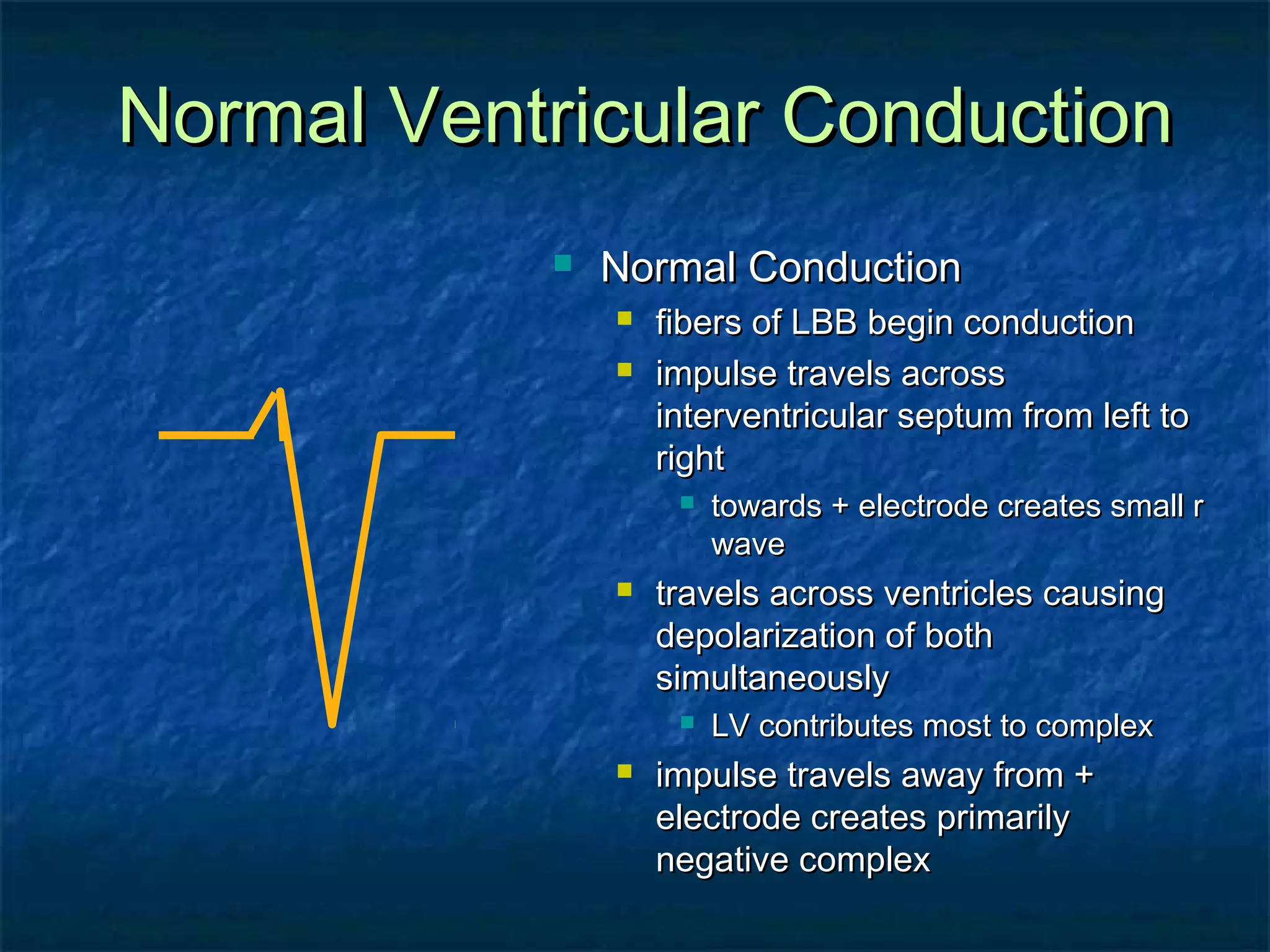
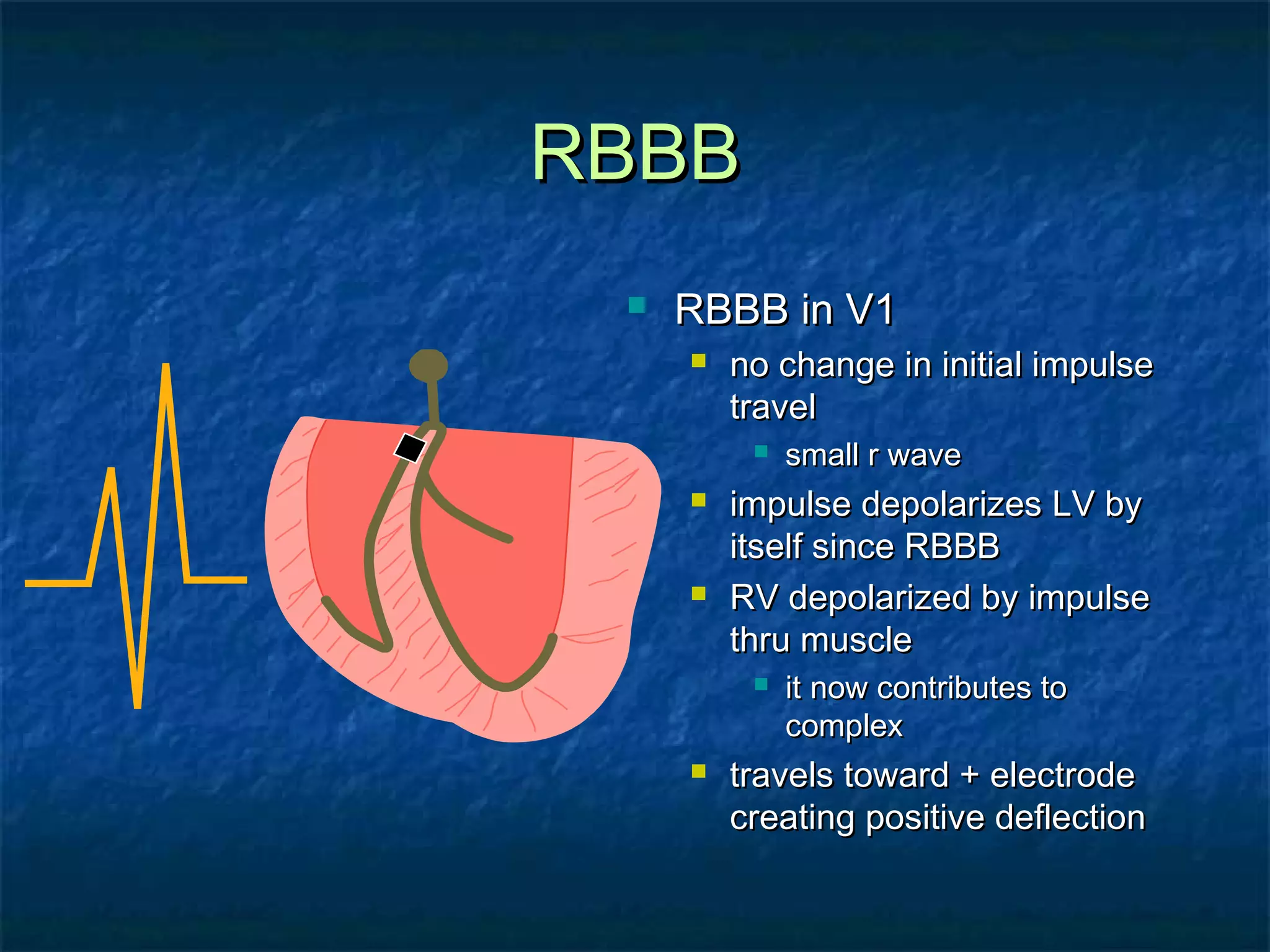
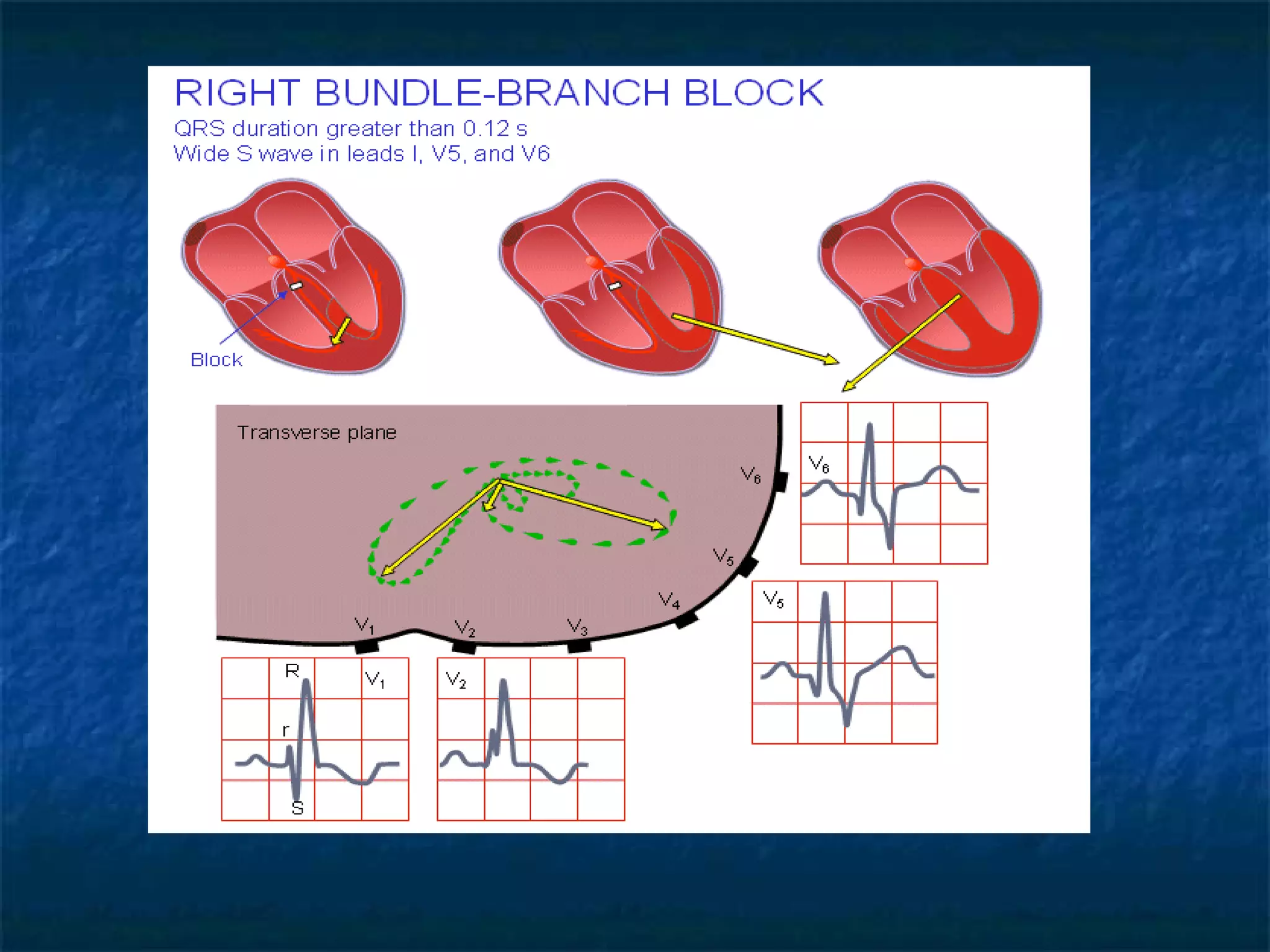
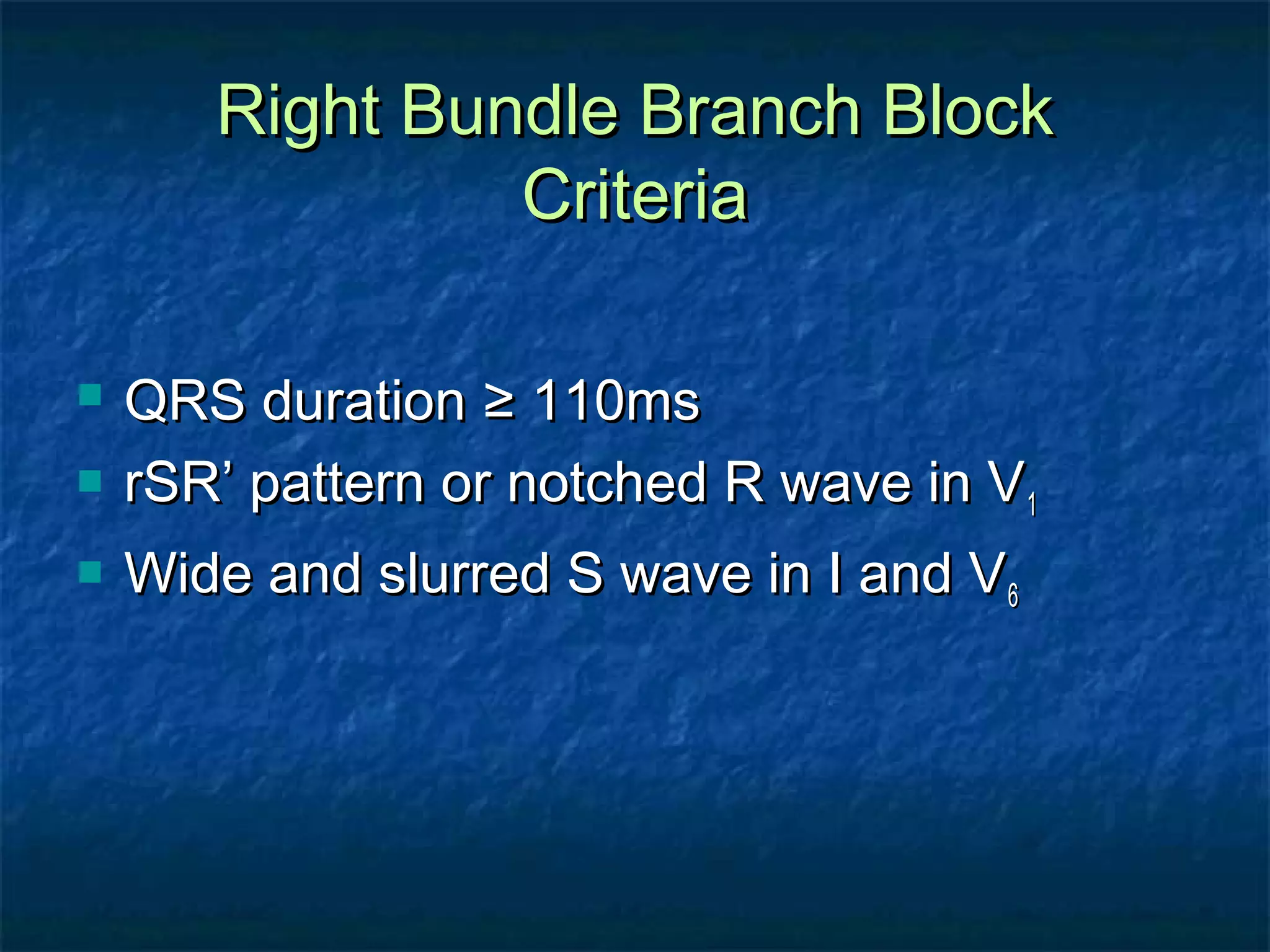
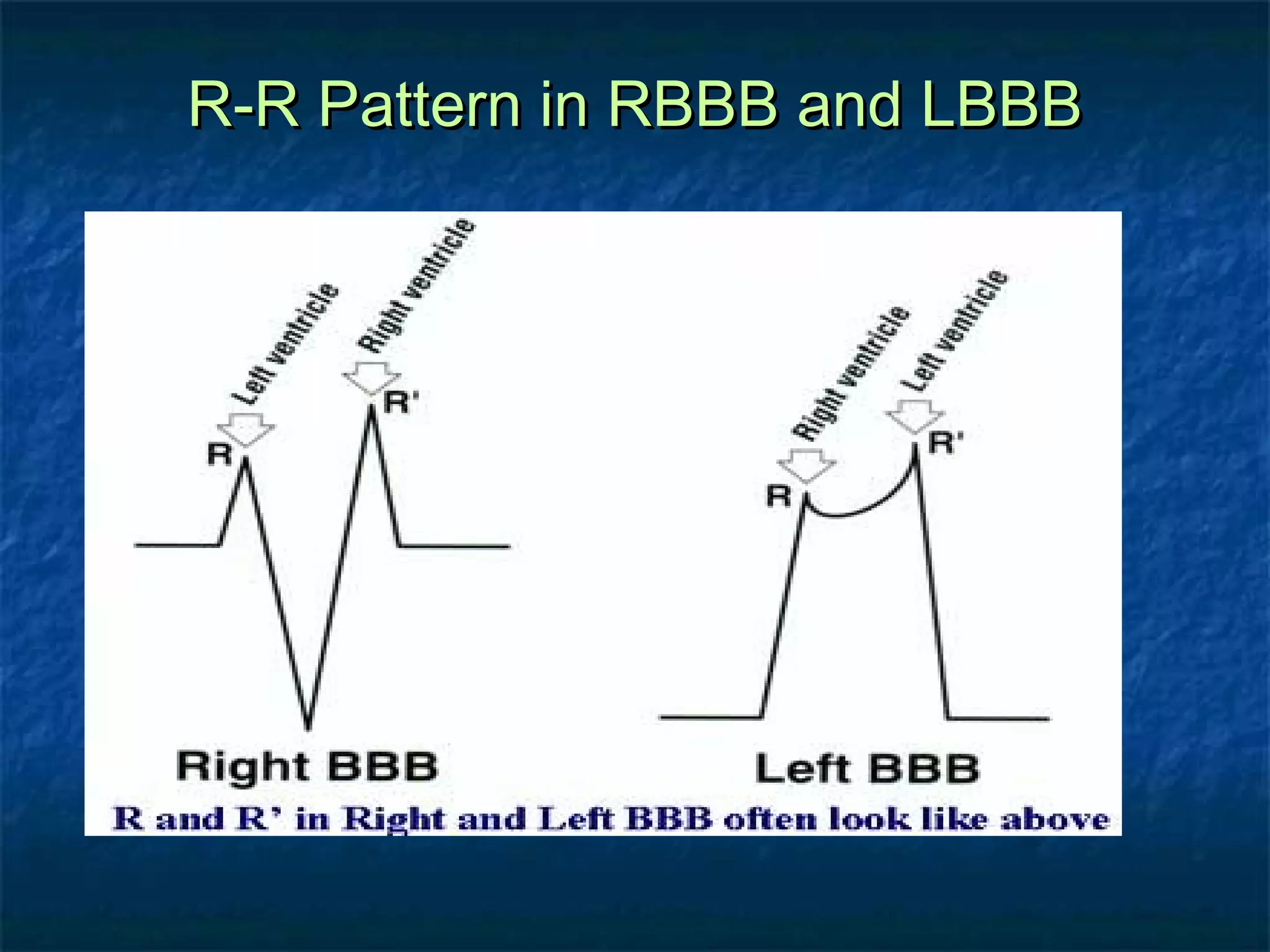
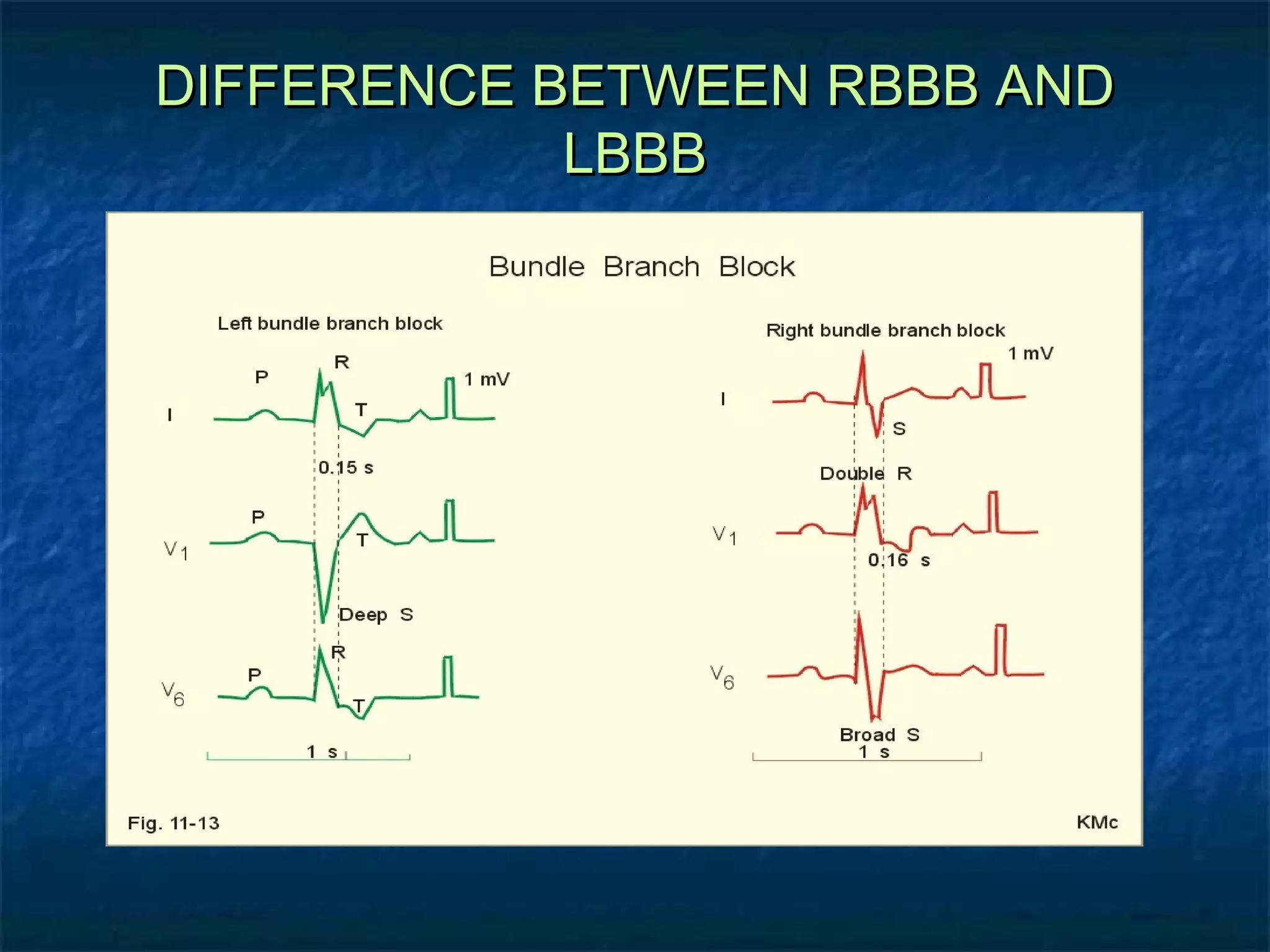

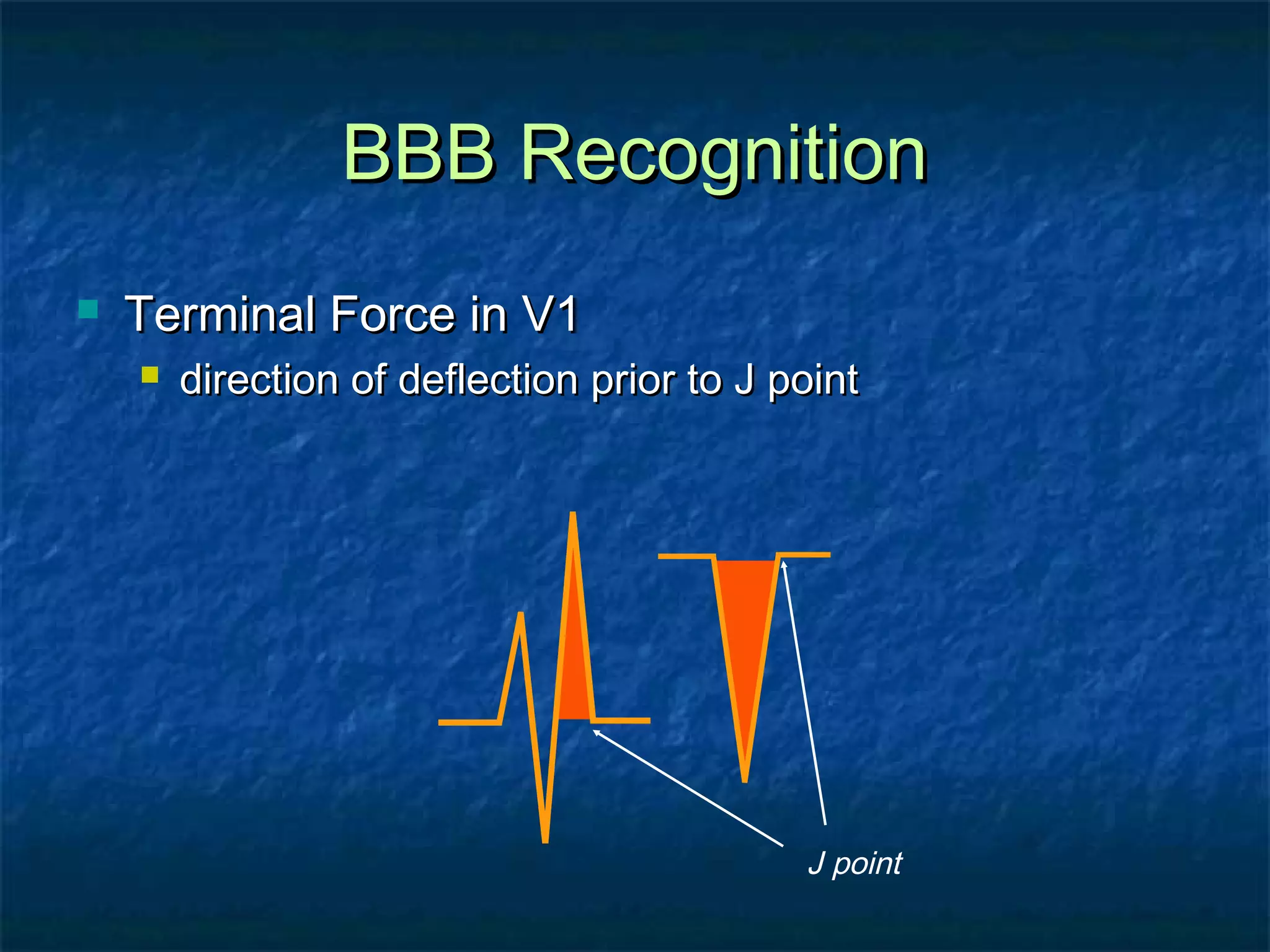
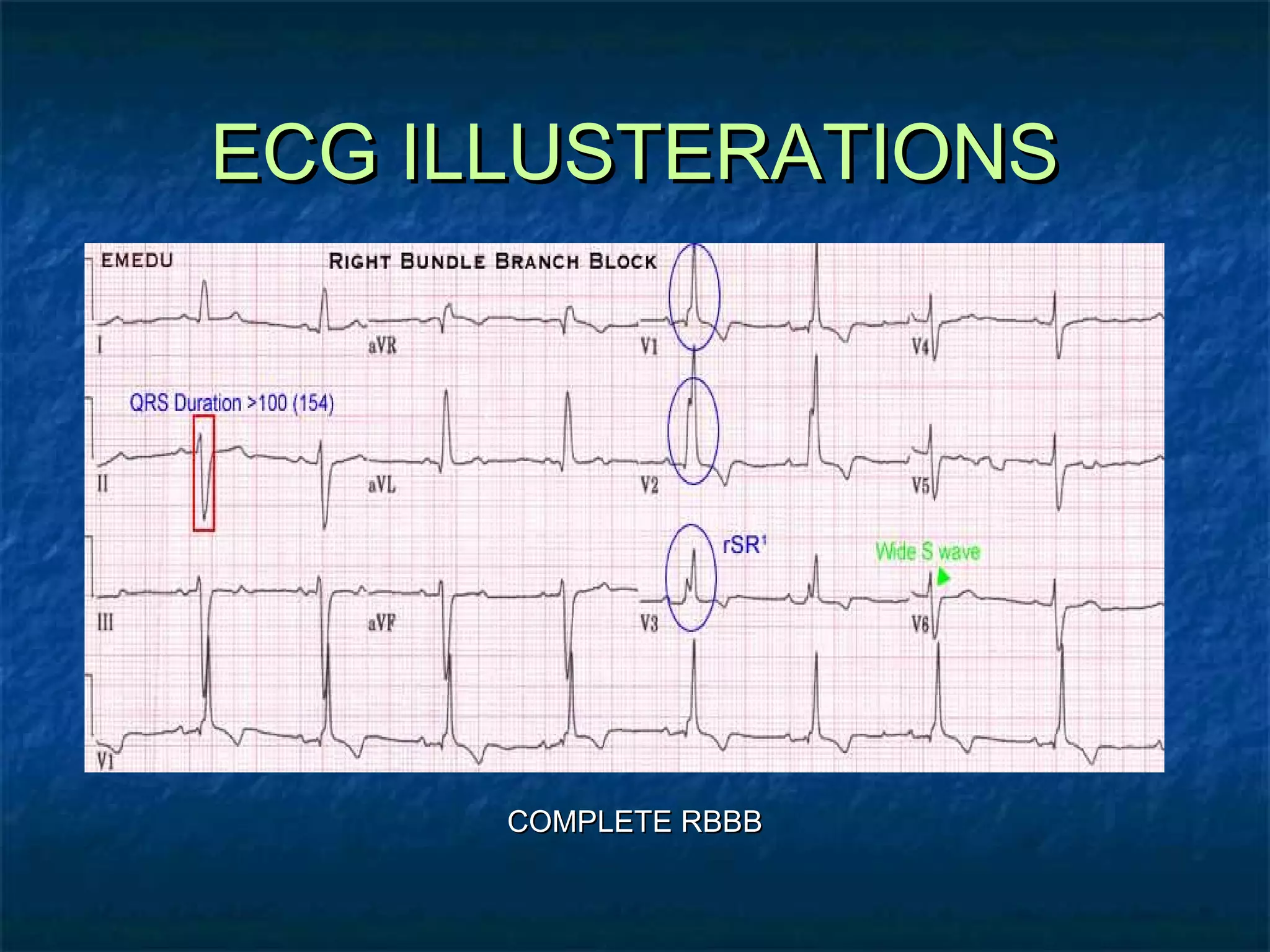
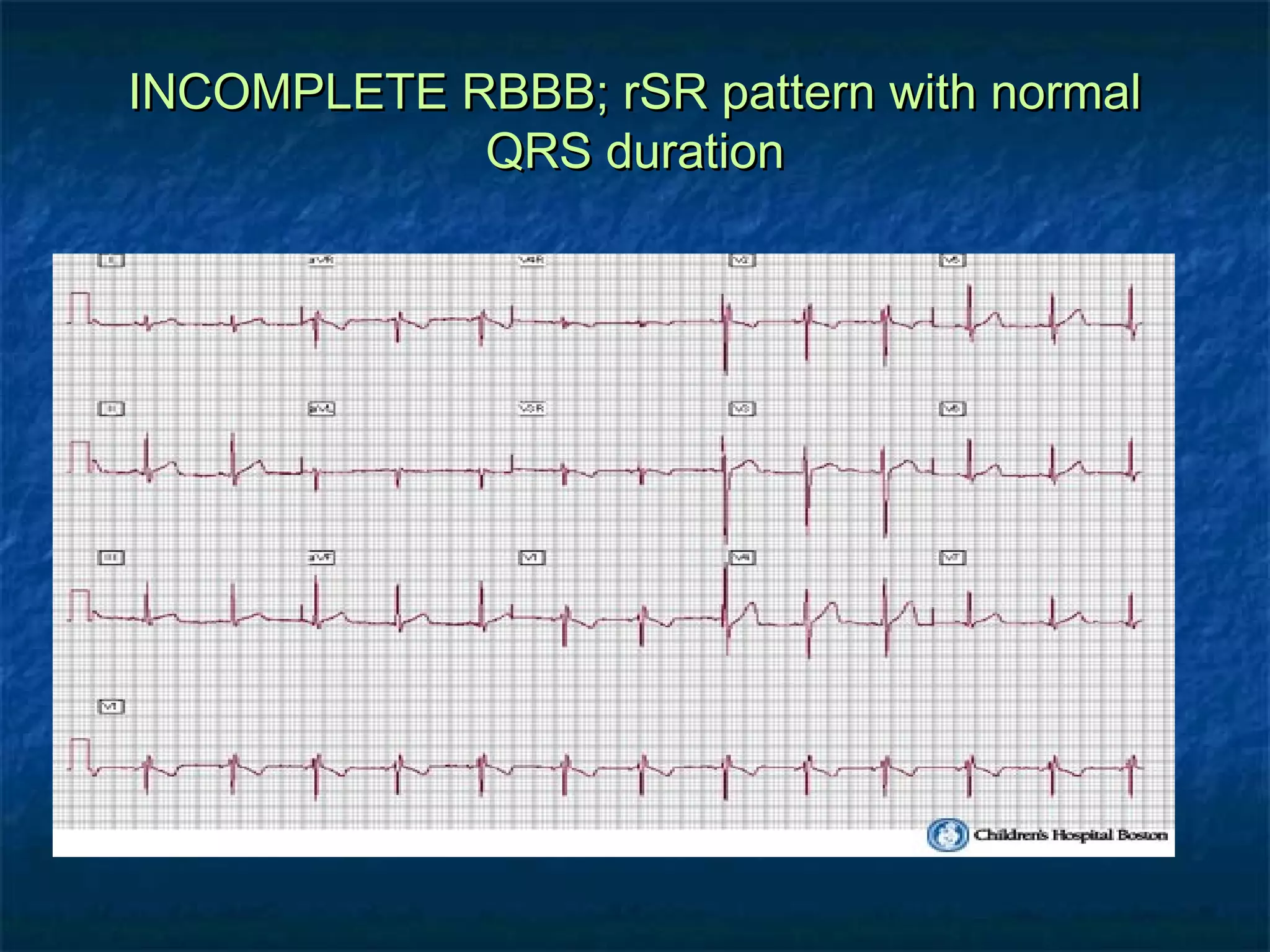
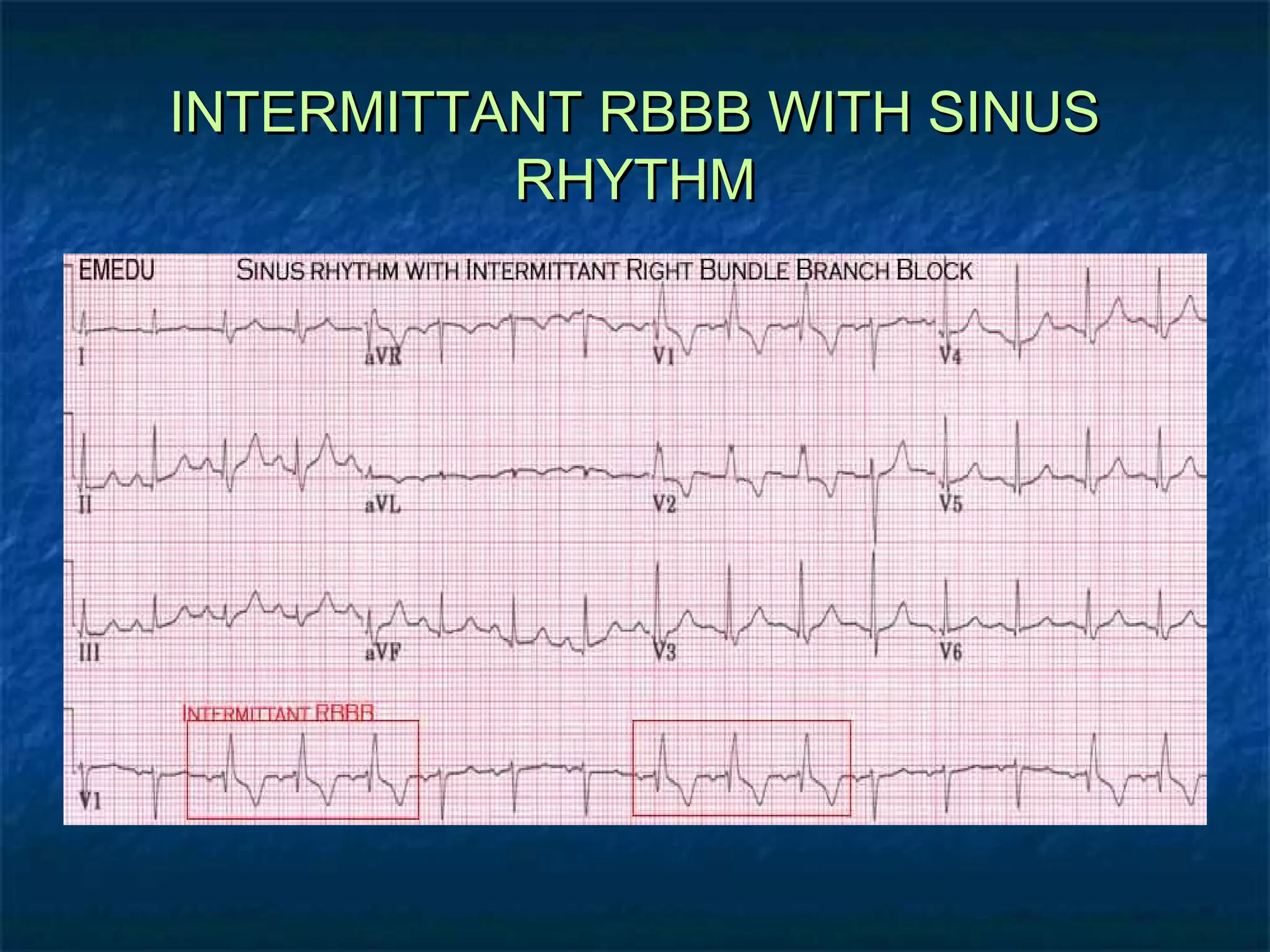
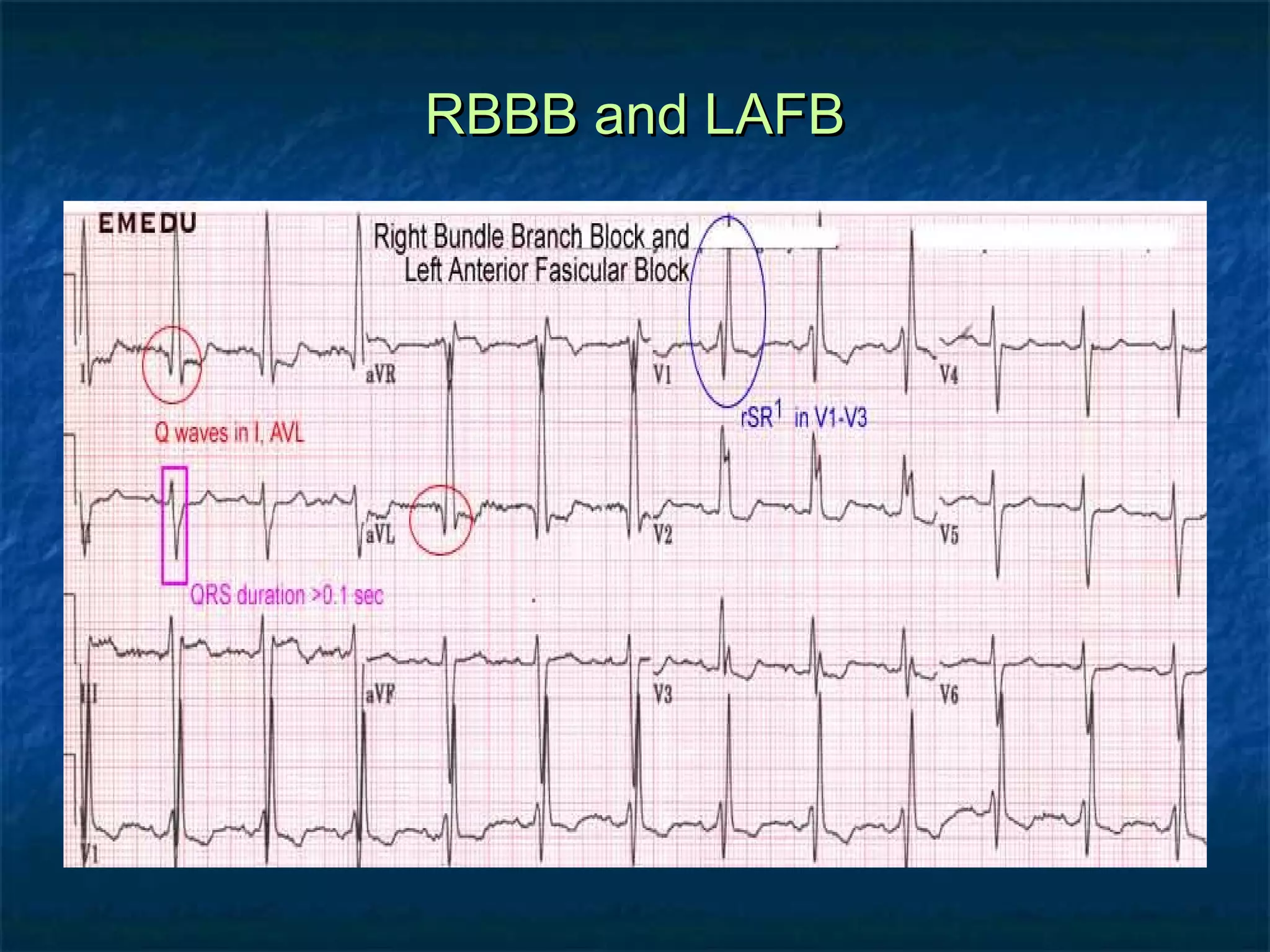
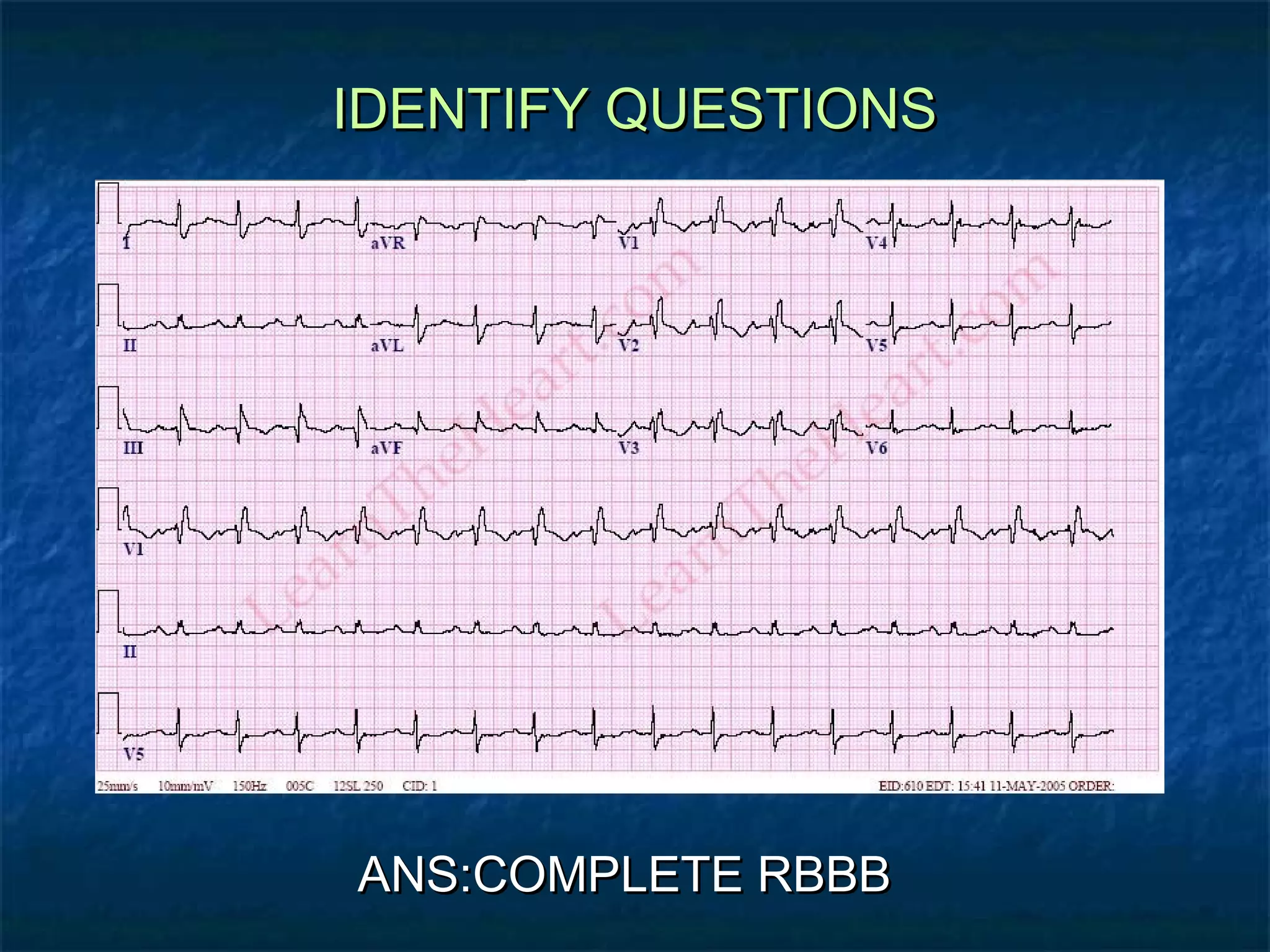
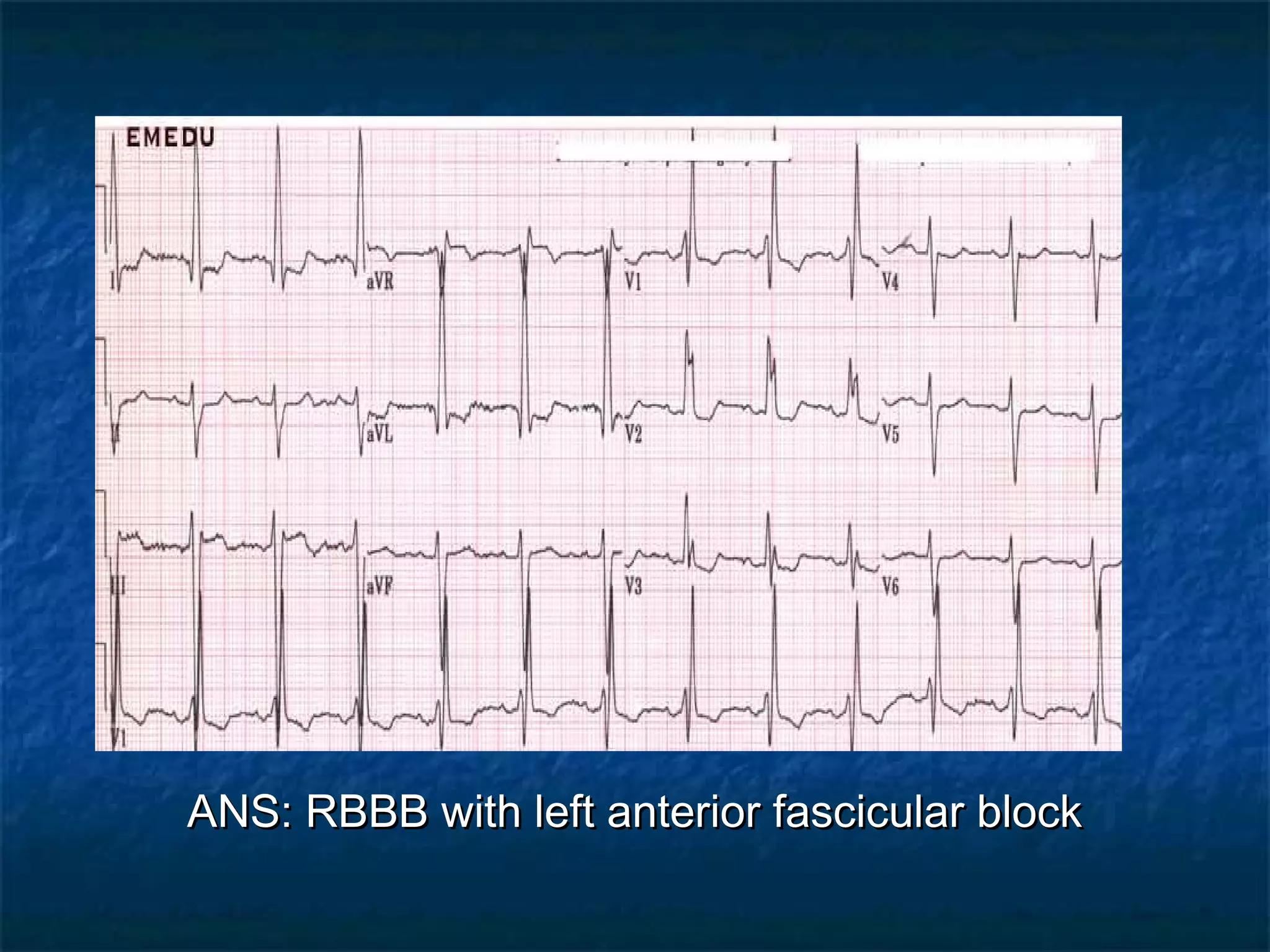
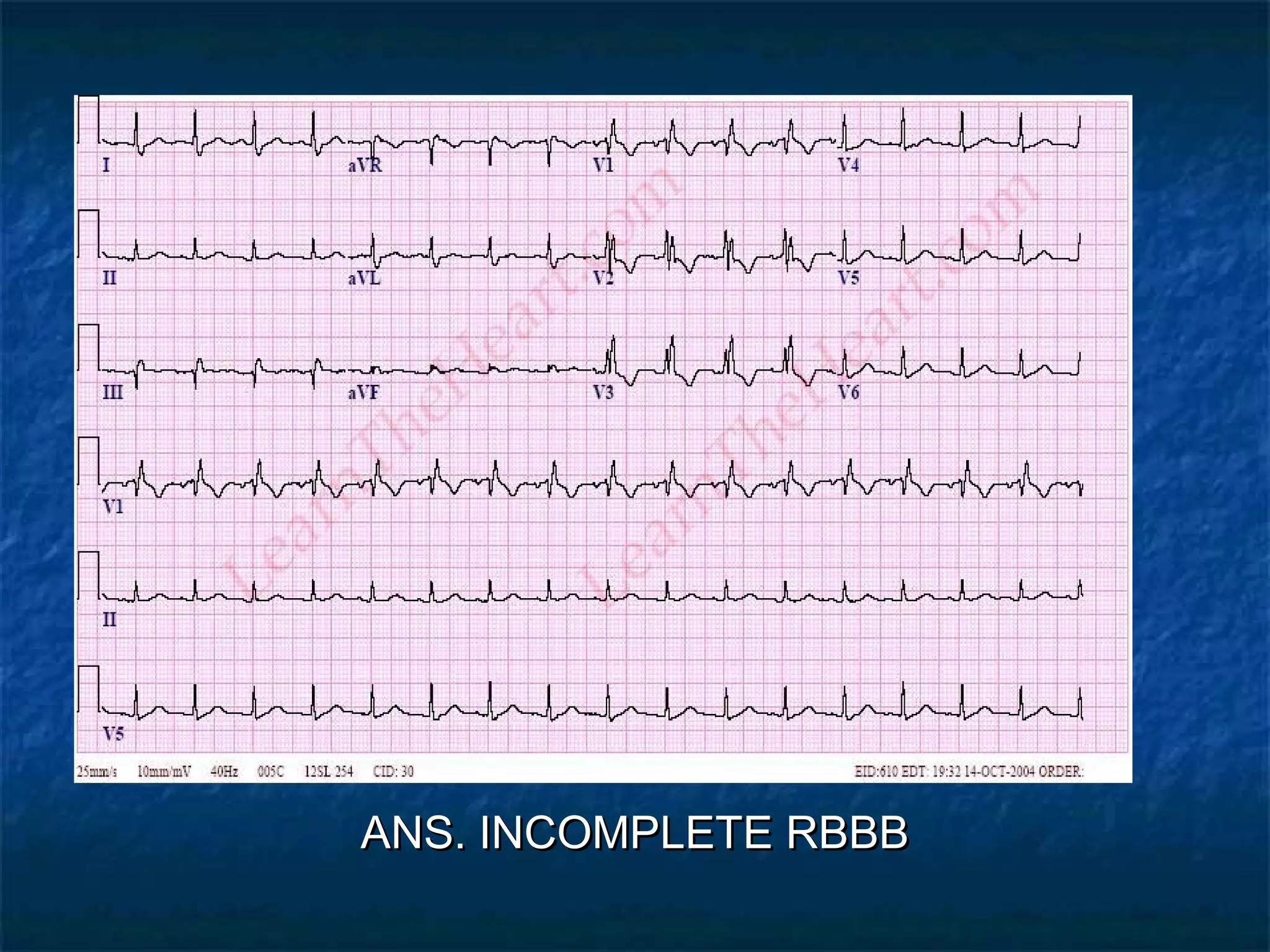
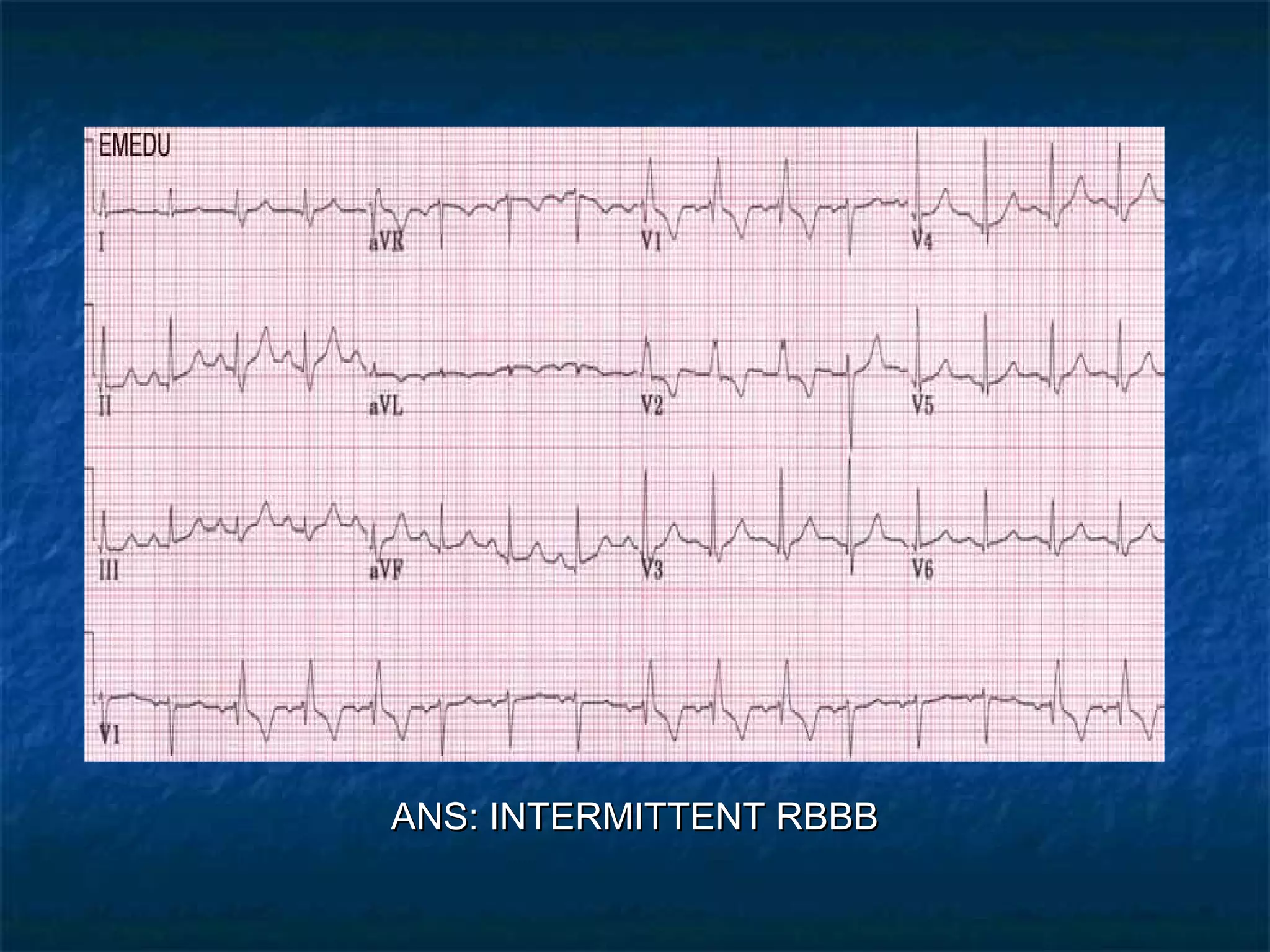

This document discusses right bundle branch block (RBBB) in the electrocardiogram (ECG). It begins by explaining normal ventricular conduction, then describes RBBB. Key points of RBBB include a QRS duration of over 110ms, an rSR' pattern or notched R wave in lead V1, and a wide and slurred S wave in leads I and V6. The document contrasts RBBB and left bundle branch block (LBBB) and provides illustrations of complete RBBB, incomplete RBBB, intermittent RBBB, and RBBB with left anterior fascicular block. It emphasizes using lead V1 and the direction of the terminal QRS force (upward for RBBB, downward for LBBB)
















